Build a Laravel REST API with Test-Driven Development
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
ở bài viết này sẽ giới thiệu cho ta cách để xây dựng một ứng dụng REST API với Test-Driven Development sử dụng framework laravel.
Test-Driven Development là gì?
TDD (Test Driven Development – Phát triển Hướng Kiểm thử) là một phương pháp phát triển phần mềm mà các hoạt động lập trình, kiểm thử và thiết kế được đan xem vào nhau.
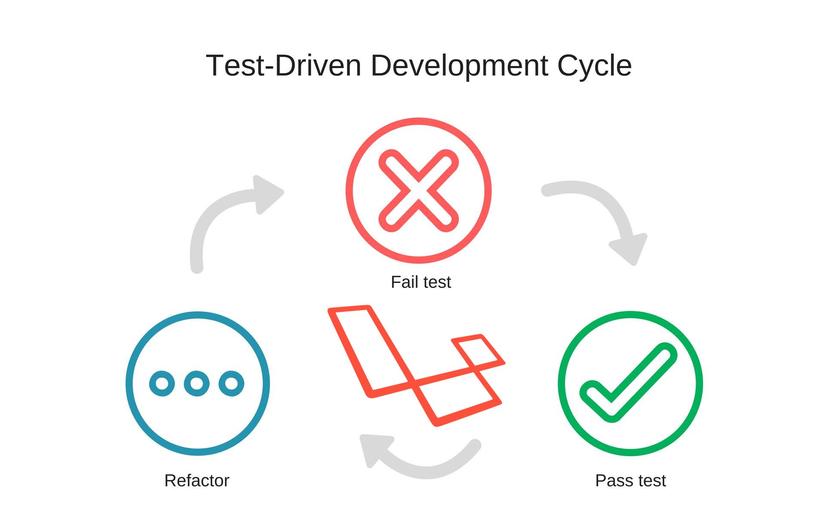
Quy tắc của TDD:
- Viết một kiểm thử đơn vị để mô tả một mặt của chương trình, kiểm thử vừa viết thường là thất bại bởi tính năng đó chưa được cài đặt.
- Viết vừa đủ mã nguồn để vượt qua kiểm thử
- Tái cấu trúc mã nguồn tới khi thỏa mãn các tiêu chí của mã tối giản (simple design)
- Lặp lại các thao tác trên
1. Cài đặt project
tạo một project laravel
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel tdd-laravel.
tiếp theo, chạy 2 lệnh:
php artisan make:auth
và
php artisan migrate.
cuối cùng của bước khởi tạo ta xóa file ExampleTest.php trong 2 thư mục tests/Unit and tests/Feature
2. Viết code cho chức năng đăng ký
- cấu hình trong file
config/auth.php
<?php
'defaults' => [
'guard' => 'api',
'passwords' => 'users',
],
'guards' => [
...
'api' => [
'driver' => 'jwt',
'provider' => 'users',
],
],
- tạo các route trong
routes/api.php
<?php
Route::group(['middleware' => 'api', 'prefix' => 'auth'], function () {
Route::post('authenticate', 'AuthController@authenticate')->name('api.authenticate');
Route::post('register', 'AuthController@register')->name('api.register');
});
- Trong model User.php
<?php
...
class User extends Authenticatable implements JWTSubject
{
...
public function getJWTIdentifier()
{
return $this->getKey();
}
public function getJWTCustomClaims()
{
return [];
}
}
- Tạo controller AuthController.php bằng câu lệnh
php artisan make:controller AuthController
<?php
...
class AuthController extends Controller
{
public function authenticate(Request $request)
{
//Validate fields
$this->validate($request,['email' => 'required|email','password'=> 'required']);
//Attempt validation
$credentials = $request->only(['email','password']);
if (! $token = auth()->attempt($credentials)) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Incorrect credentials'], 401);
}
return response()->json(compact('token'));
}
public function register(Request $request)
{
//Validate fields
$this->validate($request,[
'email' => 'required|email|max:255|unique:users',
'name' => 'required|max:255',
'password' => 'required|min:8|confirmed',
]);
// tạo mới user, tạo ra token và trả về
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->input('name'),
'email' => $request->input('email'),
'password' => Hash::make($request->input('password')),
]);
$token = JWTAuth::fromUser($user);
return response()->json(compact('token'));
}
}
Ở bước này, ta sẽ thêm 2 phương thức (hàm): phương thức authenticate() và register() . Trong phương thức authenticate, ta xác thực email và password. Trong phương thức register, ta xác thực đầu vào, tạo user mới với và tạo token sau đó thông báo cho người dùng.
- Để kiểm tra những gì vừa viết ở trên ta tạo class AuthTest để kiểm tra
chạy lệnh
php artisan make:test AuthTest
<?php
/**
* @test
* Test registration
*/
public function testRegister(){
//User's data
$data = [
'email' => 'test@gmail.com',
'name' => 'Test',
'password' => 'secret1234',
'password_confirmation' => 'secret1234',
];
//Send post request
$response = $this->json('POST',route('api.register'),$data);
//Assert it was successful
$response->assertStatus(200);
//Assert we received a token
$this->assertArrayHasKey('token',$response->json());
//Delete data
User::where('email','test@gmail.com')->delete();
}
/**
* @test
* Test login
*/
public function testLogin()
{
//Create user
User::create([
'name' => 'test',
'email'=>'test@gmail.com',
'password' => bcrypt('secret1234')
]);
//attempt login
$response = $this->json('POST',route('api.authenticate'),[
'email' => 'test@gmail.com',
'password' => 'secret1234',
]);
//Assert it was successful and a token was received
$response->assertStatus(200);
$this->assertArrayHasKey('token',$response->json());
//Delete the user
User::where('email','test@gmail.com')->delete();
}
Bây giờ để kiểm tra kết quả của đoạn test trên viết có đúng hay không ta sử dụng lệnh $vendor/bin/phpunit hoặc$ phpunit
Trường hợp ở 2 hàm trên là trong điều kiện dữ liệu ở trong database là lí tưởng. Nếu trường hợp dữ liệu không lí tưởng thì ta cần phải xem log và sửa lại cho phù hợp.
Kết luận
Qua bài viết này ta có thể hiểu hơn về khái niện TDD (Test-Driven Development) và các bước implement TDD cho một project sử dụng Laravel Framework.
Tài liệu tham khảo
All rights reserved