Thêm Unity vào trong ứng dụng iOS của bạn
 htj
Như ở tiêu đề thì hôm nay mình sẽ hướng dẫn các bạn cách để ta có thể thêm unity vào trong ứng dụng iOS của ta.
Thì ở bước đầu tiên chúng ta cần phải có một cái demo unity. Sau đó ta sẽ export cái project unity đó ra chọn platform là unity và chọn cho mình môi trường là device.
htj
Như ở tiêu đề thì hôm nay mình sẽ hướng dẫn các bạn cách để ta có thể thêm unity vào trong ứng dụng iOS của ta.
Thì ở bước đầu tiên chúng ta cần phải có một cái demo unity. Sau đó ta sẽ export cái project unity đó ra chọn platform là unity và chọn cho mình môi trường là device.
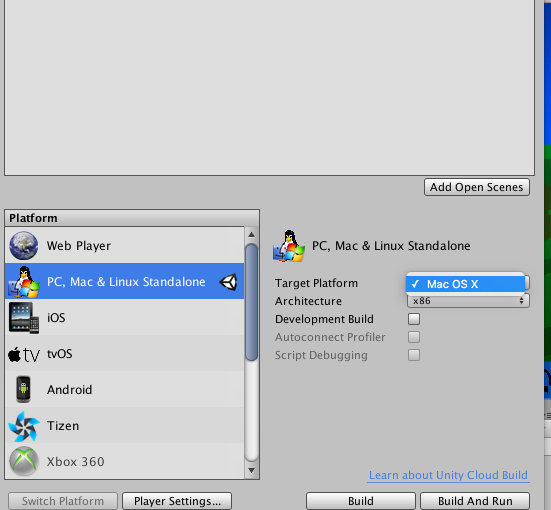
Sau khi export thành công thì ta sẽ có cho mình một bản build unity trên iOS như này
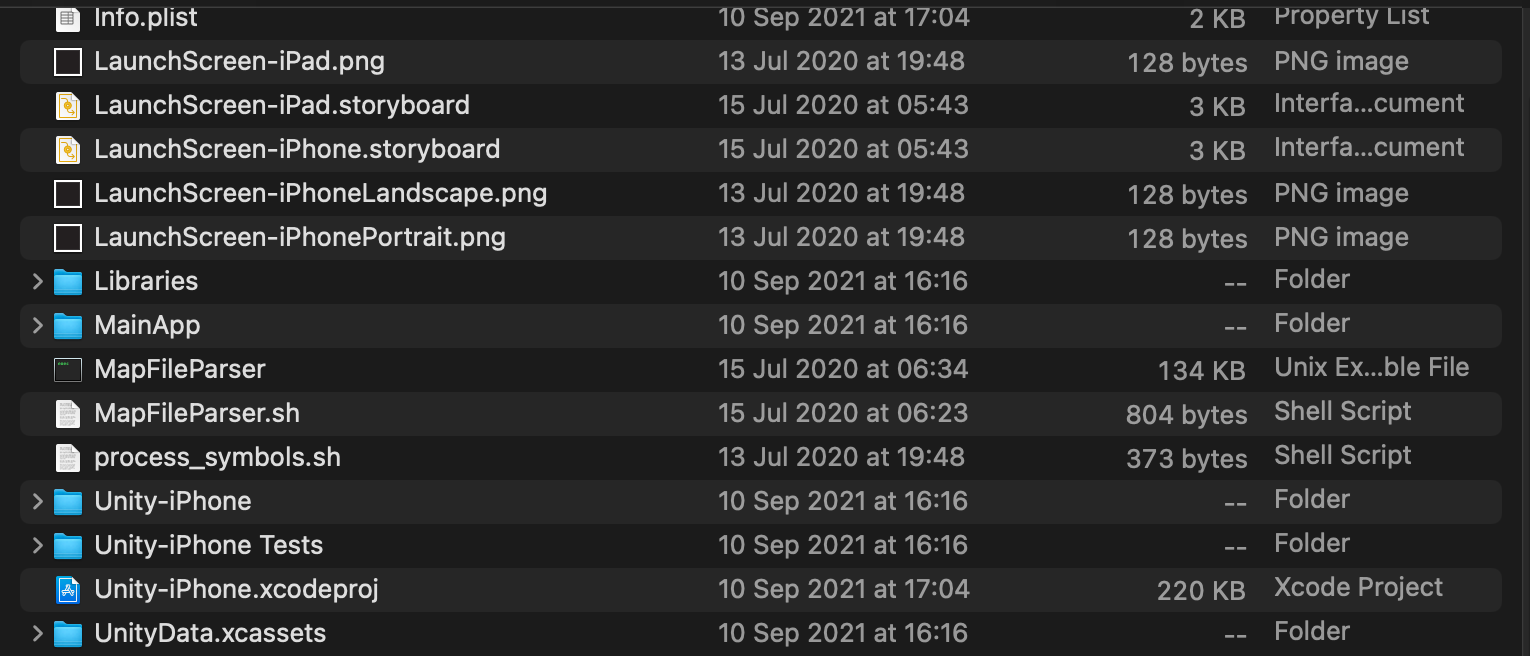
Xong bước này thì ta sẽ đến phần thêm nó vào trong ứng dụng iOS của ta. Ta tạo một cái project demo nhỏ trên Xcode để bắt đầu nhé.
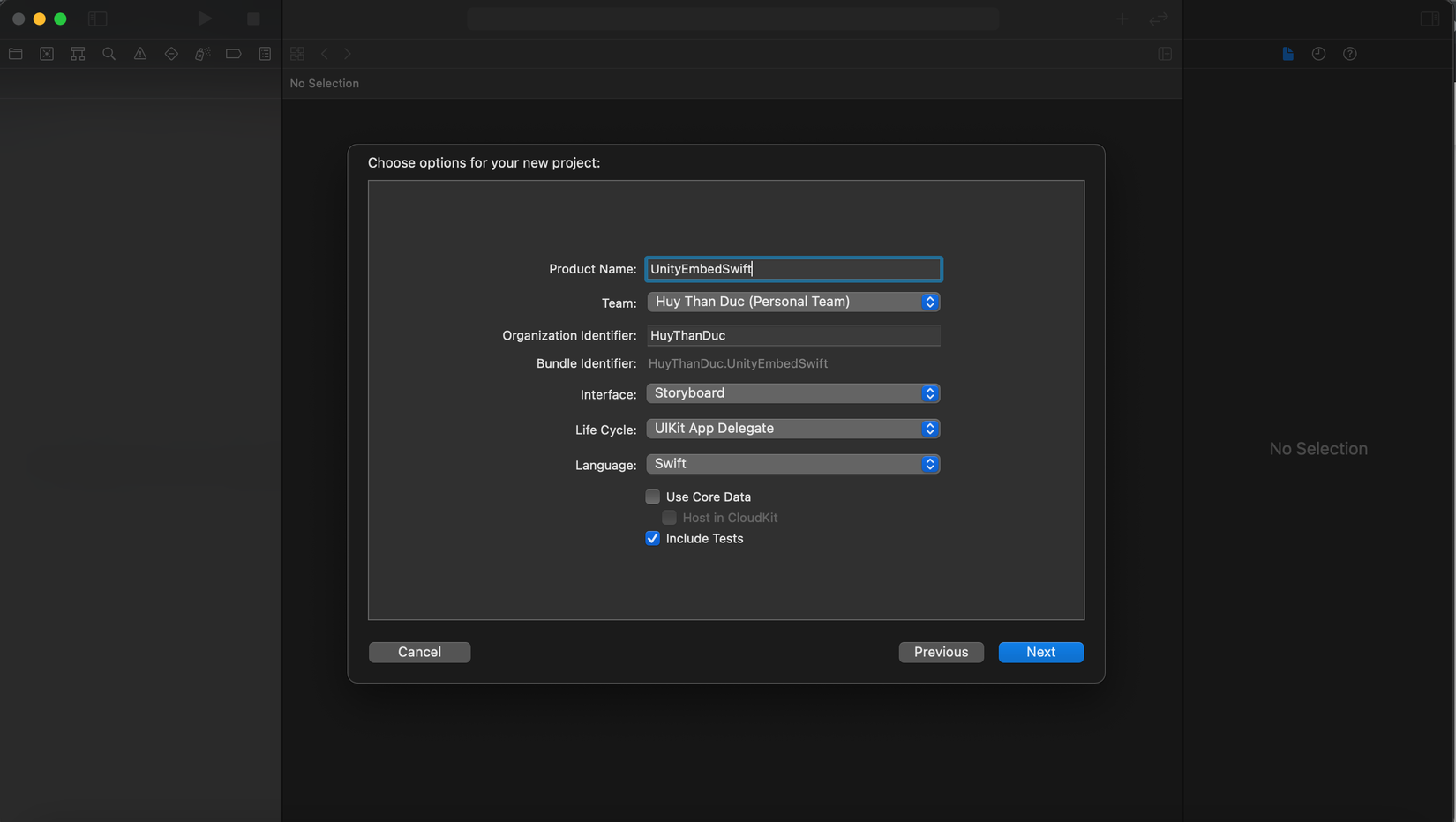
Ở những phiên bản trước của unity thì khi thêm vào trong native app thì ta phải viết các file bridge bằng object-c để liên kết qua bên unity rất là tốn thời gian. Còn ở unity phiên bản 2020 trở lên thì ta chỉ cần tạo một workspace sau đó cho project export unity và cái project iOS của ta vào chung một workspace là đc.
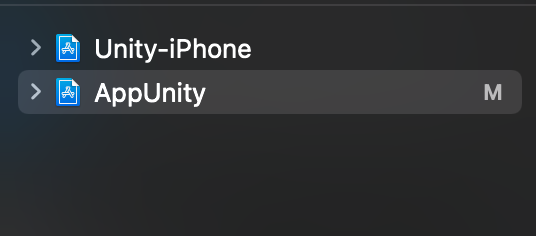
Tiếp theo ta sẽ thêm vào trong project iOS file unity framework từ project unity export đó.
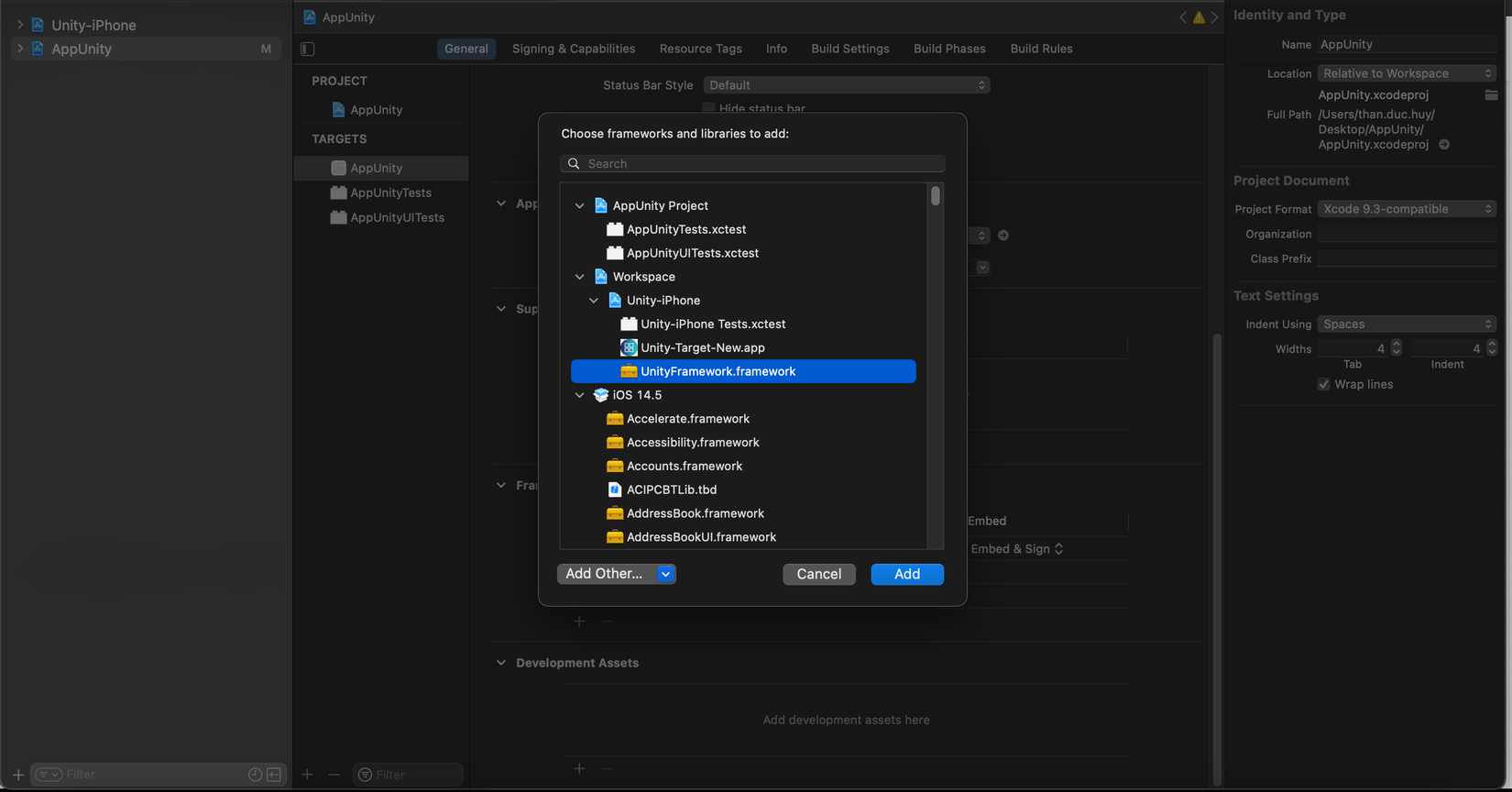
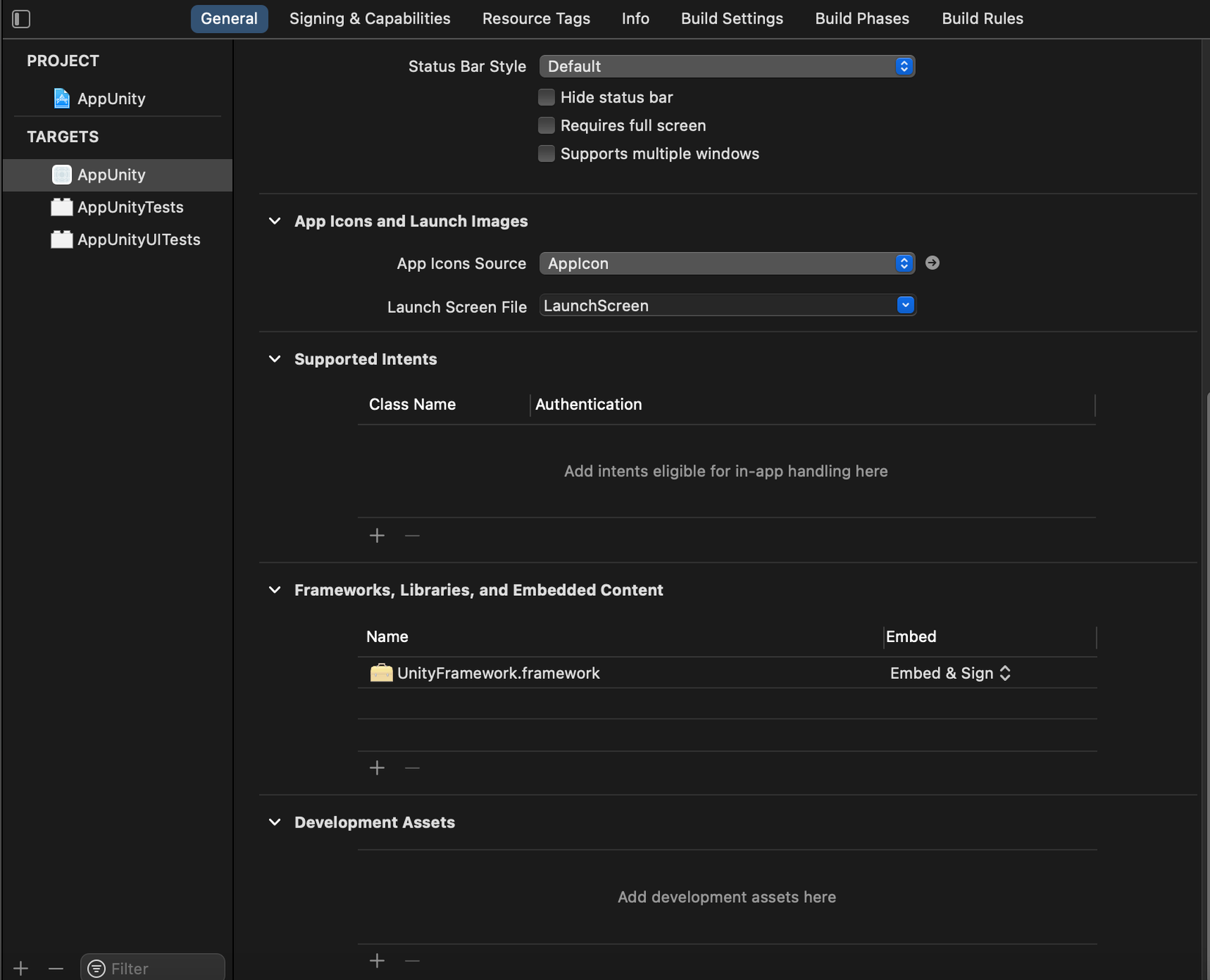
Sau khi thêm unity framework thành công thì ta sẽ thêm cho nó các hàm hổ trợ để ta có thể giao tiếp với bên unity. Ta tạo một file UnityIOS.swift trên project iOS của ta.
import UnityFramework
class UnityEmbeddedSwift: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate, UnityFrameworkListener {
private struct UnityMessage {
let objectName: String?
let methodName: String?
let messageBody: String?
}
private static var instance: UnityEmbeddedSwift!
private var unityFrameWork: UnityFramework!
private static var hostMainWindow: UIWindow! // Window to return to when exiting Unity window
private static var launchOpts: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
private static var cachedMessages = [UnityMessage]()
// MARK: - Static functions (that can be called from other scripts)
static func getUnityRootViewController() -> UIViewController! {
return instance.unityFrameWork.appController()?.rootViewController
}
static func getUnityView() -> UIView! {
return instance.unityFrameWork.appController()?.rootViewController?.view
}
static func unityWindow() -> UIWindow? {
return instance.unityFrameWork.appController().window
}
static func setHostMainWindow(_ hostMainWindow: UIWindow?) {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.hostMainWindow = hostMainWindow
let value = UIInterfaceOrientation.landscapeLeft.rawValue
UIDevice.current.setValue(value, forKey: "orientation")
}
static func setLaunchinOptions(_ launchingOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.launchOpts = launchingOptions
}
static func showUnity() {
if UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance == nil || UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance.unityIsInitialized() == false {
UnityEmbeddedSwift().initUnityWindow()
} else {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance.showUnityWindow()
}
}
static func hideUnity() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance?.hideUnityWindow()
}
static func pauseUnity() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance?.pauseUnityWindow()
}
static func unpauseUnity() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance?.unpauseUnityWindow()
}
static func unloadUnity() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance?.unloadUnityWindow()
}
static func sendUnityMessage(_ objectName: String, methodName: String, message: String) {
let msg: UnityMessage = UnityMessage(objectName: objectName, methodName: methodName, messageBody: message)
// Send the message right away if Unity is initialized, else cache it
if UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance != nil && UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance.unityIsInitialized() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance.unityFrameWork.sendMessageToGO(withName: msg.objectName,
functionName: msg.methodName,
message: msg.messageBody)
} else {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.cachedMessages.append(msg)
}
}
// MARK: Callback from UnityFrameworkListener
func unityDidUnload(_ notification: Notification!) {
unityFrameWork.unregisterFrameworkListener(self)
unityFrameWork = nil
UnityEmbeddedSwift.hostMainWindow?.makeKeyAndVisible()
}
// MARK: - Private functions (called within the class)
private func unityIsInitialized() -> Bool {
return unityFrameWork != nil && (unityFrameWork.appController() != nil)
}
private func initUnityWindow() {
if unityIsInitialized() {
showUnityWindow()
return
}
unityFrameWork = unityFrameworkLoad()!
unityFrameWork.setDataBundleId("com.unity3d.framework")
unityFrameWork.register(self)
// NSClassFromString("FrameworkLibAPI")?.registerAPIforNativeCalls(self)
unityFrameWork.runEmbedded(withArgc: CommandLine.argc,
argv: CommandLine.unsafeArgv,
appLaunchOpts: UnityEmbeddedSwift.launchOpts)
sendUnityMessageToGameObject()
UnityEmbeddedSwift.instance = self
}
private func showUnityWindow() {
if unityIsInitialized() {
unityFrameWork.showUnityWindow()
sendUnityMessageToGameObject()
}
}
private func hideUnityWindow() {
if UnityEmbeddedSwift.hostMainWindow == nil {
print("WARNING: hostMainWindow is nil! Cannot switch from Unity window to previous window")
} else {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.hostMainWindow?.makeKeyAndVisible()
}
}
private func pauseUnityWindow() {
unityFrameWork.pause(true)
}
private func unpauseUnityWindow() {
unityFrameWork.pause(false)
}
private func unloadUnityWindow() {
if unityIsInitialized() {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.cachedMessages.removeAll()
unityFrameWork.unloadApplication()
}
}
private func sendUnityMessageToGameObject() {
if UnityEmbeddedSwift.cachedMessages.count >= 0 && unityIsInitialized() {
for msg in UnityEmbeddedSwift.cachedMessages {
unityFrameWork.sendMessageToGO(withName: msg.objectName,
functionName: msg.methodName,
message: msg.messageBody)
}
UnityEmbeddedSwift.cachedMessages.removeAll()
}
}
private func unityFrameworkLoad() -> UnityFramework? {
let bundlePath: String = Bundle.main.bundlePath + "/Frameworks/UnityFramework.framework"
let bundle = Bundle(path: bundlePath )
if bundle?.isLoaded == false {
bundle?.load()
}
let ufw = bundle?.principalClass?.getInstance()
if ufw?.appController() == nil {
// unity is not initialized
// ufw?.executeHeader = &mh_execute_header
let machineHeader = UnsafeMutablePointer<MachHeader>.allocate(capacity: 1)
machineHeader.pointee = _mh_execute_header
ufw!.setExecuteHeader(machineHeader)
}
return ufw
}
}
Các hàm trên có chức năng như sau.
| HÀM | CHỨC NĂNG |
|---|---|
| getInstance | Phương thức lớp Singleton trả về một instance tới UnityFramework. |
| unloadApplication | Gọi này để dỡ Unity và nhận một cuộc gọi lại UnityFrameworkListenersau khi quá trình dỡ hoàn tất. Unity sẽ giải phóng phần lớn bộ nhớ mà nó chiếm, nhưng không phải tất cả. Bạn sẽ có thể chạy lại Unity. |
| appController | Trả về UnityAppControllerlớp con của UIApplicationDelegate. Đây là gốc rễ Unity lớp ở phía bên mẹ đẻ, và có thể truy cập đối tượng xem liên quan của ứng dụng, chẳng hạn như UIView, UIViewControllers, CADisplayLink, hoặc DisplayConnection. |
| showUnityWindow | Gọi phương thức này trong khi Chế độ xem không hợp nhất đang hiển thị cũng hiển thị Chế độ xem hợp nhất đã chạy. |
| runUIApplicationMainWithArgc | Cách mặc định để chạy Unity từ phương thức chính mà không có Chế độ xem nào khác. |
| pause | Tạm dừng Unity. |
| quitApplication | Gọi này để dỡ bỏ Unity hoàn toàn và nhận một cuộc gọi lại UnityFrameworkListenerkhi Unity thoát. Unity sẽ giải phóng tất cả bộ nhớ. |
Sau đó ở AppDelegate.swift ta sẽ liên kết window của app với window bên unity để ta có thể show ứng dụng trên unity của ta ra.
import UIKit
@main
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
UnityEmbeddedSwift.setHostMainWindow(window)
UnityEmbeddedSwift.setLaunchinOptions(launchOptions)
return true
}
Bước cuối cùng ở file ViewController ta chỉ cần gọi hàm show unity là thành công.
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
UnityEmbeddedSwift.showUnity()
let uView = UnityEmbeddedSwift.getUnityView()
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.1, execute: {
self.view.addSubview(uView!)
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.1, execute: {
self.view.sendSubviewToBack(uView!)
})
})
}
}
Đến đây thì ta đã thành công trong việc thêm unity vào trong ứng dụng của iOS của ta rồi đó. Chúc các bạn thành công 

All rights reserved