[Real-Time Emotion Detection] Xây dựng mạng nhận diện cảm xúc khuôn mặt cho người mới bắt đầu
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
1. Introduction
Xin chào các bạn, kết thúc 2 bài viết về object segmentation với MaskRCNN sẽ là các bài viết về Face Detection, thì hôm nay trong bài viết đầu tiên trong series mình xin giới thiệu tới các bạn cách xây dựng mạng cho bài toán nhận diện cảm xúc. Bài toán không còn xa lạ với mọi người nhưng mình nghĩ nó rất thiết thực với các bạn mới tìm hiểu về AI có thể tiếp cận dễ dàng hơn. Mình hi vọng qua bài toán này sẽ giúp các bạn hiểu về các bước khi mà training một mô hình sẽ như thế nào cũng như tiếp cận dễ với keras hoặc tensorflow2.
2. Dataset
Trong bài viết này mình sử dụng bộ dataset FER2013, một bộ dataset phổ biến với 35,887 grayscale ảnh khuôn mặt có kích thước 48x48 pixels. Bộ data gồm 7 loại: Angry, Disgust, Fear, Happy, Sad, Surprise, and Neutral. Các bạn có thể dowload bộ dữ liệu theo link phía dưới của mình
 Những hình ảnh dữ liệu này thì đã được lưu trữ dưới dạng file csv
Những hình ảnh dữ liệu này thì đã được lưu trữ dưới dạng file csv Hàng đầu tiên sẽ là là tên 3 cột: emotion, pixels, usage. Còn lại 35,887 row sẽ lưu thông tin của từng ảnh với các chỉ số sau: (0=Angry, 1=Disgust, 2=Fear, 3=Happy, 4=Sad, 5=Surprise, 6=Neutral ).
Hàng đầu tiên sẽ là là tên 3 cột: emotion, pixels, usage. Còn lại 35,887 row sẽ lưu thông tin của từng ảnh với các chỉ số sau: (0=Angry, 1=Disgust, 2=Fear, 3=Happy, 4=Sad, 5=Surprise, 6=Neutral ).
LInk dowload dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/deadskull7/fer2013
3. Xây dựng và training mô hình
Bài viết của mình muốn hướng tới các bạn mới tìm hiểu cũng như tiếp cận với AI nên mình sẽ hướng dẫn các bạn cụ thể từng bước, nếu bạn nào biết rồi thì có thể bỏ qua nhé. Mình sử dụng google colab để training các bạn có thể training.
B1: Mount drive
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/gdrive')
Sau đó các bạn ấn đường link phía dưới, chọn drive mình muốn liên kết rồi copy mã là oki.
B2: Import các thư viện cần dùng
Trong bài viết này mình sử dụng thư viện keras
import sys, os
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, BatchNormalization,AveragePooling2D
from keras.losses import categorical_crossentropy
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.regularizers import l2
from keras.utils import np_utils
Sau khi gọi xong các thư viện mình cần sử dụng thì bước tiếp theo chúng ta sẽ xử lý data, thì trong bộ dữ liệu đã được chia sẵn dữ liệu training và dữ liệu test.
df=pd.read_csv('path_to_csv_fer_2013')
X_train,train_y,X_test,test_y=[],[],[],[]
for index, row in df.iterrows():
val=row['pixels'].split(" ")
try:
if 'Training' in row['Usage']:
X_train.append(np.array(val,'float32'))
train_y.append(row['emotion'])
elif 'PublicTest' in row['Usage']:
X_test.append(np.array(val,'float32'))
test_y.append(row['emotion'])
except:
print(f"error occured at index :{index} and row:{row}")
Sau khi load xong dữ liệu và chia dữ liệu thành training và test thì mình cần xử lý dữ liệu và chuyển y thành dạng category:
num_features = 64
num_labels = 7
batch_size = 64
epochs = 30
width, height = 48, 48
X_train = np.array(X_train,'float32')
train_y = np.array(train_y,'float32')
X_test = np.array(X_test,'float32')
test_y = np.array(test_y,'float32')
train_y=np_utils.to_categorical(train_y, num_classes=num_labels)
test_y=np_utils.to_categorical(test_y, num_classes=num_labels)
X_train -= np.mean(X_train, axis=0) #normalize dữ liệu giữa 0 và 1
X_train /= np.std(X_train, axis=0)
X_test -= np.mean(X_test, axis=0)
X_test /= np.std(X_test, axis=0)
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], 48, 48, 1)
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], 48, 48, 1)
B3: Khởi tạo mô hình
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(X_train.shape[1:])))
model.add(Conv2D(64,kernel_size= (3, 3), activation='relu'))
# model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
#2nd convolution layer
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
# model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
#3rd convolution layer
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
# model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Flatten())
#fully connected neural networks
model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(num_labels, activation='softmax'))
# model.summary()
#Compliling the model
model.compile(loss=categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer=Adam(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
Các bạn có thể thử tạo thêm các lớp convolution cũng như các lớp nhé: Sau đó mình sẽ summary xem kiến trúc mô hình mình vừa tạo:
model.summary
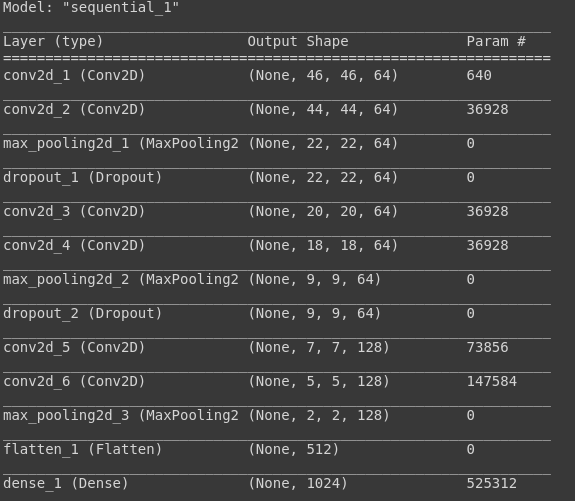
B4: Training mô hình
#Training the model
model.fit(X_train, train_y,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(X_test, test_y),
shuffle=True)
 Trong bài viết tiếp theo mình sẽ cùng các bạn thảo luận kĩ hơn về các kĩ thuật training mô hình để tránh overfitting cũng như tăng độ chính các của mô hình.
Trong bài viết tiếp theo mình sẽ cùng các bạn thảo luận kĩ hơn về các kĩ thuật training mô hình để tránh overfitting cũng như tăng độ chính các của mô hình.
Sau khi training xong mô hình thì mình sẽ save weight lại 1 file h5
#Saving the model
fer_json = model.to_json()
with open("fer.json", "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(path_to/fer_json)
model.save_weights("path_to_weight/fer.h5")
4. Detecting Real-Time Emotion
Như mình đã nói ở trên thì trong bài viết này mình sẽ dùng mô hình đã training được để phát hiện cảm xúc khuôn mặt real-time. Trước tiên thì bạn cần load weight mà đã được lưu, việc detect khuôn mặt thì mình đã dùng 1 hàm của opencv2 đó là cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml') thì trong bài viết sau mình sẽ cùng các bạn xây dựng 1 mô hình nhận diện khuôn mặt, hãy follow để xem bài viết tiếp theo của mình nhé.
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from keras.models import model_from_json
from keras.preprocessing import image
#load model
model = model_from_json(open("path_to/fer.json", "r").read())
#load weights
model.load_weights('path_to/fer.h5')
face_haar_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
## detec face
cap=cv2.VideoCapture(0) # bật webcam
while True:
ret,test_img=cap.read()# captures frame and returns boolean value and captured image
if not ret:
continue
gray_img= cv2.cvtColor(test_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
faces_detected = face_haar_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray_img, 1.32, 5)
for (x,y,w,h) in faces_detected:
cv2.rectangle(test_img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(255,0,0),thickness=7)
roi_gray=gray_img[y:y+w,x:x+h]#cropping region of interest i.e. face area from image
roi_gray=cv2.resize(roi_gray,(48,48))
img_pixels = image.img_to_array(roi_gray)
img_pixels = np.expand_dims(img_pixels, axis = 0)
img_pixels /= 255
predictions = model.predict(img_pixels)
#find max indexed array
max_index = np.argmax(predictions[0])
emotions = ('angry', 'disgust', 'fear', 'happy', 'sad', 'surprise', 'neutral')
predicted_emotion = emotions[max_index]
cv2.putText(test_img, predicted_emotion, (int(x), int(y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0,0,255), 2)
resized_img = cv2.resize(test_img, (1000, 700))
cv2.imshow('Facial emotion analysis ',resized_img)
if cv2.waitKey(10) == ord('q'):#wait until 'q' key is pressed
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows
Vậy là đã xong cùng tận hưởng thành quả. Bài viết của mình tới đây là kết thúc, cảm ơn các bạn đã theo dõi bài viết của mình. Đừng tiếc 1 nút click để upvote cũng như follow để mình có thêm động lực viết bài nhé.
All rights reserved
