Use SSH Port Forwarding to connect to resources (English)
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Bài viết tiếng Việt - Sử dụng SSH Port Forwarding để kết nối tới tài nguyên bị chặn
There are some cases where we need to connect to resources on the server, but for security reasons, those resources are on a server with a firewall or within a private network, so you can't connect to it. You can solve this problem by using a VPN or simply using SSH Port Forwarding.

Local Port Forward
The first use of SSH Port Forwarding is to use it to connect to resources on servers that have Firewall.
For example, we have a local code that needs to connect to the Redis on the server, but our server is blocked on port 6379 by the firewall, so from the outside, we cannot connect to it. We will use SSH Port Forwarding with the following syntax:
ssh -L localhost:<local-port>:localhost:<remote-address-port> <username>@<server-ip>
For example, the server has an IP of 172.168.65.117, and the username is ec2-user, in which there is a Redis child running at port 6379.
ssh -L localhost:6379:localhost:6379 ec2-user@172.168.65.117
You can remove localhost at the beginning.
ssh -L 6379:localhost:6379 ec2-user@172.168.65.117
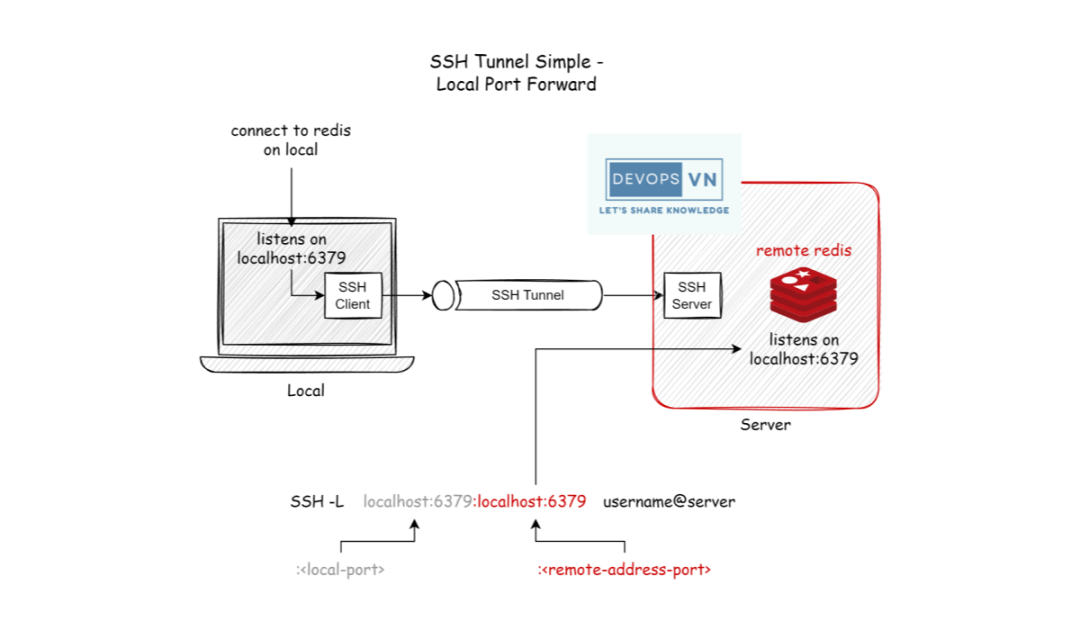
At this time, we only need to connect to localhost:6379 to be able to access the Redis child on the server.
Bastion Host
The next use case of SSH Port Forwarding is to use it to connect to resources located in the Private Network.
We will encounter this case the most when we use the Cloud, for example with AWS we will create Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) in a private network, of course, because the network is closed, we will not be able to connect to it. RDS from the outside, the common way people use it is to create a Bastion Host, and we will connect to RDS through this bastion host.
We will use SSH Port Forwarding with the following syntax:
ssh -L localhost:<local-port>:<remote-address>:<remote-address-port> <username>@<bastion-host-ip>
For example, with the bastion host with IP 172.168.65.117, the username of a bastion host is ec2-user, the address of RDS is postgres.123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com that running on port 5432.
ssh -L 5432:postgres.123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:5432 ec2-user@172.168.65.117

At this point, we only need to connect to localhost:5432 to be able to access the RDS in the private network.
Conclusion
The above are two common use cases of SSH Port Forwarding, you can refer to other use cases here: SSH Port Forwarding - Why and How. Hope this article will be useful to you.
All rights reserved