Software Testing Strategies - Part 1
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Software Testing
Testing is the process of exercising a program with the specific intent of finding errors prior to delivery to the end user.
What Testing Shows
- Errors
- Requirements Conformance
- Performance
- An indication of quality
Strategic Approach
- To perform effective testing, you should conduct effective technical reviews. By doing this, many errors will be eliminated before testing commences.
- Testing begins at the component level and works "outward" toward the integration of the entire computer based system.
- Different testing techniques are appropriate for different software engineering approaches and at different points in time.
- Testing is conducted by the developer of the software and (for large projects) an independent test group.
- Testing and debugging are different activities, but debugging must be accommodated in any testing strategy.
V & V
- Verification refers to the set of tasks that ensure that software correctly implements a specific function.
- Validation refers to a different set of tasks that ensure that the software that has been built is traceable to customer requirements. Boehm [Boe81] states this another way:
- Verification: "Are we building the product right?"
- Validation: "Are we building the right product?"
Who Tests the Software?
- Developer
- Understands the system but, will test "gently“ and, is driven by "delivery“
- Independent tester
- Must learn about the system, but, will attempt to break it and, is driven by quality
Testing Strategy
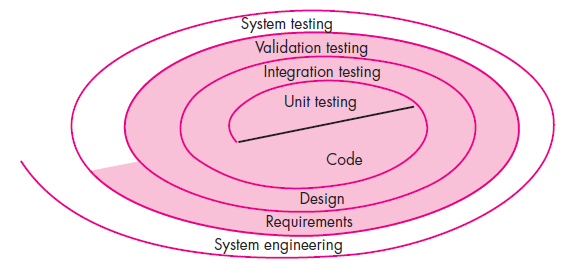
- We begin by ‘testing-in-the-small’ and move toward ‘testing-in-the-large’
- For conventional software
- The module (component) is our initial focus
- Integration of modules follows
- For OO software
- our focus when “testing in the small” changes from an individual module (the conventional view) to an OO class that encompasses attributes and operations and implies communication and collaboration
Strategic Issues
- Specify product requirements in a quantifiable manner long before testing commences.
- State testing objectives explicitly.
- Understand the users of the software and develop a profile for each user category.
- Develop a testing plan that emphasizes “rapid cycle testing.”
- Build “robust” software that is designed to test itself
- Use effective technical reviews as a filter prior to testing
- Conduct technical reviews to assess the test strategy and test cases themselves.
- Develop a continuous improvement approach for the testing process.
Unit Testing
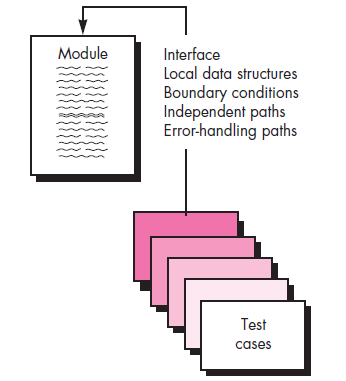
Unit Test Environment
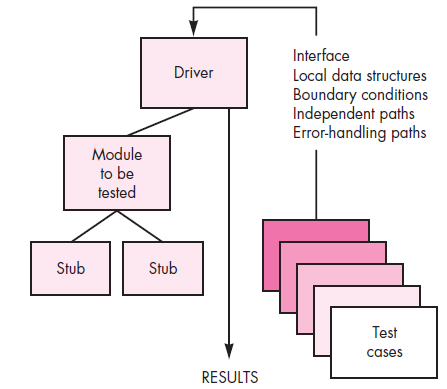
Integration Testing Strategies
Top Down Integration
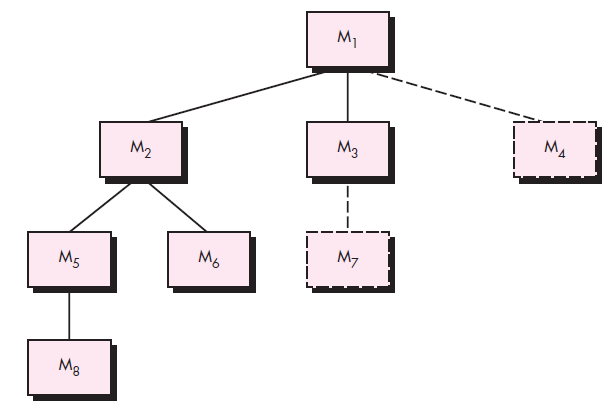
Bottom-Up Integration
Regression Testing
- Regression testing is the re-execution of some subset of tests that have already been conducted to ensure that changes have not propagated unintended side effects
- Whenever software is corrected, some aspect of the software configuration (the program, its documentation, or the data that support it) is changed.
- Regression testing helps to ensure that changes (due to testing or for other reasons) do not introduce unintended behavior or additional errors.
- Regression testing may be conducted manually, by re- executing a subset of all test cases or using automated capture/playback tools.
Reference: Software Engineering A Practitioner's Approach (7th Ed.) ~ Roger S. Pressman
All rights reserved