What is AWS DynamoDB? AWS DynamoDB with Java
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Giới Thiệu
Hôm nay mình xin giới thiệu tới mọi người triển khai 1 dự án java sử dụng Amazon DynamoDB, trong ví dụ hôm nay mình sử dụng Spring Boot để làm demo, việc triển khai trên các framework khác như Quarkus cũng tương tự.
Bắt đầu thôi
Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB là một dịch vụ cơ sở dữ liệu NoSQL được quản lý hoàn toàn bởi AWS, DynamoDB cung cấp hiệu suất ghi/đọc rất nhanh và có thể tự scale để đáp ứng nhu cầu cao của hệ thống. Sử dụng DynamoDB của AWS giúp bạn giảm bớt gánh nặng quản trị và vận hành hệ thống máy chủ cũng như các vấn đề về phần cứng hệ thống. Ngoài ra Amazon DynamoDB cũng hỗ trợ rất tốt các vấn đề bảo mật giảm gánh nặng quản lý các dữ liệu nhạy cảm.
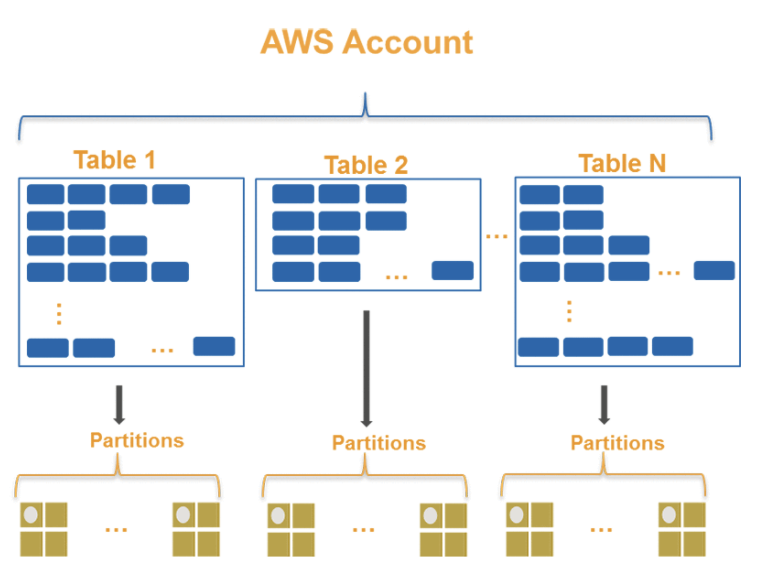
- DynamoDB không có database chỉ có table. Table không có ràng buộc cột
- Các items trong cùng 1 table có chung partition key, sort key. Các attributes còn lại hoàn toàn tuỳ biến. Kích thước tối đa 400kb
- Attributes là các thuộc tính có thể mở rộng, Attributes có 3 dạng chính
- Scalar types: String, Number, Binary (ghi binary data qua SDK), Boolean, Null
- Document types: List (mảng có thể chứa Number, String), Map (dạng key-value)
- Set types: String Set, Number Set, Binary Set (tập hợp không chứa phần tử lặp)
RDBMS VS DynamoDB
| Relational Database Management System | DynamoDB |
|---|---|
| Insert, update data must conform schema columns | Insert, update data without schema constrains |
| Scaling: mostly vertical. To scale horizontal need to use replication and very complicated | Horizontal scale. Store items in many partitions |
| Database > Table > Colum > Row | Table > Item > Attributes |
| Primary key (single or composite keys) | Partition key & Sort key |
| Column type: scalar (Postgresql: jsonb, array, hset) | Attribute type: String, Number, Binary, Boolean, Null, Document type: List, Map, Set Types: String Set, Number Set, Binary Set |
| SQL query: join, group by | PartiQL (subset of SQL), no join, no aggregate functio |
| Has stored procedure, trigger, views | DynamoDB Stream: time ordered event of create/update/delete item |
| ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) | Không hỗ trợ |
Primary Key
Primary Key trong DynamoDB hỗ trợ chúng ta :
- Unique (đảm bảo là duy nhất)
- Fast look up (làm sao truy vấn nhanh)
- Less storage (tốn ít dung lượng lưu trữ) Primary key được tạo một các tự động, tuy nhiên có 2 trường hợp để sinh Primary key như sau 1.Chỉ có Partition key, thì lúc này Partition Key sẽ được đặt làm Primary key.
- Có Partition key và Sort key, lúc này tổ hợp hợp của Partition Key và Sort Key sẽ được đặt làm Primary key.
Trong DynamoDB có hỗ trợ auto increment integer làm partition key tuy nhiên không được khuyến khích sử dụng vì khi đảm bảo số tăng tuần tự khiến các lệnh write item phải chuyển từ song song đồng thời sang tuần tự. Tốc độ ghi chậm lại, không đảm bảo scalability.
Read – Write capacity mode
DynamoDB có 2 chế độ dự trù thông lượng ghi / đọc. Có thể chuyển qua lại giữa 2 chế độ 1 lần trong 24h.
- Provisioned Mode (mặc định)
- Rẻ hơn nhưng cần dự trù đúng. Nếu dự trù quá lố thì tốn tiền, dự trù quá thấp thì gây lỗi quá tải
- On Demand (tuỳ theo nhu cầu thực tế từng thời điểm)
- Đắt hơn 2.5 lần. Chỉ nên dùng cho tác vụ đột xuất, ngắn
- AWS tự động co dãn partition theo tần suất read / write thực tế
Secondary Indexes
Partition Key, Sort Key tạo thành Primary Key Index. Nếu bạn tìm kiếm với attribute khác bạn sẽ phải dùng cơ chế scan, quét toàn bộ item ở tất cả các partition > tốc độ rất chậm. Secondary indexes giúp tìm kiếm trên các attributes khác nhanh hơn.
- Global secondary index chỉ mục với bộ partition key, sort key hoàn toàn mới
- Local secondary index : chỉ mục với partition key hiện có nhưng sort key là attribute khác.
- Một bảng tối đa 20 global secondary indexes và 5 local secondary indexes.
- Bạn phải trả thêm phí khi tạo thêm secondary indexes
Read Capacity Unit
1 RCU = 01 strongly consistent read per second OR 02 eventually consistent reads per second, for an item up to 4 KB in size Chú ý làm tròn lên (round up) đơn vị 4KB
Một ví dụ nhỏ cho các bạn dễ hình dung

Read Consistency
DynamoDB có 2 chế độ đọc đồng nhất:
-
Eventually Consistency: cuối cùng sẽ đồng nhất. Có nghĩa vẫn có những thời điểm, dữ liệu đọc ra không phải là mới nhất.
-
Strong Consistency: chắc chắn đồng nhất. Thời gian đọc ra sẽ lâu hơn để chắc chắn rằng nếu item vừa được ghi, thì nán thêm chút nữa để kiểm tra xem còn phiên bản mới của item được ghi đồng bộ lên các AZ.
Ngoài ra bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về AWS DynamoDB tại đây
AWS DynamoDB with Java
Trong ví dụ hôm nay mình sẽ xử dụng Spring Boot để làm demo nhé.
Trước tiên các bạn có thể tạo prpject mới tại https://start.spring.io/
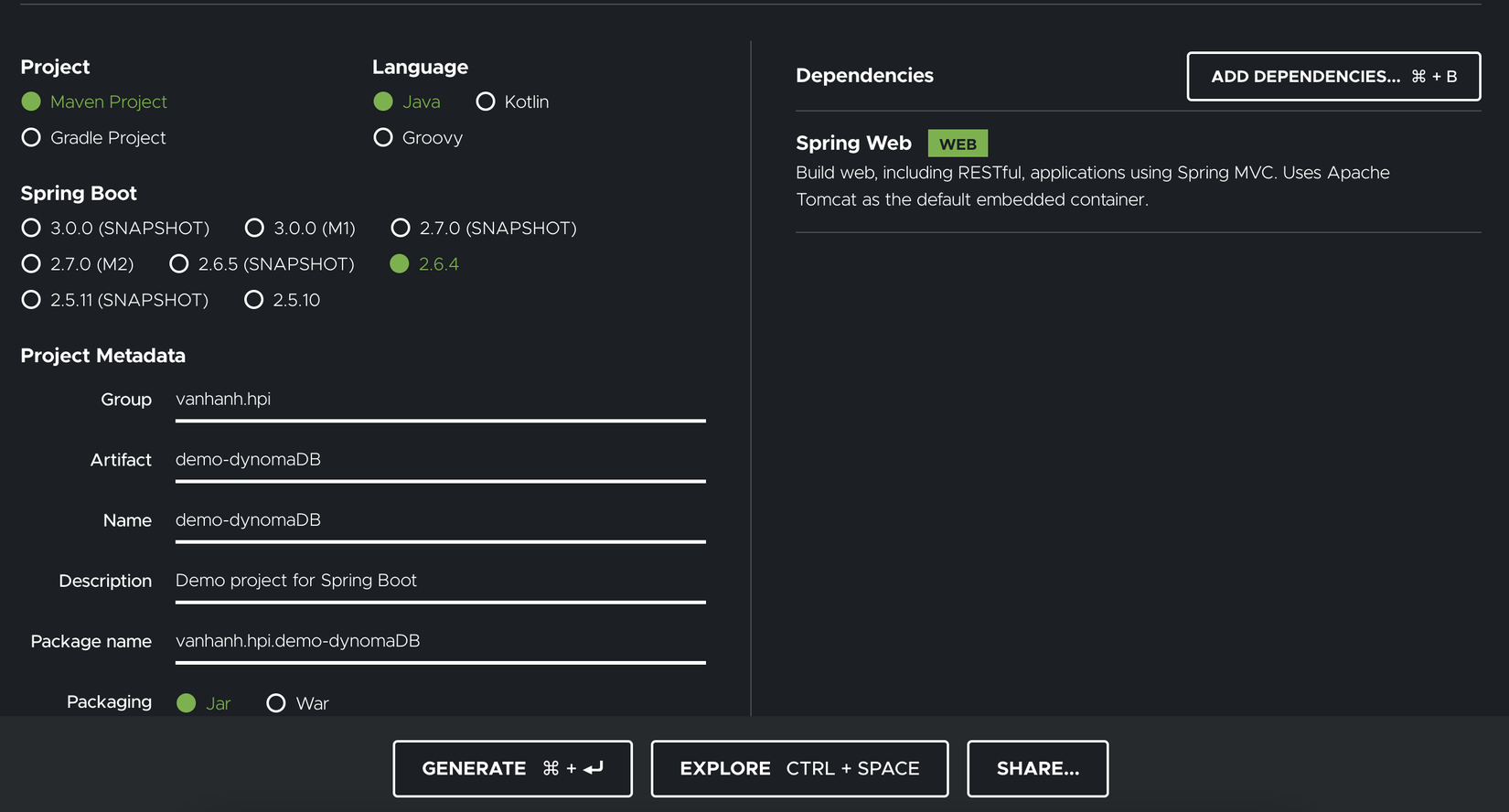
Sau đó thêm dependency sau vào project.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-java-sdk-dynamodb</artifactId>
<version>1.12.177</version>
</dependency>
Để kết nối được tới AWS DynamoDB bạn cần sử dụng cài đặt AWS CLI tại https://aws.amazon.com/vi/cli/ sau khi cài đặt tiến hành cấu hình credentials để kết nối DynamoDB
nano ~/.aws/credentials
Đối với windown bạn có thể dụng lệnh
type nul > %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials
coppy nội dung phía dưới vào file mới tạo
[default]
aws_access_key_id=xxx
aws_secret_access_key=xxx
Trong đó: aws_access_key_id và aws_secret_access_key là 2 giá trị được cung cấp khi bạn tạo tài khoản AWS.
Bạn có thể kiểm tra bằng 1 câu lệnh bất kỳ, ví dụ mình sử dụng lệnh lấy danh sách tất cả table để kiểm tra.
aws dynamodb list-tables
Aws Cli sẽ trả ra cho bạn 1 danh sách TableNames, nếu không kết nối được Aws Cli sẽ văng lỗi.
Nếu bạn không có tài khoản AWS sẵn để thực hành, bạn có thể sử dụng docker để dựng DynamoDB ngay trên máy của mình.
docker pull amazon/dynamodb-local
docker run -p 8000:8000 amazon/dynamodb-local
Tiếp theo chúng ta sẽ kết nối với DynomaDB bằng Java Spring Boot.
Mình tạo file DemoController.java và khởi tạo kết nối tới DynomaDB
package vanhanh.hpi.demodynomaDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.DynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.model.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@Component
public class DemoController {
AmazonDynamoDB client = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.defaultClient();
DynamoDB dynamoDB = new DynamoDB(client);
}
Mình sử dụng defaultClient để kết nối thì mặc định sẽ kết nối theo cấu hình credentials đã cấu hình phía trên, nếu bạn dùng docker để dựng DynamoDB thì bạn có thể thay thế bằng đoạn code sau
AmazonDynamoDB client = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.standard()
.withEndpointConfiguration(new AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration("http://localhost:8000", "us-west-2"))
.build();
Tiếp theo chúng ta viết 1 hàm api để khởi tạo table, hoặc bạn cũng có thể vô Aws Console để theo tác bằng giao diện trực quan.
@GetMapping("/dynoma-createtable")
public String createtable() {
try {
System.out.println("Attempting to create table; please wait...");
Table table = dynamoDB.createTable("hpi-movies",
Arrays.asList(new KeySchemaElement("year", KeyType.HASH), // Partition key
new KeySchemaElement("title", KeyType.RANGE)), // Sort key
Arrays.asList(new AttributeDefinition("year", ScalarAttributeType.N),
new AttributeDefinition("title", ScalarAttributeType.S)),
new ProvisionedThroughput(10L, 10L));
table.waitForActive();
System.out.println("Success. Table status: " + table.getDescription().getTableStatus());
return "Thành công";
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Unable to create table: ");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
return "Thất bại";
}
}
Hoặc bạn muốn 1 cái gì đó ngầu hơn thì Cli bên dưới là giành cho bạn
aws dynamodb create-table \
--table-name hpi-movies \
--key-schema AttributeName=year,KeyType=HASH AttributeName=title,KeyType=RANGE \
--provisioned-throughput ReadCapacityUnits=1,WriteCapacityUnits=1 \
--table-class STANDARD
Lúc này quay lại Aws Console thì bạn sẽ thấy giao diện như hình
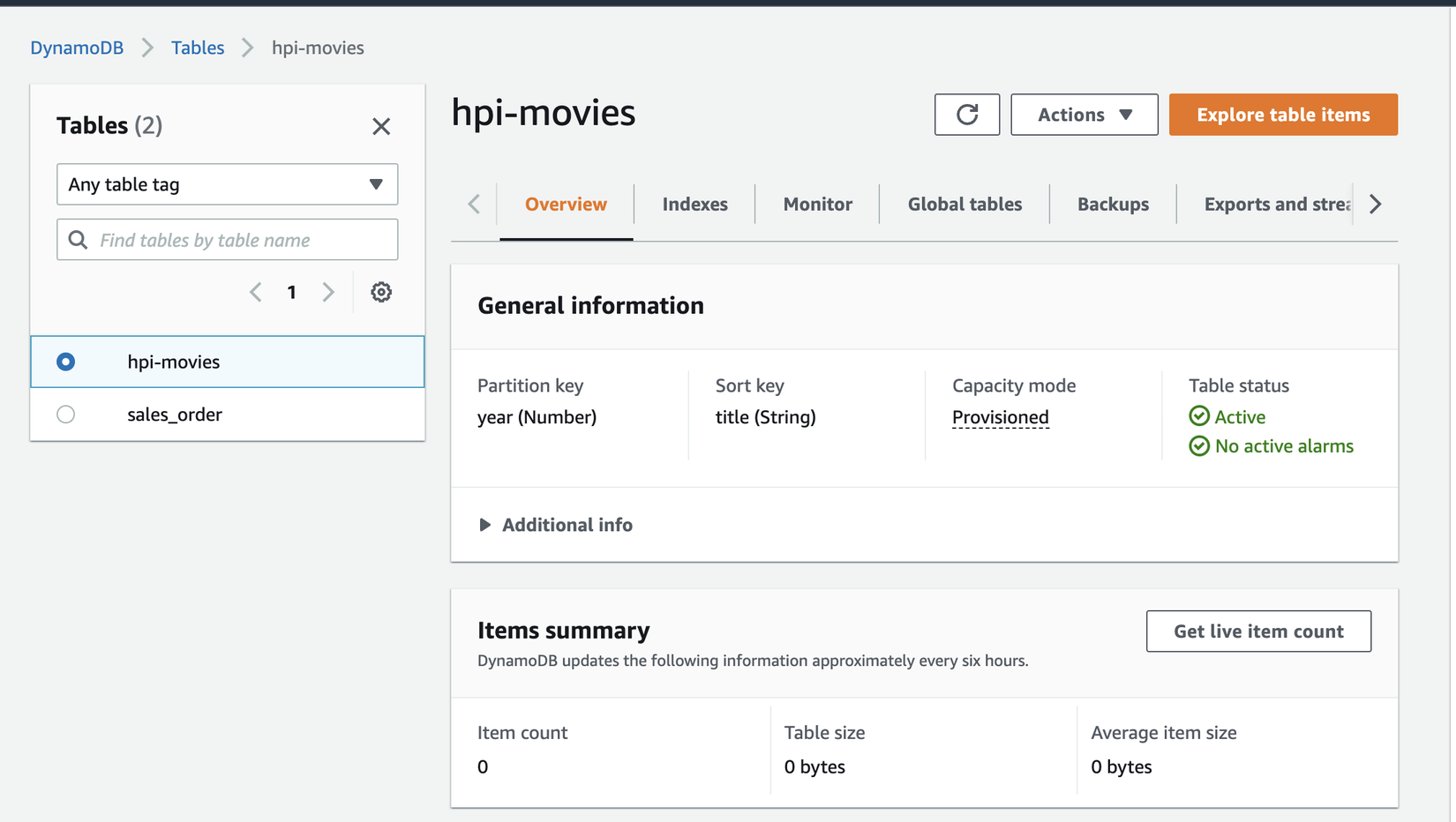
Tiếp tới hàm bên dưới sẽ giúp bạn tạo item trong DynamoDB
@GetMapping("/dynoma-inser")
public String gettable(String title, int year, String attributeOptional) {
try {
Map<String, Object> partitionKey = new HashMap<>();
partitionKey.put("year", year);
partitionKey.put("title", title);
var partition = partitionKey.entrySet().iterator().next();
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable("hpi-movies");
Item item = new Item().withPrimaryKey(partition.getKey(), partition.getValue());
item.with("attributeOptional", attributeOptional);
PutItemOutcome outcome = table.putItem(item);
System.out.println("PutItem succeeded:\n" + outcome.getPutItemResult());
return "Thành công";
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Unable to create table: ");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
return "Thất bại";
}
}
Khi gọi bạn dưới 1 item sẽ được khởi tạo, bạn có thể kiểm tra nó trong Aws Console
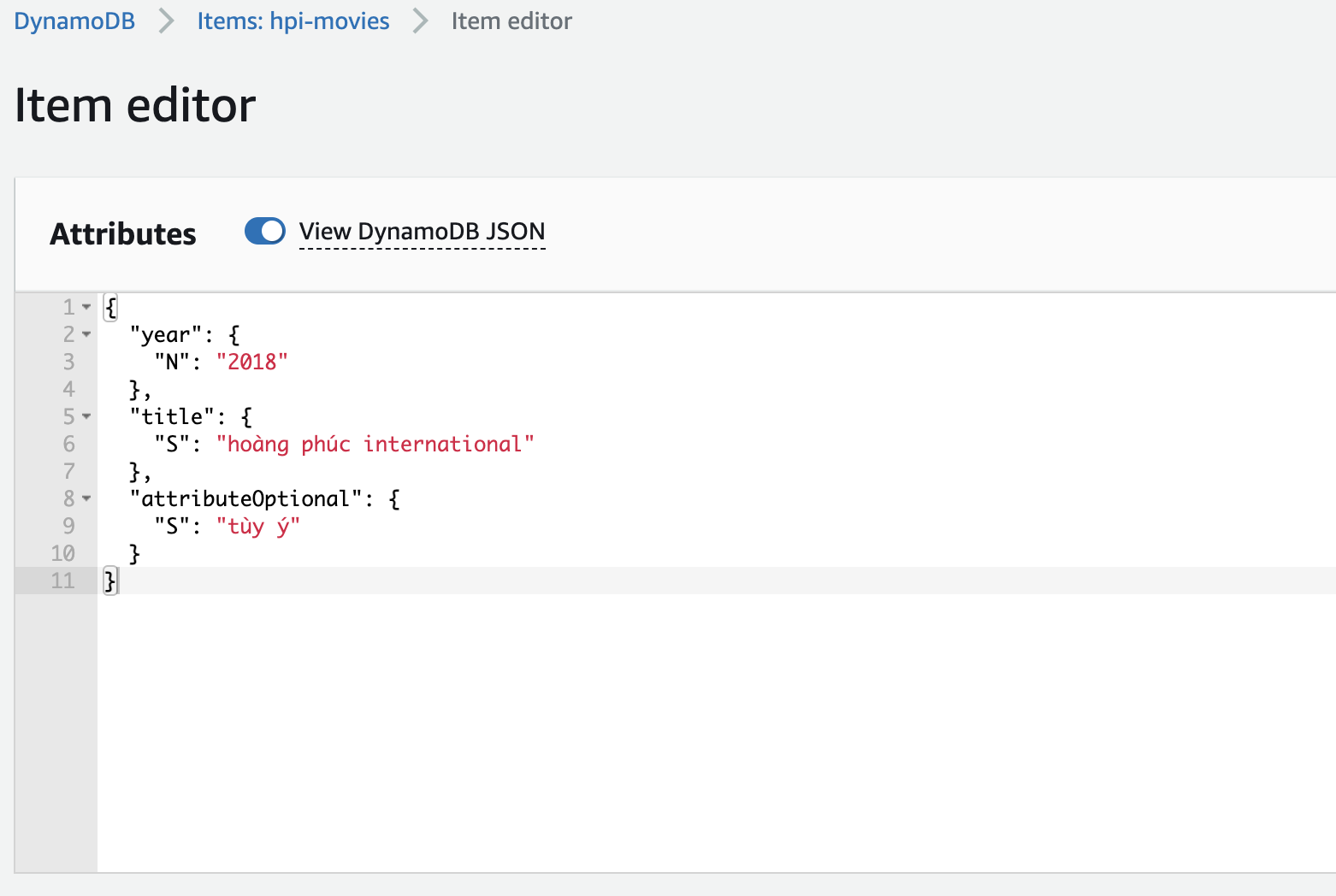
Và cuối cùng là hàm lấy item bằng primarykey
@GetMapping("/dynoma-getData")
public String getData(String title, int year) {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable("hpi-movies");
GetItemSpec spec = new GetItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("title", title, "year", year);
Item outcome = table.getItem(spec);
System.out.println("GetItem succeeded: " + outcome);
return outcome.toJSONPretty();
}
Và kết quả nhận được sẽ là
GetItem succeeded: { Item: {year=2018, attributeOptional=tùy ý, title=hoàng phúc international} }
Bên dưới là code hoàn chính cho các bạn tham khảo thêm
package vanhanh.hpi.demodynomaDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.DynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.Item;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.PutItemOutcome;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.Table;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.spec.GetItemSpec;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.model.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@Component
public class DemoController {
AmazonDynamoDB client = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.defaultClient();
DynamoDB dynamoDB = new DynamoDB(client);
@GetMapping("/dynoma-createtable")
public String createtable() {
try {
System.out.println("Attempting to create table; please wait...");
Table table = dynamoDB.createTable("hpi-movies",
Arrays.asList(new KeySchemaElement("year", KeyType.HASH), // Partition
// key
new KeySchemaElement("title", KeyType.RANGE)), // Sort key
Arrays.asList(new AttributeDefinition("year", ScalarAttributeType.N),
new AttributeDefinition("title", ScalarAttributeType.S)),
new ProvisionedThroughput(10L, 10L));
table.waitForActive();
System.out.println("Success. Table status: " + table.getDescription().getTableStatus());
return "Thành công";
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Unable to create table: ");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
return "Thất bại";
}
}
@GetMapping("/dynoma-inser")
public String gettable(String title, int year, String attributeOptional) {
try {
Map<String, Object> partitionKey = new HashMap<>();
partitionKey.put("year", year);
partitionKey.put("title", title);
var partition = partitionKey.entrySet().iterator().next();
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable("hpi-movies");
Item item = new Item().withPrimaryKey(partition.getKey(), partition.getValue());
item.with("attributeOptional", attributeOptional);
PutItemOutcome outcome = table.putItem(item);
System.out.println("PutItem succeeded:\n" + outcome.getPutItemResult());
return "Thành công";
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Unable to create table: ");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
return "Thất bại";
}
}
@GetMapping("/dynoma-getData")
public String getData(String title, int year) {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable("hpi-movies");
GetItemSpec spec = new GetItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("title", title, "year", year);
Item outcome = table.getItem(spec);
System.out.println("GetItem succeeded: " + outcome);
return outcome.toJSONPretty();
}
}
Kết luận
DynamoDB để đi sâu vào nó thì tương đối nhiều, trong bài này mình chỉ để cập nhiều hơn về lý thuyết mà 1 chút thực hành bằng Java.
các bạn có thể tham khảo thêm tại link này
Hẹn gặp lại các bạn trong các bài sau.
All rights reserved