Spring Boot In Action: Bean overriding under the hood
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 2 năm
I. Introduction
Chúng ta biết rằng Spring Boot không cho phép hai bean có cùng tên vì giả sử nếu có hai bean có tên myBean thì làm thế nào để Spring Boot có thể biết bean nào sẽ trả về khi đoạn mã sau được thực thi?
MyBean myBean = context.getBean("myBean");
Đến đây Spring Boot sẽ phải chọn một trong hai và do đó có thể dẫn đến kết quả không mong muốn. Vì thế mà từ version Spring Boot 2.1 trở đi thì Spring Boot chỉ cho phép mỗi bean có một tên duy nhất.
Tất nhiên những gì nói trên chỉ là ở mức độ lý thuyết. Hãy cùng quan sát ví dụ dưới đây để hiểu rõ hơn.
Mình có entity AppBean và hai Configuration class lần lượt khai báo 2 bean của nó có cùng tên là appBean như sau:
AppBean.java
public class AppBean {
private String message;
public AppBean (String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage () {
return message;
}
}
MyConfig1.java
@Configuration
public class MyConfig1 {
@Bean
AppBean appBean() {
return new AppBean("from config 1");
}
}
MyConfig2.java
@Configuration
public class MyConfig2 {
@Bean
AppBean appBean() {
return new AppBean("from config 2");
}
}
Bây giờ mình sẽ viết một hàm Main để lấy bean appBean ra để sử dụng. Các bạn thử đoán xem điều gì sẽ xảy ra với đoạn code dưới đây?
Main.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(SpringBootVersion.getVersion()); //2.7.2 > 2.1
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Main.class);
AppBean bean = context.getBean(AppBean.class);
System.out.println(bean.getMessage());
}
}
Có phải bạn đang mong chờ một message lỗi thông báo kiểu như thế này không?
A bean with that name has already been defined in class path ....
Thật tiếc là điều mà có thể các bạn đang mong chờ (có cả mình) đã không xảy ra. Chương trình vẫn chạy ngon lành và âm thầm in ra dòng chữ sau trong console:
from config 2
Bạn hãy thử đoán xem tại sao không phải from config 1 mà lại là from config 2 nhé, mình sẽ giải thích cụ thể ở phần tiếp theo.
II. Analyze Spring Boot's source code
Ở đoạn code ở phần I, vì mình khai báo bean trong @Configuration class nên để lấy bean ra sử dụng cần thông qua AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Main.class);
Việc khởi tạo instance của AnnotationConfigApplicationContext cần làm những việc sau:
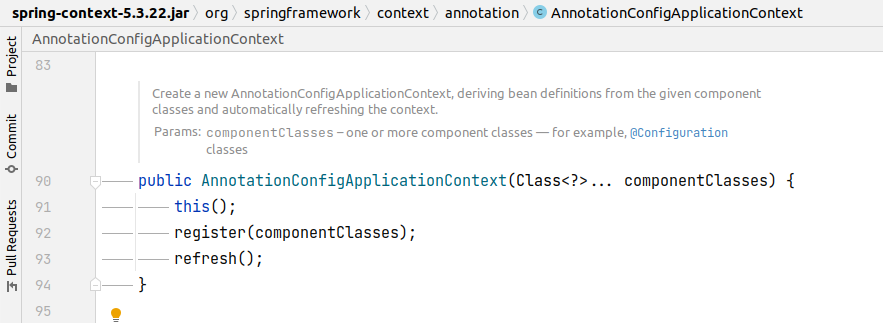
1. this()
Khởi tạo reader và scanner
2. register(componentClasses);
Register componentClass sẽ tiến hành register bean với DefaultListableBeanFactory.
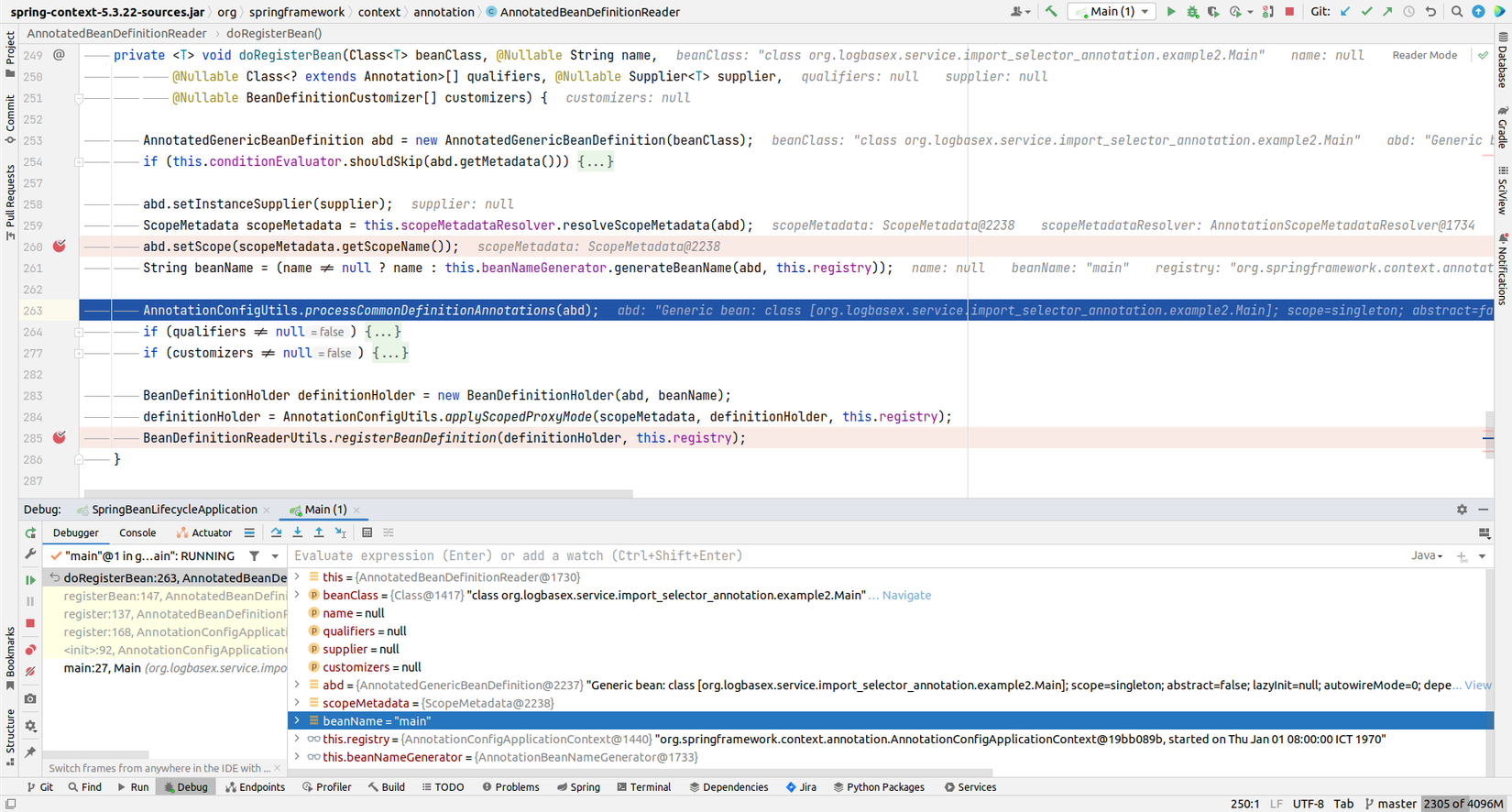
Sau khi đã đăng kí xong componentClass (@SpringBootApplication) Main thì chúng ta đã có bean tên là main với class tương ứng.
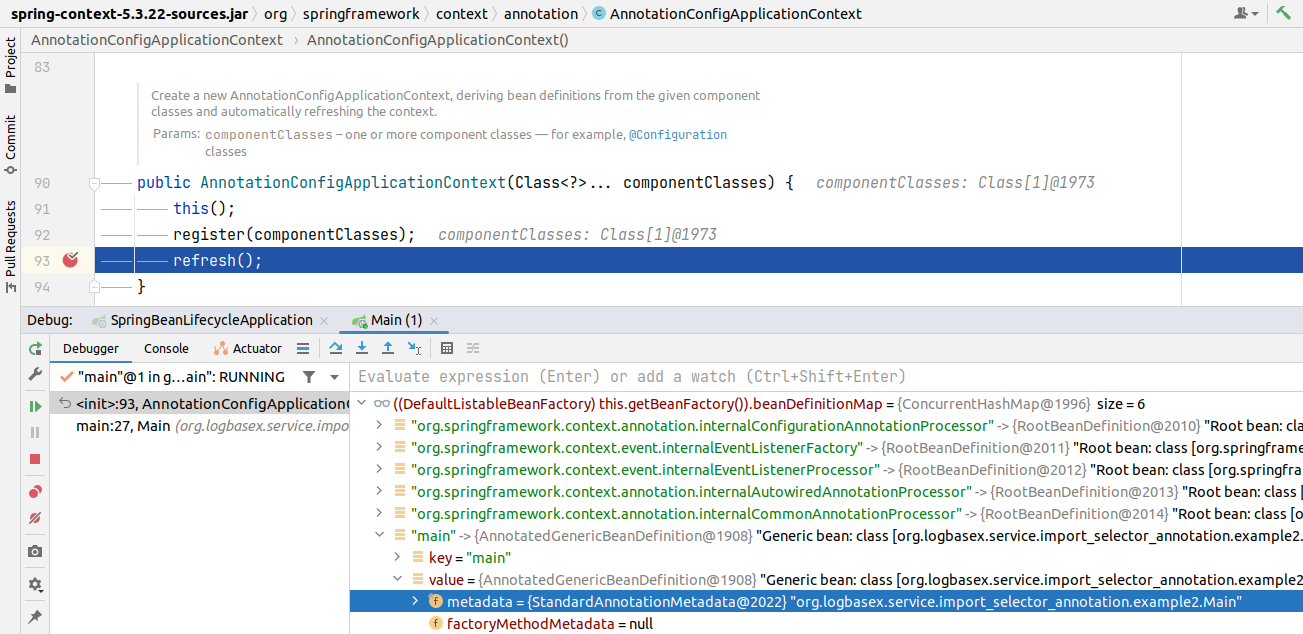
Vì class được đánh dấu là @SpringBootApplication sẽ tiến hành scan current package và sub-packages để tìm kiếm bean nên chắc hẳn các bạn đã hình dung ra Spring Boot sẽ làm gì tiếp theo =)).
When @Configuration classes are provided as input, the @Configuration class itself is registered as a bean definition, and all declared @Bean methods within the class are also registered as bean definitions.
├── example2
│ ├── AppBean.java
│ ├── Main.java
│ ├── MyConfig1.java
│ └── MyConfig2.java
3. refresh();
Trong hàm này Spring Boot xử lý rất nhiều việc khác nhau, nhưng trong phạm vi bài viết này cái chúng ta cần quan tâm nhất chính là phương thức invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors sẽ được dùng để load và khởi tạo bean.

Để bớt lan man thì như đã giới thiệu ở phần trước, mình sẽ đi luôn vào ConfigurationClassPostProcessor class để xem luồng đi như thế nào nhé. Callstack mình sẽ để ở phía cuối bài viết.
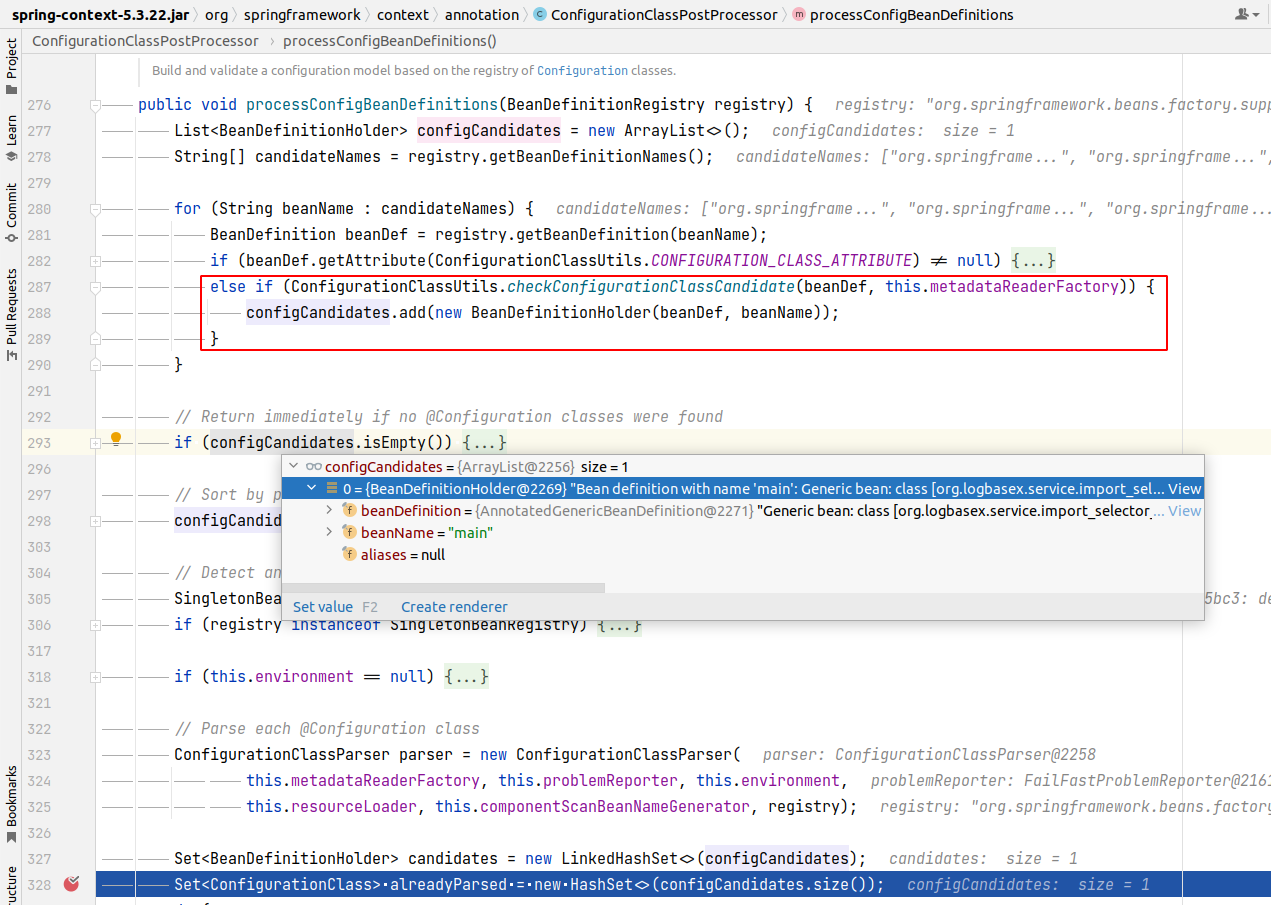
Idea về cơ bản là đi tìm base packages của component class rồi sau đó đi scan @Configuration class thui.
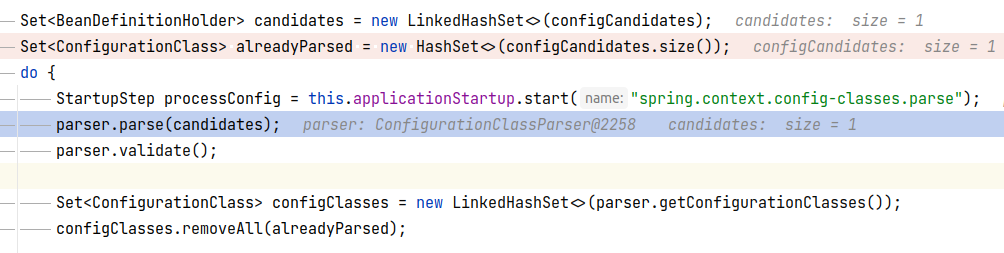
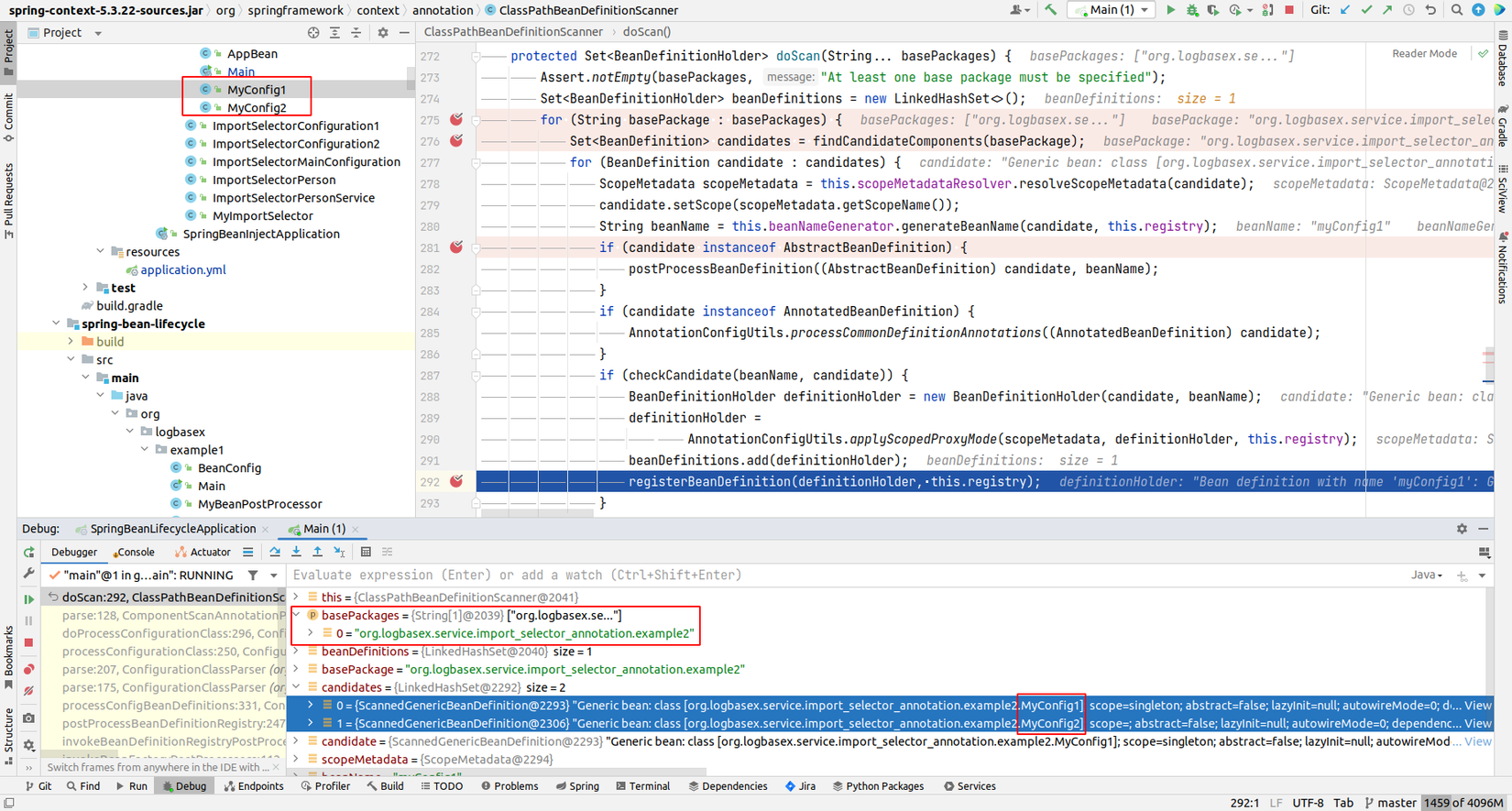
Callstack:
doScan:292, ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:128, ComponentScanAnnotationParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
doProcessConfigurationClass:296, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigurationClass:250, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:207, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:175, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigBeanDefinitions:331, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry:247, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors:311, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:112, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:746, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:564, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
<init>:93, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.annotation)
main:27, Main (org.logbasex.service.import_selector_annotation.example2)
Sau khi scan xong thì chúng ta được thêm 2 configClasses sau:
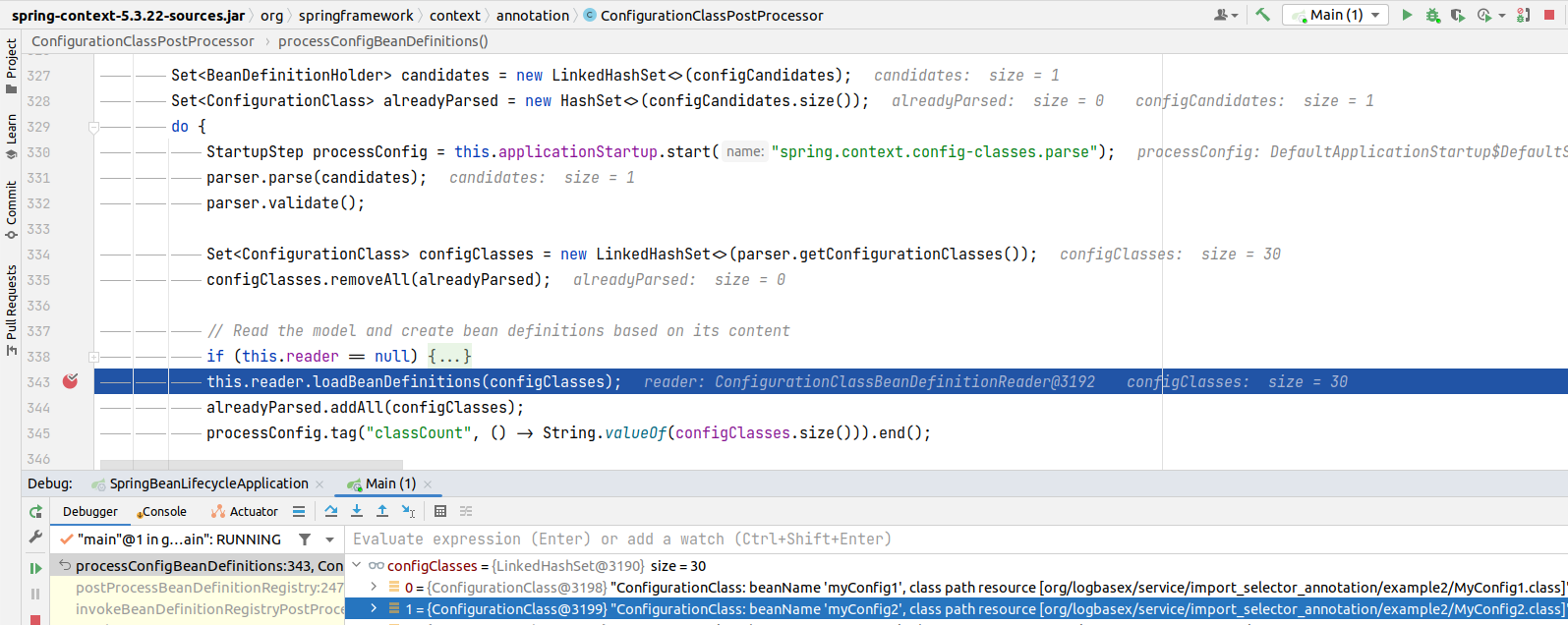
Bây giờ đến giai đoạn quan trọng là load/register BeanDefinitions từ configClasses.
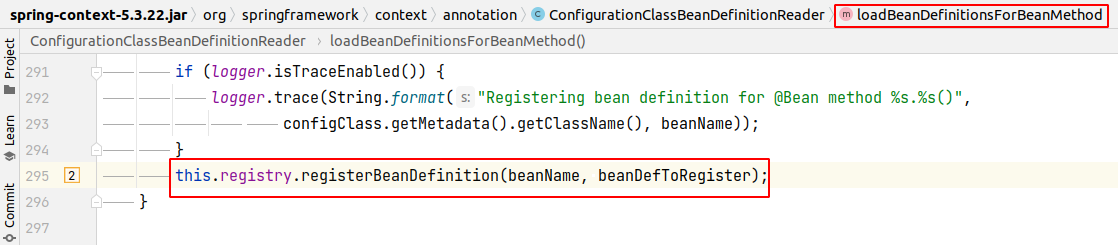
Chúng ta có thể thấy rằng khi register bean thì biến allowBeanDefinitionOverriding của instance DefaultListableBeanFactory class có giá trị = true. Cho nên trong trường hợp bean appBean đã tồn tại thì không có Exception nào được ném ra cả. Và bean appBean đến từ configuration class MyConfig2 sẽ override bean cùng tên đến từ class MyConfig1. Điều này hoàn toàn dễ hiểu vì Spring bean default là singleton scope.
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
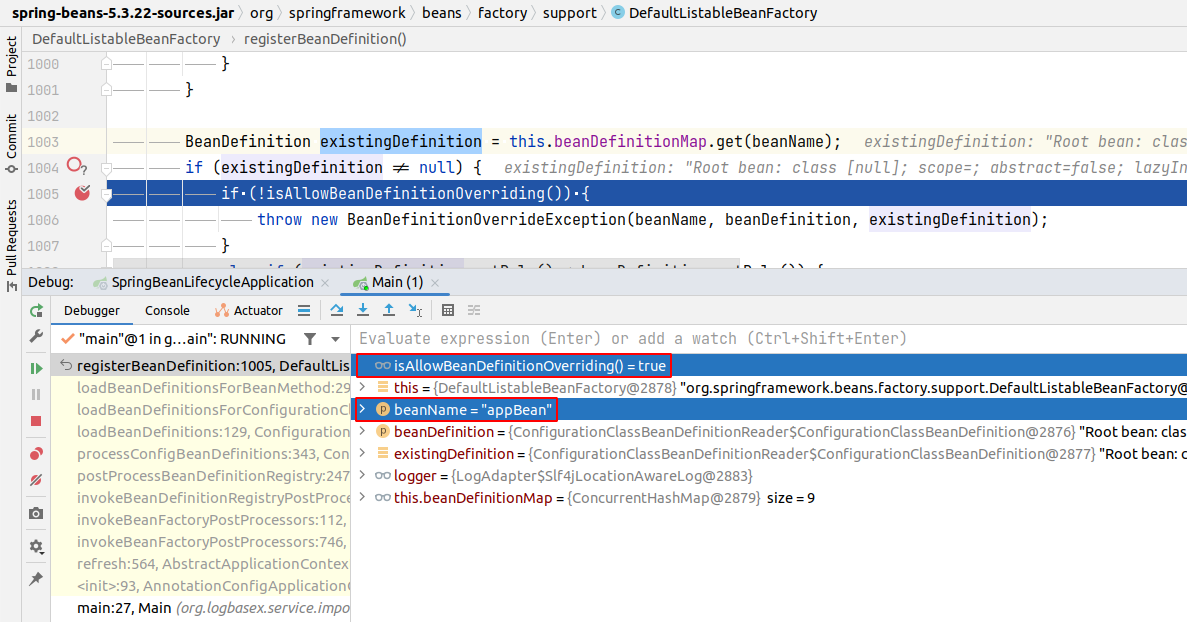
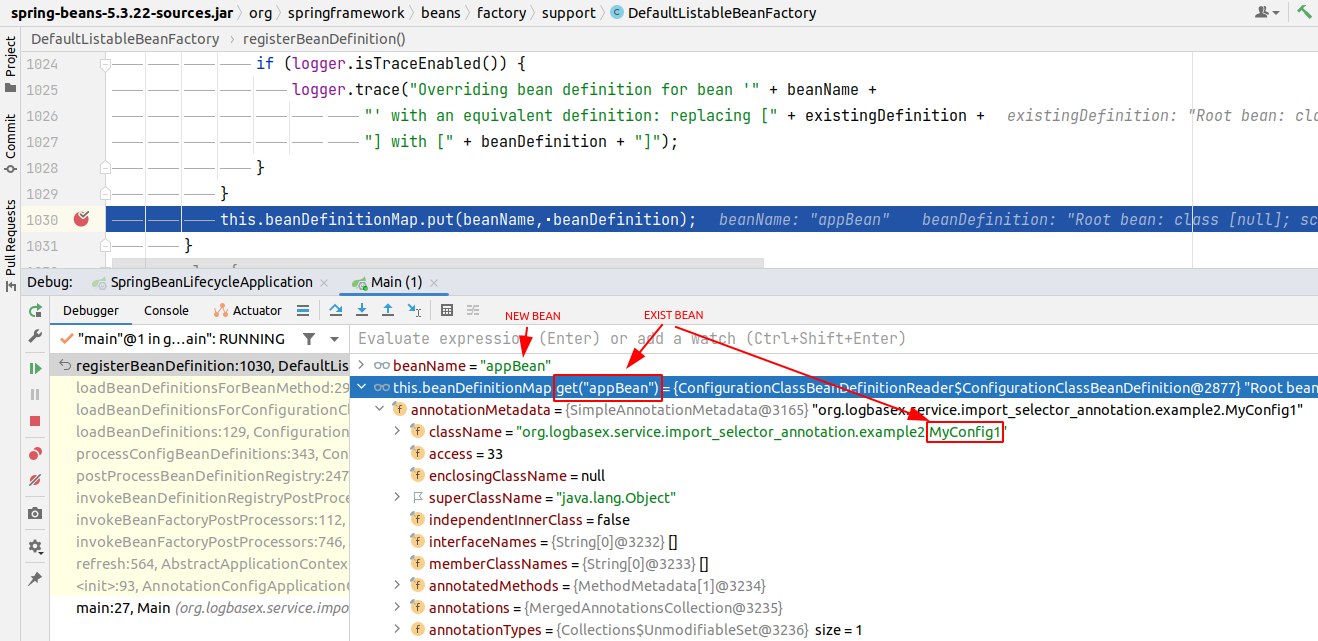
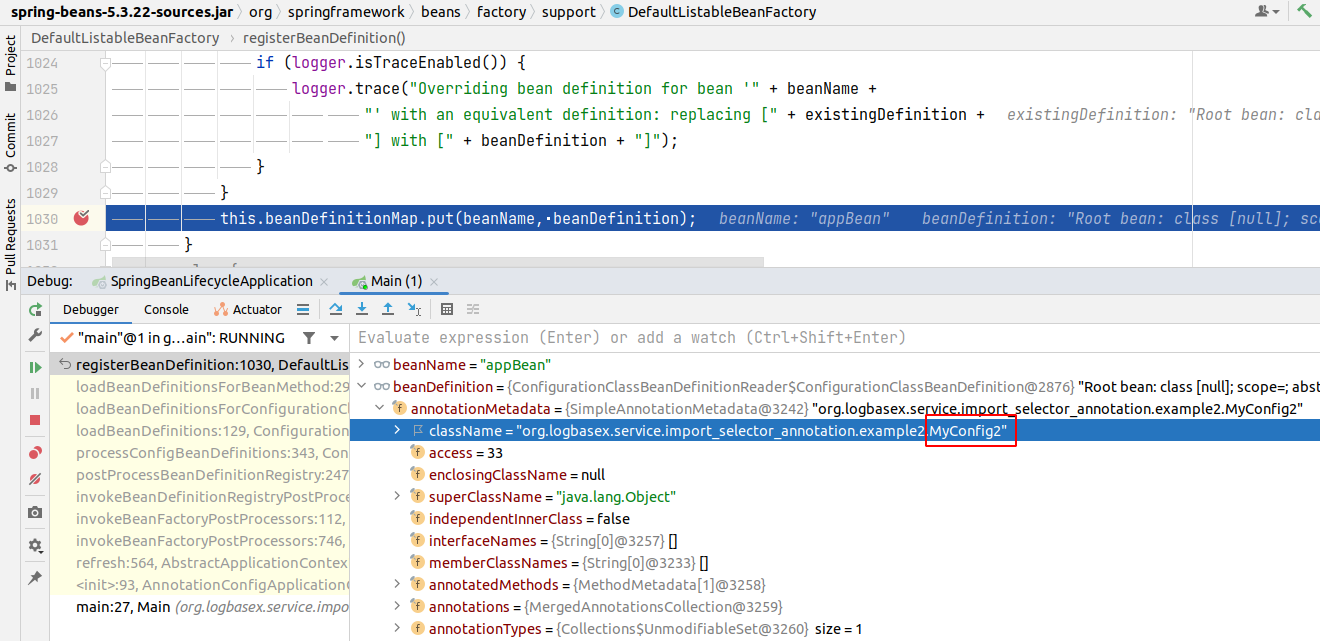
Callstack:
registerBeanDefinition:1005, DefaultListableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod:295, ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader (org.springframework.context.annotation)
loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass:153, ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader (org.springframework.context.annotation)
loadBeanDefinitions:129, ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigBeanDefinitions:343, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry:247, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors:311, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:112, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:746, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:564, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
<init>:93, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.annotation)
main:27, Main (org.logbasex.service.import_selector_annotation.example2)
III. Run with SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args)
Từ Spring boot 2.1 thì bean overriding disable by default cho nên nếu bạn thực thi đoạn code sau thì từ version 2.1 onward thì ắt hẳn sẽ gặp lỗi.
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(SpringBootVersion.getVersion());
// ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Main.class);
// isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding() = true (vì khởi tạo context bằng từ khóa news)
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Main2.class);
AppBean2 bean = context.getBean(AppBean2.class);
System.out.println(bean.getClass().getName());
// set isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding() = false rồi mới khởi tạo.
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
AppBean configurableBean = run.getBean(AppBean.class);
System.out.println(configurableBean.getMessage());
}
}
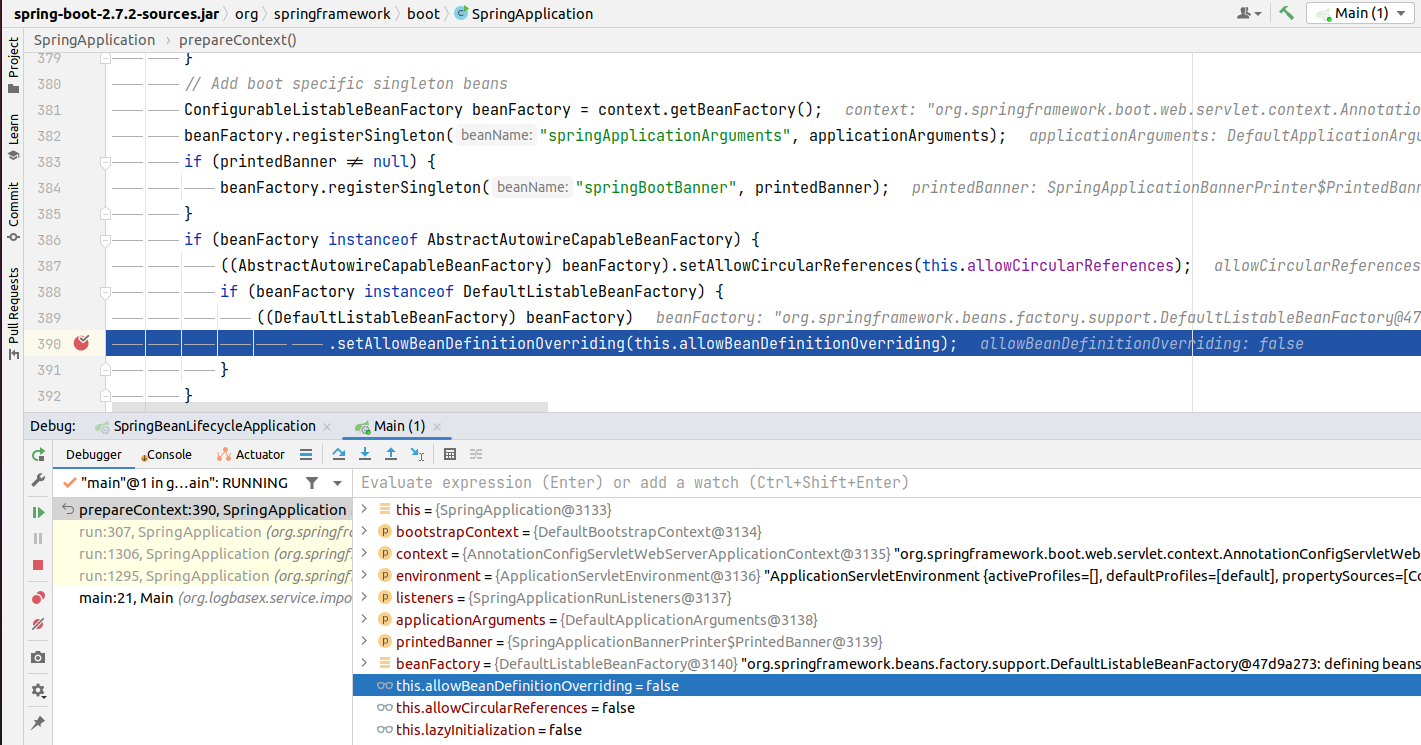
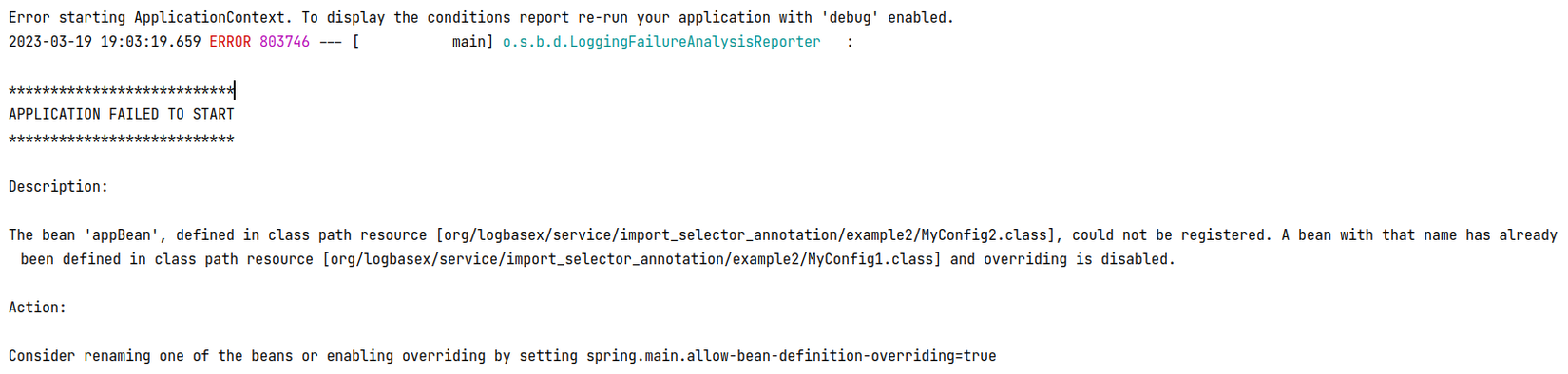
Tuy bị disable by default nhưng chúng ta vẫn có thể override beans bằng cách thay đổi setting trong application.yml
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding:
true

IV. References
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/59960793/will-declaring-configuration-on-a-class-make-it-a-spring-bean
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-bean-definition-override-exception#4-beans-coming-from-3rd-party-libraries ===
Thanks for reading.
All rights reserved