Chương 5: QUEUES - Lý thuyết cơ bản
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 2 năm
5.1 Queue là gì?
Queue(Hàng đợi) là một cấu trúc dữ liệu được sử dụng để lưu trữ dữ liệu (tương tự như Linked Lists và Stacks). Trong hàng đợi, thứ tự dữ liệu đến là điều quan trọng. Nói chung, bạn có thể tưởng tượng hàng đợi là một dòng người đang chờ được phục vụ theo thứ tự tuần tự bắt đầu từ đầu hàng hoặc tuần tự.
Định nghĩa: Hàng đợi là một danh sách có thứ tự trong đó việc thêm được thực hiện ở một đầu (phía sau) và việc xóa được thực hiện ở đầu kia (phía trước). Phần tử đầu tiên được thêm là phần tử đầu tiên sẽ bị xóa. Do đó, nó được gọi là First in First out (FIFO) hoặc Last in Last out (LILO).
Tương tự như Ngăn xếp, có 2 tên đặc biệt được đặt cho hai thay đổi có thể được thực hiện đối với hàng đợi. Khi một phần tử được chèn vào hàng đợi, khái niệm được gọi là EnQueue và khi một phần tử bị xóa khỏi hàng đợi, khái niệm được gọi là DeQueue. DeQueing một hàng đợi trống sẽ gây ra underflow và EnQueue một phần tử trong một hàng đợi đã đầy được gọi là overflow. Nói chung, chúng tôi coi chúng là những trường hợp ngoại lệ.
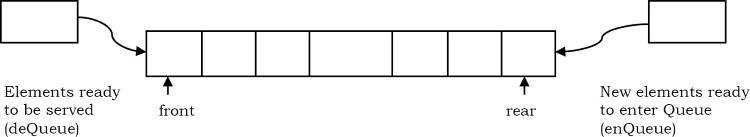
5.2 Queue được sử dụng như thế nào?
Khái niệm hàng đợi có thể được giải thích bằng cách quan sát một hàng tại quầy đặt chỗ.
Khi vào hàng chúng ta đứng ở cuối hàng và người đứng đầu hàng là người sẽ được phục vụ tiếp theo.
Anh ta sẽ thoát khỏi hàng đợi và được phục vụ.
Khi điều này xảy ra, người tiếp theo sẽ đến ở đầu hàng, sẽ thoát ra khỏi hàng đợi và sẽ được phục vụ.
Khi mỗi người ở đầu hàng tiếp tục thoát ra khỏi hàng đợi, chúng ta sẽ di chuyển về phía người đứng đầu hàng.
Cuối cùng chúng ta sẽ đến đầu hàng và chúng ta sẽ thoát khỏi hàng đợi và được phục vụ.
Hành vi này rất hữu ích trong những trường hợp cần duy trì thứ tự đến.
5.3 Queue ADT
Các hoạt động sau đây làm cho một hàng đợi trở thành một ADT. Việc chèn và xóa trong hàng đợi phải tuân theo cơ chế FIFO. Để đơn giản, chúng ta giả sử các phần tử là số nguyên.
Main Queue Operations
- enQueue (int data): Chèn một phần tử vào cuối hàng đợi
- int deQueue(): Loại bỏ và trả về phần tử ở phía trước hàng đợi
Auxiliary Queue Operations
- int Front (): Trả về phần tử ở phía trước mà không xóa nó
- int QueueSize (): Trả về số phần tử được lưu trữ trong hàng đợi
- int IsEmptyQueue (): Cho biết không có phần tử nào được lưu trữ trong hàng đợi hay không
5.4 Exceptions(Ngoại lệ)
Tương tự như các ADT khác, việc thực thi DeQueue trên hàng đợi trống sẽ ném ra “Empty Queue Exception” và thực thi EnQueue trên hàng đợi full sẽ ném ra “Full Queue Exception”.
5.5 Ứng dụng
Sau đây là một số ứng dụng sử dụng hàng đợi.
Ứng dụng trực tiếp
- Hệ điều hành lập lịch công việc (với mức độ ưu tiên ngang nhau) theo thứ tự đến (ví dụ: hàng đợi in).
- Mô phỏng các hàng đợi trong thế giới thực chẳng hạn như các hàng tại quầy bán vé hoặc bất kỳ tình huống nào đến trước được phục vụ trước yêu cầu một hàng đợi.
- Multiprogramming
- Truyền dữ liệu không đồng bộ (file IO, pipes, sockets).
- Thời gian chờ đợi của khách hàng tại tổng đài.
- Xác định số lượng nhân viên thu ngân cần có tại siêu thị.
Ứng dụng gián tiếp
- Cấu trúc dữ liệu bổ trợ cho các thuật toán
- Thành phần của cấu trúc dữ liệu khác
5.6 Implementation
Có nhiều cách (tương tự như Stacks) để thực hiện các queue operations và một số phương pháp thường được sử dụng được liệt kê dưới đây.
- Implement dựa trên mảng tròn đơn giản
- Implement dựa trên mảng tròn động
- Implement danh sách liên kết
Tại sao lại là Circular Arrays(Mảng tròn)?
Đầu tiên, hãy xem liệu chúng ta có thể sử dụng các mảng đơn giản để triển khai hàng đợi như chúng ta đã làm với ngăn xếp hay không.
Chúng ta biết rằng, trong hàng đợi, việc chèn được thực hiện ở một đầu và việc xóa được thực hiện ở đầu kia.
Sau khi thực hiện một số thao tác chèn và xóa, quá trình này trở nên dễ hiểu.
Trong ví dụ được hiển thị bên dưới, có thể thấy rõ ràng rằng các vị trí ban đầu của mảng đang bị lãng phí.
Vì vậy, triển khai mảng đơn giản cho hàng đợi không hiệu quả.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng ta giả sử các mảng là mảng tròn.
Điều đó có nghĩa là, chúng ta coi phần tử cuối cùng và các phần tử đầu tiên của mảng là liền nhau.
Với cách biểu diễn này, nếu có bất kỳ vị trí trống nào ở đầu, con trỏ phía sau có thể dễ dàng đi đến vị trí trống tiếp theo của nó.
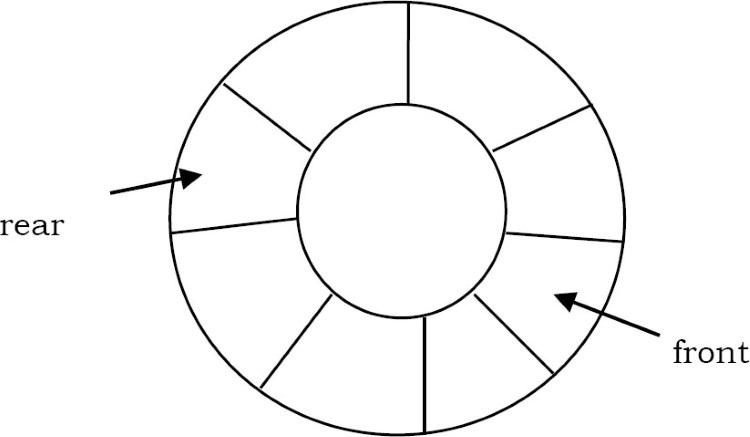
Simple Circular Array Implementation(Implement dựa trên mảng tròn đơn giản)
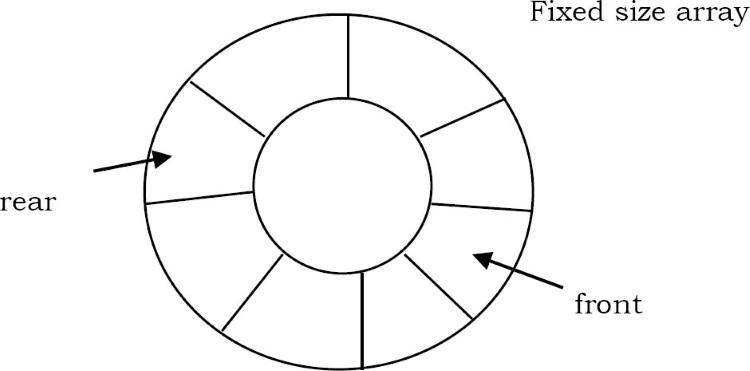
Việc triển khai Queue ADT đơn giản này sử dụng một mảng.
Trong mảng, chúng ta thêm các phần tử theo hình tròn và sử dụng hai biến để theo dõi phần tử bắt đầu và phần tử kết thúc.
Nói chung, phía trước được sử dụng để chỉ ra phần tử bắt đầu và phía sau được sử dụng để chỉ ra phần tử kết thúc trong hàng đợi.
Mảng lưu trữ các phần tử hàng đợi có thể full.
Một hoạt động EnQueue sau đó sẽ ném ra một full queue exception.
Tương tự, nếu chúng ta thử xóa một phần tử khỏi hàng đợi trống, nó sẽ ném ra empty queue exception.
Note: Ban đầu, cả phía trước và phía sau đều trỏ đến -1 cho biết hàng đợi trống.
public class FixedSizeArrayQueue {
// Array used to implement the queue
private int[] queueRep;
private int size, front, rear;
// Length of the array used to implement the queue
private static final int CAPACITY = 16; //Default Queue size
// Initializes the queue to use an array of default length
public FixedSizeArrayQueue() {
queueRep = new int[CAPACITY];
size = 0;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
// Initializes the queue to use an array of given length
public FixedSizeArrayQueue(int cap) {
queueRep = new int[cap];
size = 0;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
// Inserts an element at the rear of the queue. This method runs in O(1) time
public void enQueue(int data) {
if(size == CAPACITY) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue is fullL: Overflow");
} else {
size++;
queueRep[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % CAPACITY;
}
}
//Removes the front element from the queue. This method runs in O(1) time.
public int deQueue() {
if(size == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue is empty: Underflow");
} else {
size++;
int data = queueRep[front % CAPACITY];
queueRep[front] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
front = (front + 1) % CAPACITY;
return data;
}
}
// Checks whether the queue is empty. This method runs in O(1) time.
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (size == 0);
}
// Checks whether the queue is full. This method runs in O(1) time.
public boolean isFull() {
return (size == CAPACITY);
}
// Returns the number of elements inthe queue. This method runs in O(1) time.
public int size() {
return size;
}
// Returns a string representation of the queue as a list of elements,
// with the front element at the end: [..., prev, rear]. This method runs in O(n) time, where n is size of the queue.
public String toString() {
String result = "[";
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
result += Integer.toString(queueRep[(front+i) % CAPACITY]);
if(i < size - 1) {
result += ", ";
}
}
result += "]";
return result;
}
}
Đây là code của tác giả, cá nhân mình thấy chưa chuẩn lắm vì có hàm khởi tạo cho phép truyền độ lớn của queue vào, nhưng cả 2 hàm enQueue và deQueue 2 tham số rear và front đều đang tính toán theo CAPACITY.
Nên mình có tham khảo thêm code ở đây
// Java program for insertion and
// deletion in Circular Queue
import java.util.ArrayList;
class CircularQueue{
// Declaring the class variables.
private int size, front, rear;
// Declaring array list of integer type.
private ArrayList<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Constructor
CircularQueue(int size)
{
this.size = size;
this.front = this.rear = -1;
}
// Method to insert a new element in the queue.
public void enQueue(int data)
{
// Condition if queue is full.
if((front == 0 && rear == size - 1) ||
(rear == (front - 1) % (size - 1)))
{
System.out.print("Queue is Full");
}
// condition for empty queue.
else if(front == -1)
{
front = 0;
rear = 0;
queue.add(rear, data);
}
else if(rear == size - 1 && front != 0)
{
rear = 0;
queue.set(rear, data);
}
else
{
rear = (rear + 1);
// Adding a new element if
if(front <= rear)
{
queue.add(rear, data);
}
// Else updating old value
else
{
queue.set(rear, data);
}
}
}
// Function to dequeue an element
// form th queue.
public int deQueue()
{
int temp;
// Condition for empty queue.
if(front == -1)
{
System.out.print("Queue is Empty");
// Return -1 in case of empty queue
return -1;
}
temp = queue.get(front);
// Condition for only one element
if(front == rear)
{
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
else if(front == size - 1)
{
front = 0;
}
else
{
front = front + 1;
}
// Returns the dequeued element
return temp;
}
// Method to display the elements of queue
public void displayQueue()
{
// Condition for empty queue.
if(front == -1)
{
System.out.print("Queue is Empty");
return;
}
// If rear has not crossed the max size
// or queue rear is still greater then
// front.
System.out.print("Elements in the " +
"circular queue are: ");
if(rear >= front)
{
// Loop to print elements from
// front to rear.
for(int i = front; i <= rear; i++)
{
System.out.print(queue.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// If rear crossed the max index and
// indexing has started in loop
else
{
// Loop for printing elements from
// front to max size or last index
for(int i = front; i < size; i++)
{
System.out.print(queue.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
// Loop for printing elements from
// 0th index till rear position
for(int i = 0; i <= rear; i++)
{
System.out.print(queue.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialising new object of
// CircularQueue class.
CircularQueue q = new CircularQueue(5);
q.enQueue(14);
q.enQueue(22);
q.enQueue(13);
q.enQueue(-6);
q.displayQueue();
int x = q.deQueue();
// Checking for empty queue.
if(x != -1)
{
System.out.print("Deleted value = ");
System.out.println(x);
}
x = q.deQueue();
// Checking for empty queue.
if(x != -1)
{
System.out.print("Deleted value = ");
System.out.println(x);
}
q.displayQueue();
q.enQueue(9);
q.enQueue(20);
q.enQueue(5);
q.displayQueue();
q.enQueue(20);
}
}
Performance and Limitations
Performance: Gọi n là số phần tử trong hàng đợi:
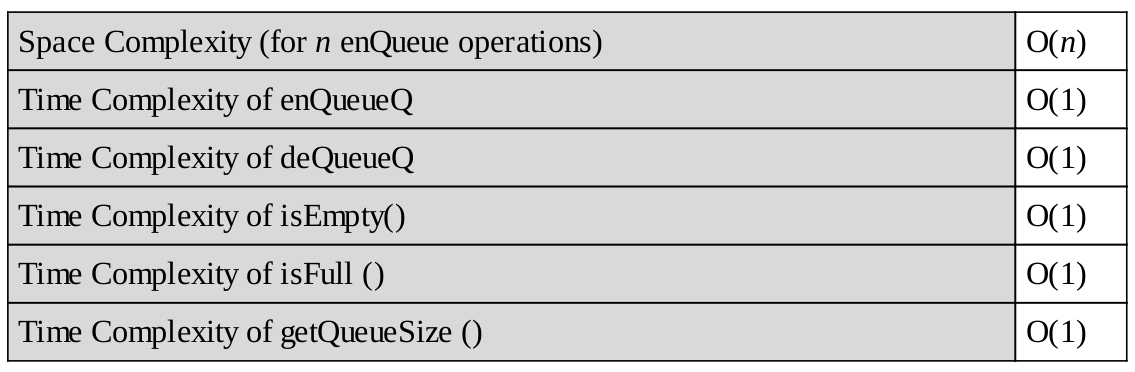
Limitations Kích thước tối đa của hàng đợi phải được xác định trước đó và không thể thay đổi. Cố gắng EnQueue một phần tử mới vào một hàng đợi full sẽ gây ra một exception.
Dynamic Circular Array Implementation
Mình tham khảo code ở đây
public class DynamicQueueImpl {
private int capacity = 2;
int queueArr[];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int currentSize = 0;
public DynamicQueueImpl(){
queueArr = new int[this.capacity];
}
/**
* this method adds element at the end of the queue.
* @param item
*/
public void enqueue(int item) {
if (isQueueFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full, increase capacity...");
increaseCapacity();
}
rear++;
if(rear >= queueArr.length && currentSize != queueArr.length){
rear = 0;
}
queueArr[rear] = item;
currentSize++;
System.out.println("Adding: " + item);
}
/**
* this method removes an element from the top of the queue
*/
public void dequeue() {
if (isQueueEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Underflow ! Unable to remove element from Queue");
} else {
front++;
if(front > queueArr.length-1){
System.out.println("removed: "+queueArr[front-1]);
front = 0;
} else {
System.out.println("removed: "+queueArr[front-1]);
}
currentSize--;
}
}
/**
* This method checks whether the queue is full or not
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean isQueueFull(){
boolean status = false;
if (currentSize == queueArr.length){
status = true;
}
return status;
}
/**
* This method checks whether the queue is empty or not
* @return
*/
public boolean isQueueEmpty(){
boolean status = false;
if (currentSize == 0){
status = true;
}
return status;
}
private void increaseCapacity(){
//create new array with double size as the current one.
int newCapacity = this.queueArr.length*2;
int[] newArr = new int[newCapacity];
//copy elements to new array, copy from rear to front
int tmpFront = front;
int index = -1;
while(true){
newArr[++index] = this.queueArr[tmpFront];
tmpFront++;
if(tmpFront == this.queueArr.length){
tmpFront = 0;
}
if(currentSize == index+1){
break;
}
}
//make new array as queue
this.queueArr = newArr;
System.out.println("New array capacity: "+this.queueArr.length);
//reset front & rear values
this.front = 0;
this.rear = index;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
DynamicQueueImpl queue = new DynamicQueueImpl();
queue.enqueue(4);
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(56);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(67);
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(24);
queue.enqueue(98);
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(435);
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
}
}
Performance
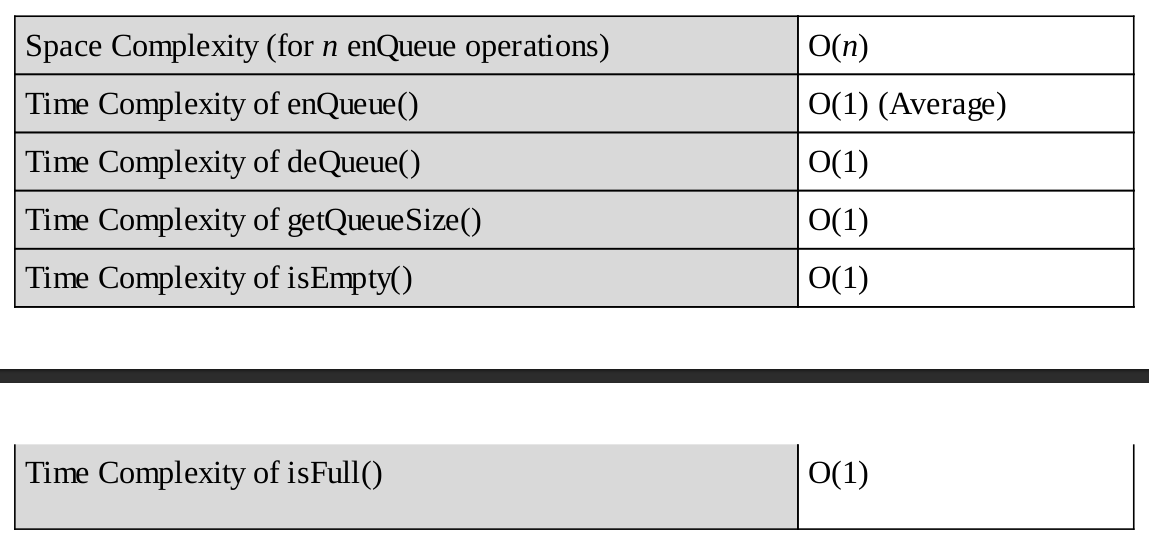
Linked List Implementation
Một cách khác để triển khai hàng đợi là sử dụng Linked lists. Hoạt động EnQueue được thực hiện bằng cách chèn một phần tử vào cuối danh sách. Thao tác DeQueue được thực hiện bằng cách xóa một phần tử khỏi đầu danh sách.
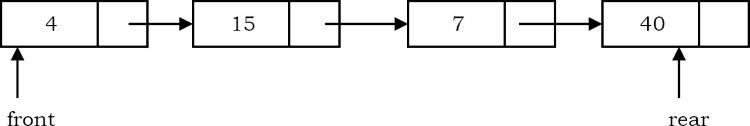
public class LinkedQueue {
private int length;
private ListNode front, rear;
//Creates an empty queue
public LinkedQueue() {
length = 0;
front = rear = null;
}
// Adds the specified data to the rear of the queue
public void enqueue(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(isEmpty()) {
front = node;
} else {
rear.setNext(node);
}
rear = node;
length++;
}
// Removes the data at the front of the queue and returns a reference to it.
// Throws an Exception if the queue is empty
public int dequeue() throws Exception {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("queue is empty");
}
int result = front.getData();
front = front.getNext();
length--;
if(isEmpty()) {
rear = null;
}
return result;
}
// Returs a reference to the data at the front of the queue.
// The data is not removed from the queue. Throws an Exception if the queue is empty.
public int first() throws Exception {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("queue is empty");
}
return front.getData();
}
//Return true if this queue is empty and false otherwise
public boolean isEmpty() {
return length == 0;
}
// Returns the number of the elements in this queue.
public int size() {
return length;
}
//Returns a string representation of this queue.
public String toString() {
String result = "";
ListNode current = front;
while(current != null) {
result = result + current.toString() + "\n";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result;
}
}
Performance
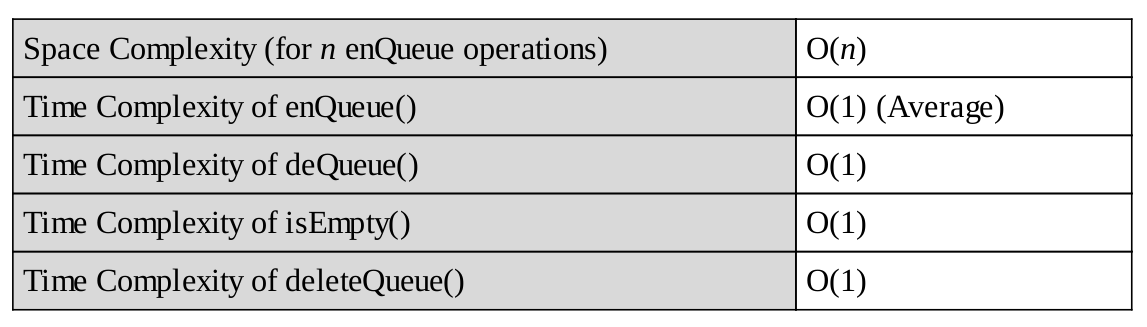
So sánh các cách Implement
Note: Việc so sánh này tương tự với stack Implementations trong chương Stack mình đã trình bày. Các bạn có thể xem lại ở đây.
All rights reserved