Chương 6: TREES - 3.Binary Trees: Problems & Solutions(01-12)
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 2 năm
Problem-1
Đưa ra thuật toán tìm phần tử lớn nhất trong cây nhị phân.
Solution: Một cách đơn giản để giải quyết vấn đề này là: tìm phần tử lớn nhất trong cây con bên trái, tìm phần tử lớn nhất trong cây con bên phải, so sánh chúng với dữ liệu gốc và chọn phần tử cho giá trị lớn nhất.
Cách tiếp cận này có thể dễ dàng thực hiện với đệ quy.
public int maxInBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode root) {
int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(root != null) {
int leftMax = maxInBinaryTree(root.left);
int rightMax = maxInBinaryTree(root.right);
if(leftMax > rightMax) {
maxValue = leftMax;
} else {
maxValue = rightMax;
}
if(root.data > maxValue) {
maxValue = root.data;
}
}
return maxValue;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-2
Đưa ra thuật toán tìm phần tử lớn nhất trong cây nhị phân mà không sử dụng đệ quy.
Solution: Sử dụng level order traversal: chỉ cần quan sát dữ liệu của phần tử trong khi xóa.
public int maxInBinaryTreeLevelOrder(BinaryTreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = q.poll();
if(tmp.data > max) {
max = tmp.data;
}
if(tmp != null) {
if(tmp.left != null) {
q.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right != null) {
q.offer(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return max;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-3
Đưa ra thuật toán tìm kiếm một phần tử trong cây nhị phân.
Solution: Cho một cây nhị phân, trả về true nếu tìm thấy một nút có dữ liệu trong cây. Truy hồi xuống cây, chọn nhánh trái hoặc nhánh phải, so sánh dữ liệu với dữ liệu từng nút.
public static boolean findInBT(BinaryTreeNode root, int data) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
if(root.data == data) {
return true;
}
return findInBT(root.left, data) || findInBT(root.right, data);
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-4
Đưa ra thuật toán tìm kiếm một phần tử trong cây nhị phân không sử dụng đệ quy.
Solution: Sử dụng level order traversal: chúng ta chỉ cần kiểm tra xem dữ liệu gốc có bằng phần tử mà chúng ta muốn tìm kiếm hay không.
public boolean maxInBinaryTreeLevelOrder(BinaryTreeNode root, int data){
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = q.poll();
if(tmp.data == data) {
return true;
}
if(tmp != null) {
if(tmp.left != null) {
q.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right != null) {
q.offer(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return false;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-5
Đưa ra thuật toán insert một phần tử vào cây nhị phân.
Solution: Vì cây đã cho là cây nhị phân nên chúng ta có thể chèn phần tử vào bất cứ đâu chúng ta muốn. Để chèn một phần tử, chúng ta có thể sử dụng level order traversal và chèn phần tử vào bất cứ nơi nào chúng ta tìm thấy nút có con trái hoặc con phải là NULL.
public BinaryTreeNode insertInBinaryTreeLevelOrder(BinaryTreeNode root, int data){
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = q.poll();
if(tmp != null) {
if(tmp.left != null) {
q.offer(tmp.left);
}else {
tmp.left = new BinaryTreeNode(data);
return root;
}
if(tmp.right != null) {
q.offer(tmp.right);
}else {
tmp.right = new BinaryTreeNode(data);
return root;
}
}
}
return root;
}
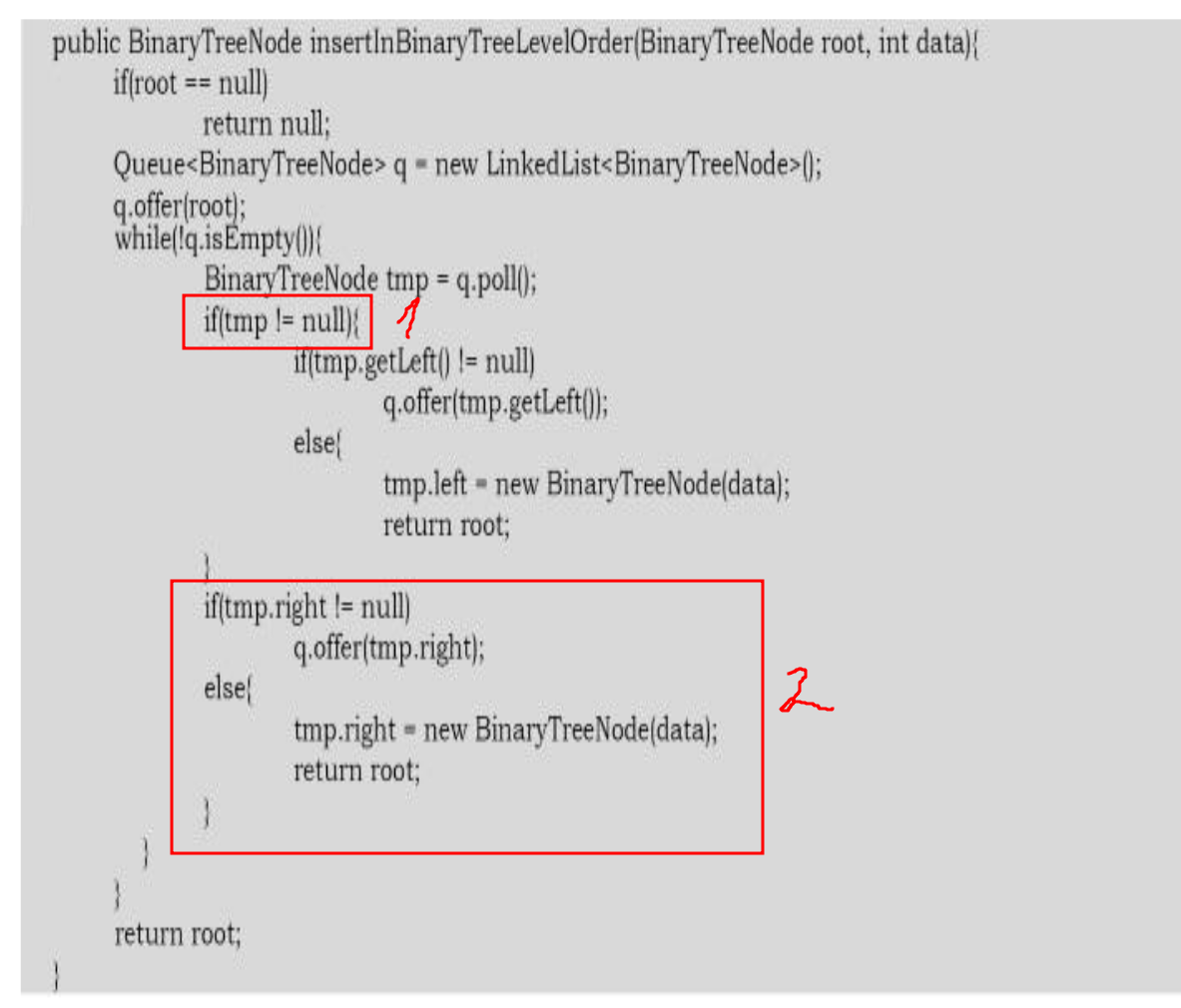
Nếu các bạn đọc trong sách thì có thể thấy code mình hơi khác 1 chút, khối 2 mình sẽ vẫn để nằm trong if của 1. Không biết tác giả có nhầm lẫn chỗ này không, nếu tmp = null, thì tmp.right sẽ gây ra exception.
Recursive Approach
public void insertHelper(BinaryTreeNode root, int data) {
if(root.data >= data){//Không nhất thiết phải có điều kiện này(Sử dụng tạo cây nhị phân cân bằng)
if(root.left == null) {
root.left = new BinaryTreeNode(data);
}else {
insertHelper(root.left, data);
}
}else {
if(root.right == null) {
root.right = new BinaryTreeNode(data);
}else {
insertHelper(root.right, data);
}
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-6
Đưa ra một thuật toán tìm kiếm kích thước của binary tree.
Solution: Tính toán kích thước của các cây con bên trái và bên phải theo cách đệ quy, thêm 1 (nút hiện tại) và trở về nút cha của nó.
public int size(BinaryTreeNode root) {
int leftCount = root.left == null ? 0 : size(root.left);
int rightCount = root.right == null ? 0 : size(root.right);
return 1 + leftCount + rightCount;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-7
Chúng ta có thể giải Problem-6 mà không cần đệ quy không?
Solution: Yes, sử dụng level order traversal.
public int size(BinaryTreeNode root, int data){
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = q.poll();
count++;
if(tmp != null) {
if(tmp.left != null) {
q.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right != null) {
q.offer(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return count;
}
Problem-8
Đưa ra thuật toán xóa cây.
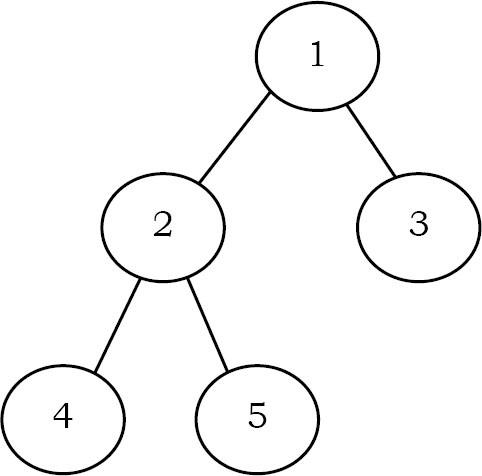
Solution: Để xóa một cây, chúng ta phải duyệt qua tất cả các nút của cây và xóa từng nút một. Vì vậy, chúng ta nên sử dụng giao dịch nào: Inorder, Preorder, Postorder hay Level order Traversal? Trước khi xóa nút cha, chúng ta nên xóa các nút con của nó trước. Chúng ta có thể sử dụng Postorder vì nó hoạt động mà không cần lưu trữ bất cứ thứ gì. Chúng ta có thể xóa cây với các đường ngang khác với độ phức tạp không gian bổ sung. Như ảnh dưới, các nút bị xóa theo thứ tự 4,5,2,3,1.
public void deleteBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode root){
root = null;
}
Trong các ngôn ngữ khác mà bạn phải tự mình quản lý bộ nhớ thì bạn có thể làm như soloution, còn java chỉ cần root = null, Garbage Collector sẽ lo phần còn lại.
Quản lý bộ nhớ và cơ chế của GC trong Java là những câu hỏi khá khó, mình thường thấy dành cho pv từ middle và senior trở lên(Các bạn có ai sắp phỏng vấn nên đọc thêm về phần này 😄)
Problem-9
Đưa ra thuật toán in dữ liệu thứ tự mức theo thứ tự ngược lại. Ví dụ: đầu ra cho cây bên dưới phải là: 4 5 6 7 2 3 1
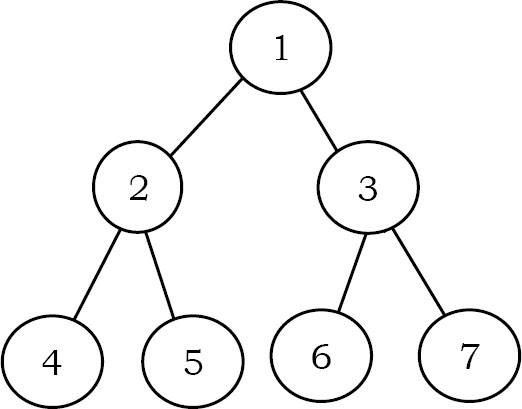
Solution: Đơn giản là sử dụng thêm một stack trong Level Order Traversal
public void levelOrderTraversalInReverse(BinaryTreeNode root, int data){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = q.poll();
if(tmp != null) {
if(tmp.left != null) {
q.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right != null) {
q.offer(tmp.right);
}
}
s.push(tmp);
}
System.out.println(s);
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-10
Đưa ra thuật toán tìm chiều cao (hoặc chiều sâu) của cây nhị phân.
Solution: Tính toán đệ quy chiều cao của các cây con bên trái và bên phải của một nút và gán chiều cao cho nút bằng chiều cao tối đa của hai phần tử con cộng với 1. Điều này tương tự với tính năng duyệt cây PreOrder (và DFS của thuật toán Đồ thị).
public int maxDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftCount = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightCount = maxDepth(root.right);
return leftCount > rightCount ? 1 + leftCount : 1 + rightCount;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
Problem-11
Giải quyết Problem-10 không sử dụng đệ quy
Solution: Chúng ta có thể sử dụng ngăn xếp để mô phỏng đệ quy.
public int maxDepthIterative(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
s.push(root);
int maxDepth = 0;
BinaryTreeNode prev = null;
while(!s.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode curr = s.peek();
if(prev == null || prev.left == curr || prev.right == curr) {
if(curr.left != null) {
s.push(curr.left);
} else {
if(curr.right != null) {
s.push(curr.right);
}
}
} else {
if(curr.left == prev) {
if(curr.right != null) {
s.push(curr.right);
}
} else {
s.pop();
}
}
prev = curr;
if(s.size() > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = s.size();
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
Problem-12
Giải quyết Problem-10 không sử dụng đệ quy(Cách khác Problem-11)
Solution: Yes. Sử dụng level order traversal. Điều này tương tự như BFS của các thuật toán Đồ thị. Kết thúc cấp độ được xác định bằng NULL.
public static int maxDepthLevelOrderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
q.offer(null);
int count = 1;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode curr = q.poll();
if(curr != null) {
if(curr.left != null) {
q.offer(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right != null) {
q.offer(curr.right);
}
} else {
if(!q.isEmpty()) {
count++;
q.offer(null);
}
}
}
return count;
}
Time Complexity: O(n). Space Complexity: O(n).
All rights reserved