How SSL works? (English)
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Bài tiếng Việt - SSL hoạt động như thế nào?
HTTPS is a very standard protocol, people often say HTTPS is more secure than HTTP because it has SSL added. But why is that? To better understand that, we will learn about SSL and how it works in this article.
What is SSL?
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is a security protocol used to encrypt data transmitted over a connection between two systems.
The most common example of two systems communicating with each other that use SSL is the communication between a browser and a web server. If we visit a website that we see that its protocol is HTTP, then the communication between the browser and the server is not secure, the data is being transmitted in plain text. And if we visit a website and see its protocol as HTTPS, it means that it is using SSL and the data transmitted between the browser and the server is encrypted.
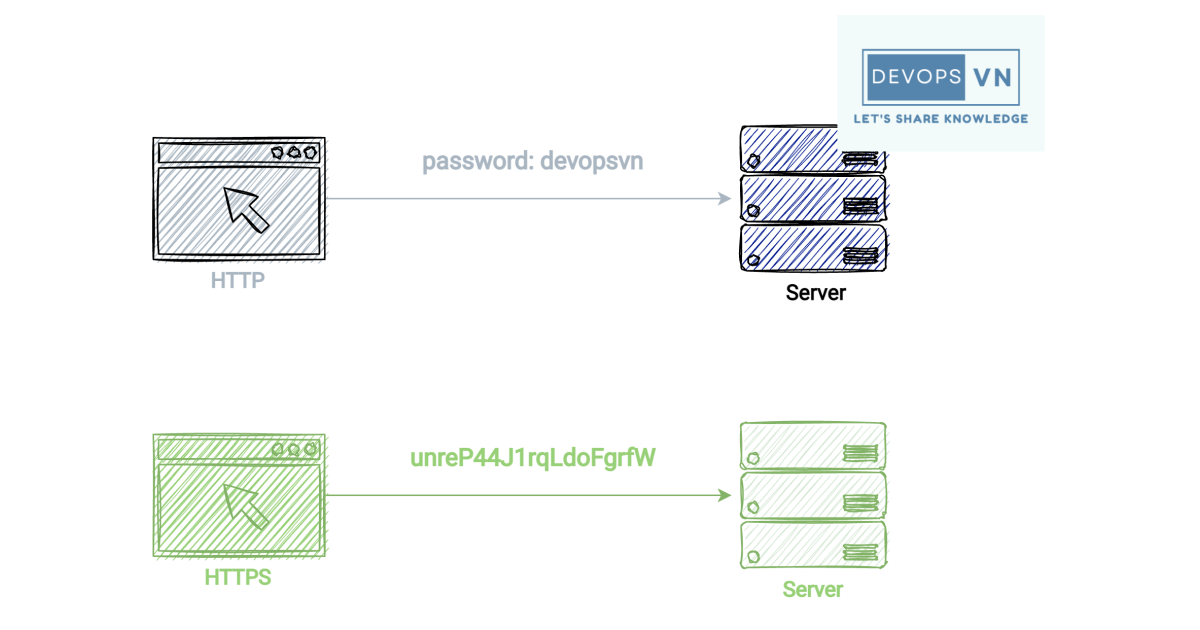
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a newer version of SSL, and nowadays most HTTPS protocols are implemented over TLS, but because of habit, people still call it SSL.
So how does SSL work?
How SSL works?
Before learning about how SSL works, first, we need to understand the following two concepts: Asymmetric Cryptography and Symmetric Cryptography. These are the two ways of encrypting data that SSL uses.
Asymmetric Cryptography
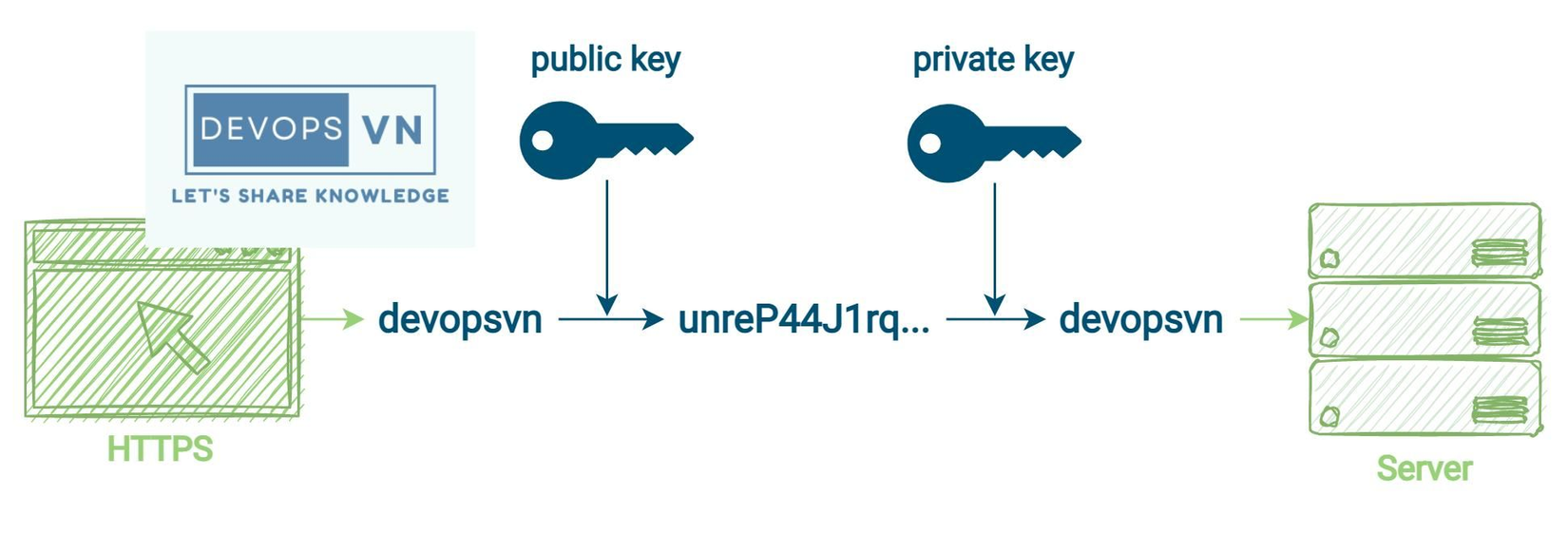
Asymmetric Cryptography, also known as Public Key Cryptography, is a way of encrypting data using a public key and a private key pair.
With Public Key is the key that will be shared with the outside for anyone who wants to communicate, and the Private Key is the security key that is kept on the server and is not shared.
When communicating, the sender will use the Public Key to encrypt the data, and the receiver will use the Private Key to decrypt the data that it received.
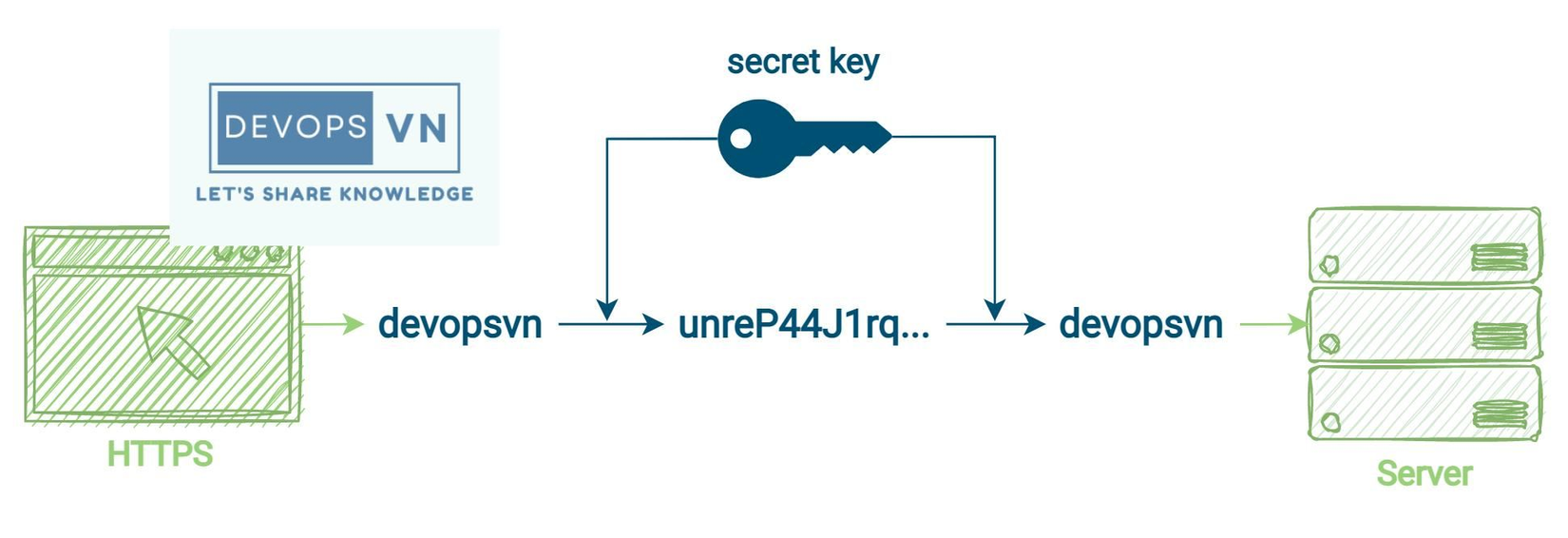
Symmetric Cryptography
Symmetric Cryptography is also a way of encrypting data like Asymmetric Cryptography, except that instead of using a key pair, it uses only one key for encrypting and decrypting the data.
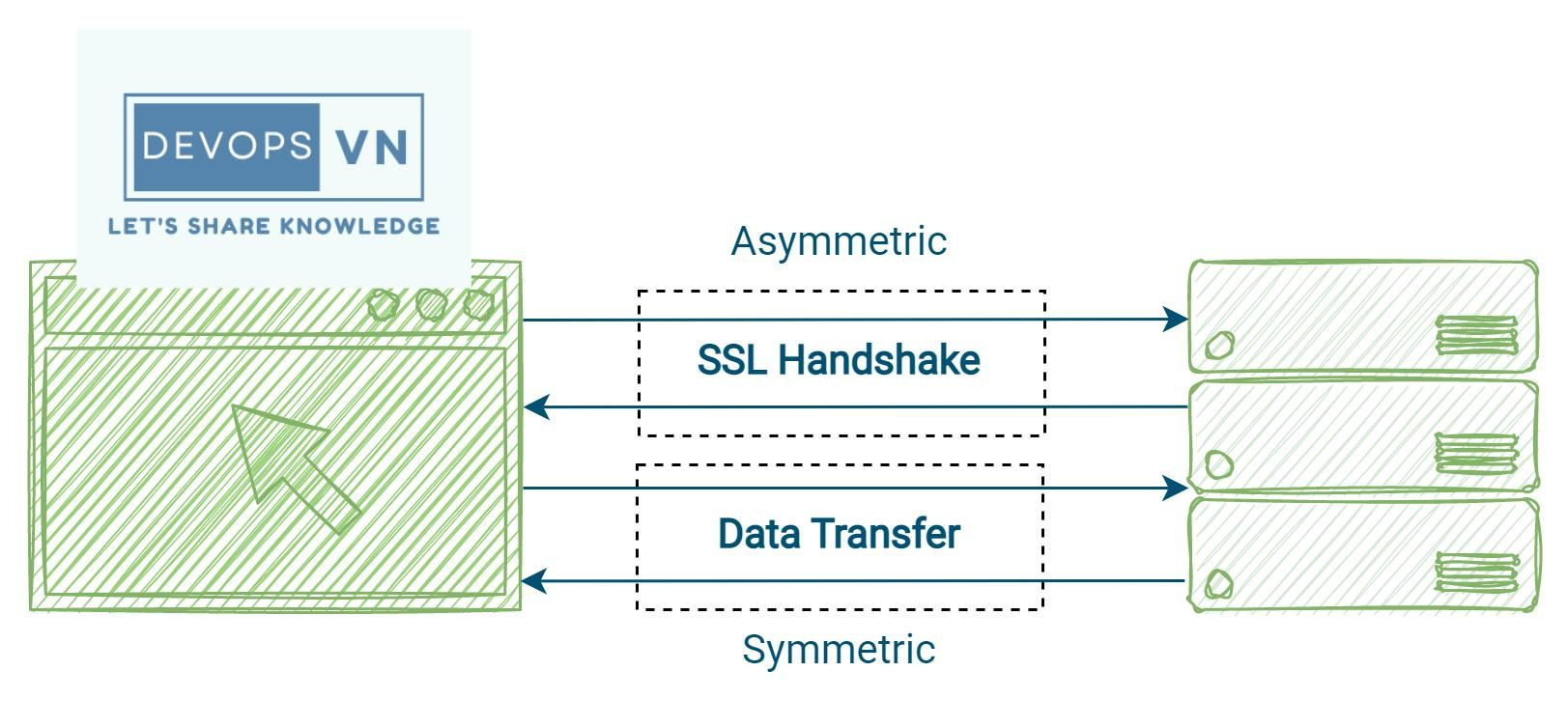
SSL data processing
SSL uses both Asymmetric and Symmetric for encrypting data, the communication between two systems using SSL will have two steps as follows: SSL handshake and Data Transfer.
Asymmetric Cryptography is used in the SSL handshake step. Symmetric Cryptography is used for data transfer after the SSL handshake step.
SSL Handshake
We will take the example of communication between a browser and a web server.
The SSL connection between the two systems will begin with an SSL handshake using Asymmetric Cryptography. This SSL handshake step is for the browser to authenticate the SSL with the server. The process is as follows:
- The browser sends a message saying “client hello” to the server
- The server will reply with the content "server hello", which contains SSL certificate information and the public key of that SSL
- The browser will confirm whether the SSL authentication information is real or not, if successful, the browser will generate a Session Key
- This Session Key will be encrypted with the Public Key and sent to the server
- The server will receive this encrypted Session Key and use the Private Key to decrypt it and save this Session Key, then it will return a signal to the browser that the Session Key has been received

At the end of the SSL handshake process, both the browser and the server have a Session Key, this is the Key that will be used to encrypt and decrypt data during the communication of the two systems later.
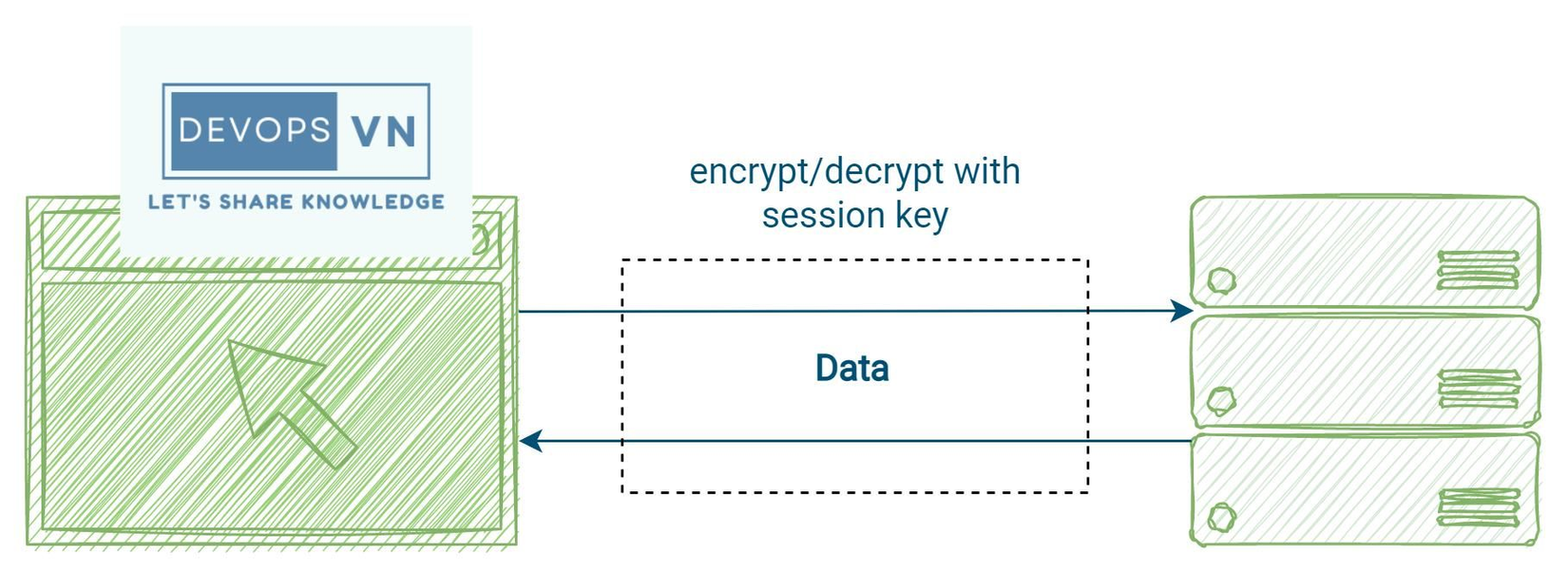
Data Transfer
This is the process of transferring data between two systems, Symmetric Cryptography will be used in this step, and both use Session Key to encrypt and decrypt data.
Conclusion
This is how SSL works, in server installation work, SSL is very important, understanding how SSL works will make it easier to work with it.
You can learn more about SSL here Learn HTTPS (SSL)
tags: devops
All rights reserved