(Phần 2) Tìm hiểu về ansible.
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Ở phần1 chúng ta được làm quen với những module đơn giản và playbook thuần. Phần tiếp theo sau đây, chúng ta sẽ đi làm thêm về Item, handles, facts, variables,
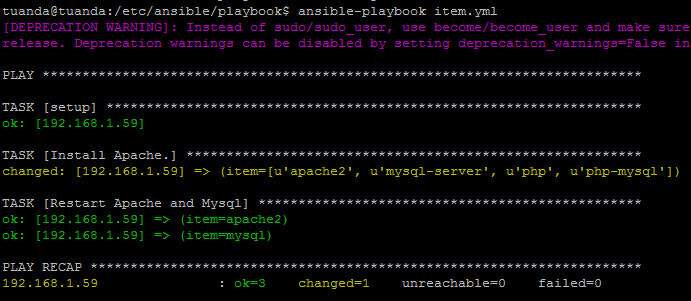
A. Loop Item
Phần trước, thay vì viết module apt cho từng gói cài đặt. Giờ ta sẽ nhóm vào Item để chạy 1 lần luôn.
cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[allone]
192.168.88.88
### VD cho Ubuntu###
---
- hosts: allone
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Apache.
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- mysql-server
- php
- php-mysql
- name: Restart Apache and Mysql
service:
name: "{{item}}"
state: running
loop:
- apache2
- mysql
### VD cho Centos7###
--
- hosts: allone
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Apache.
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- nginx
- redis
- name: Restart Apache and Mysql
service:
name: "{{item}}"
state: restarted
loop:
- nginx
- redis
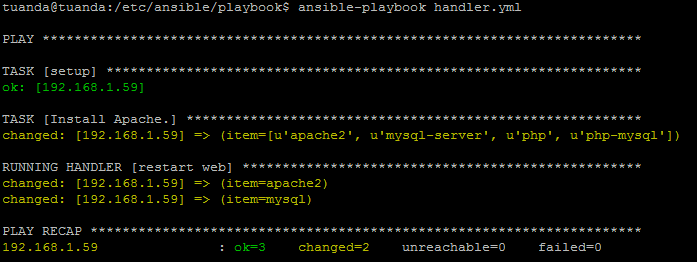
B. Handlers
Handlers giúp chúng ta gọi lại hành động thực thi nhiều lần (notify) mà không cần phải viết lại.
---
- hosts: allone
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Apache.
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- mysql-server
- php
- php-mysql
- name: deploy html file
template:
src: /tmp/index.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
notify: restart web
handlers:
- name: restart web
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: running
loop:
- apache2
- mysql
### Ví dụ handlers cho Centos
---
- hosts: allone
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install Apache.
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- nginx
- redis
notify: restart service
handlers:
- name: restart service
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- nginx
- redis
 Nếu handlers không chạy (do file không có sự thay đổi), bạn hãy thử sửa file /tmp/index.html và chạy lại. Ansible nhận ra sự thay đổi của file index nên sẽ thực thi Handlers.
Nếu handlers không chạy (do file không có sự thay đổi), bạn hãy thử sửa file /tmp/index.html và chạy lại. Ansible nhận ra sự thay đổi của file index nên sẽ thực thi Handlers.
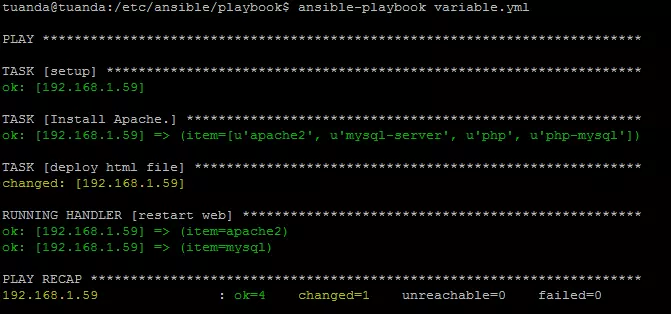
C.Variables và Template
Đặt giá trị cho biến cố định
---
- hosts: allone
become: yes
vars:
- domain_name: "tuanduong.com"
- index_file: "index.html"
- config_file: "tuanduong.conf"
tasks:
- name: Install Apache.
apt:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- apache2
- mysql-server
- php
- php-mysql
- name: deploy html file
template:
src: /tmp/{{ index_file }}
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
notify: restart web
handlers:
- name: restart web
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: running
loop:
- apache2
- mysql
Sử lại file index.html ở trên server ansible.
vim /tmp/index.html
This is <BR>
FILE_NAME: {{ index_file }} <BR>
DOMAIN NAME: {{ domain_name }} <BR>
Ta có kết quả như sau
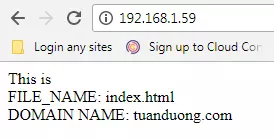
kết quả cho ta biết là Variable có thể ăn đến tận file được deploy nhờ Template.
D.Fact và when
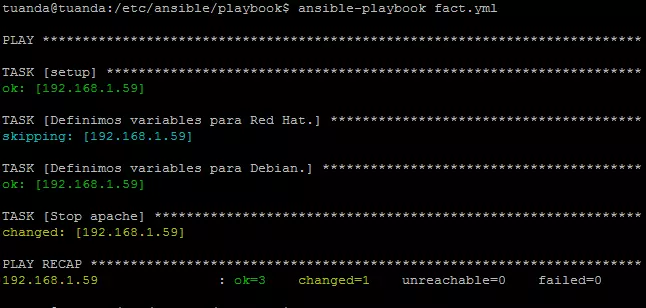
Ở phần 1 tôi đã hứa với các bạn là hướng dẫn ansible tự detect được OS và lựa chọn cài yum/apt. Ở đây ta sẽ dùng Fact để lấy thông tin và dùng when để thiết lập varriable. Ta có nhìn qua thông tin của Fact client bằng lệnh sau
#ansible 192.168.1.59 -m setup
---
- hosts: allone
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Define Red Hat.
set_fact:
package_name: "httpd"
when:
ansible_os_family == "Red Hat"
- name: Define Debian.
set_fact:
package_name: "apache2"
when:
ansible_os_family == "Debian"
- name: Stop apache
service:
name: "{{ package_name }}"
state: stopped
Phần 3: Phần tiếp theo, Long sẽ hướng dẫn các bạn sử dụng Role, Ansible galaxy. https://viblo.asia/p/tim-hieu-ansible-phan-3-yMnKMN0aZ7P
Cảm ơn Mai Gia Long (cùng team group) tiếp tục phần 3 của bộ Ansible.
Nếu có lỗi trong bài viết, mong các bạn comment góp ý. Cảm ơn.
All rights reserved