Software Development Process Model - Part 2
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Incremental development
- Rather than deliver the system as a single delivery, the development and delivery is broken down into increments with each increment delivering part of the required functionality.
- User requirements are prioritised and the highest priority requirements are included in early increments.
- Once the development of an increment is started, the requirements are frozen though requirements for later increments can continue to evolve.
Incremental Model
- Deliver the core product first
- Add on / refine features
- Provide a platform for evaluation by user
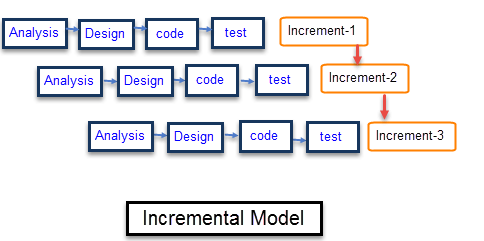
Incremental development advantages
- Customer value can be delivered with each increment so system functionality is available earlier
- Early increments act as a prototype to help elicit requirements for later increments
- Lower risk of overall project failure
- The highest priority system services tend to receive the most testing
Spiral Development
- Process is represented as a spiral rather than as a sequence of activities with backtracking
- Each loop in the spiral represents a phase in the process.
- No fixed phases such as specification or design - loops in the spiral are chosen depending on what is required
- Risks are explicitly assessed and resolved throughout the process
Spiral model of the software process

Spiral model sectors
- Objective setting
- Specific objectives for the phase are identified
- Risk assessment and reduction
- Risks are assessed and activities put in place to reduce the key risks
- Development and validation
- A development model for the system is chosen which can be any of the generic models
- Planning
- The project is reviewed and the next phase of the spiral is planned
RAD Model
- Rapid application development model (RAD)
- Characteristics:
- Extremely short development cycle
- Component based construction i.e. develop a small component rather than a system
- Used for information system applications
- Drawbacks:
- Need more resource for large projects
- Need commitment from all parties
- Not suitable for high performance and when technical risk is high
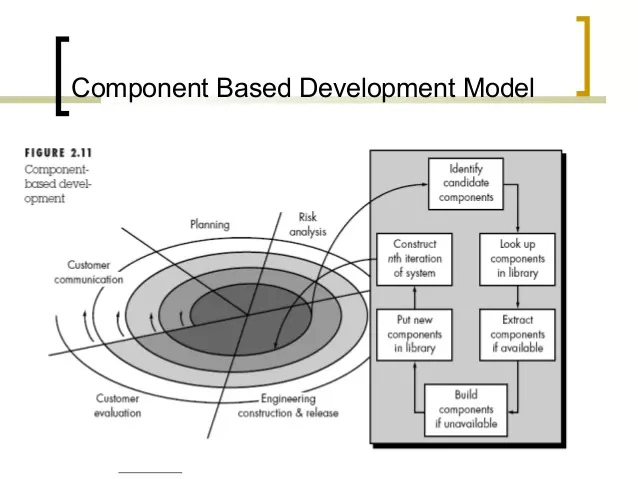
Component Based Development Model
- Suitable for re-usable object oriented classes
- Apply characteristics of spiral model
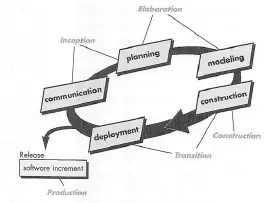
Unified Process
- Work of Ivar Jacobson Grady Booch and James Rumbaugh
- use case driven
- architecture-centric
- iterative and
- incremental
Iterative Development Produces an Executable
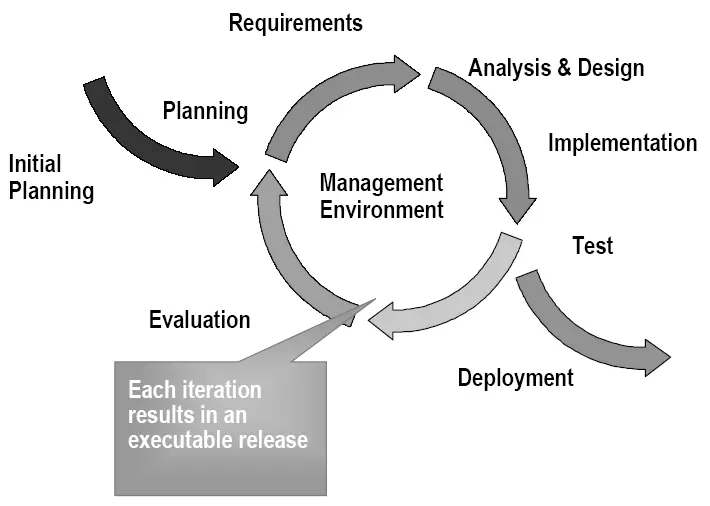
Initial and evolution cycles & Time
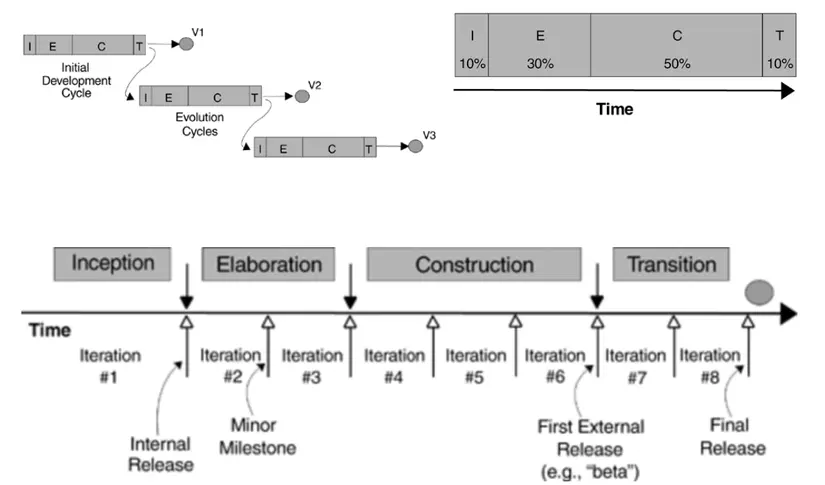
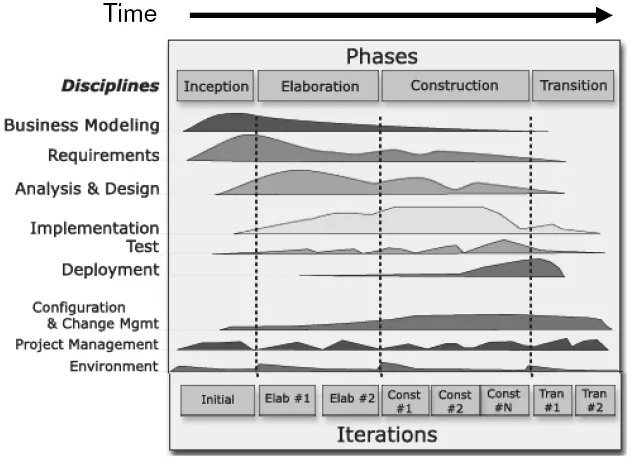
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
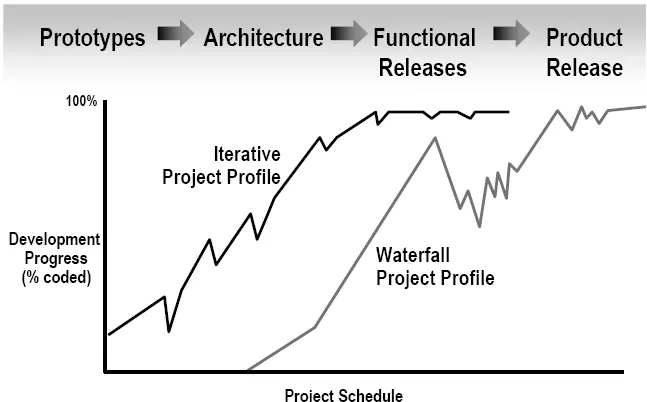
Risk Profiles
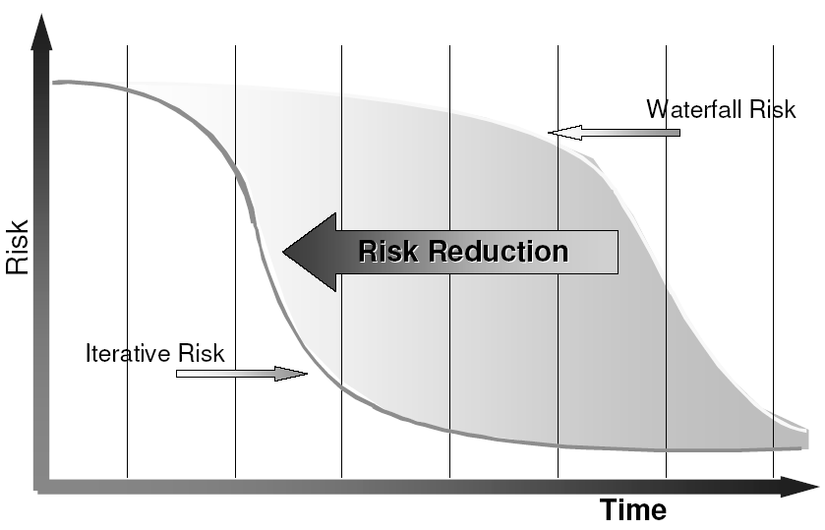
Reduce Scrap/Rework: Use an Iterative Process
**Reference:** *Software Engineering A Practitioner's Approach (7th Ed.) ~ Roger S. Pressman*
All rights reserved