Kubernetes Architecture
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
What is Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a popular open source platform for container orchestration. It is similar to Docker Compose, but much more powerful and design to deploy application to multiple marchines making developing, deploying, maintaining and scaling applications up and down across a cluster of physical or virtual machines easy.
Architecture Overview
A Kubernetes cluster consists of two main components:
- Master Nodes (Control Plane)
- Worker Nodes
Master Nodes has following components.
- etcd distributed key value store.
- API Server.
- Controller Manager
- Scheduler
These components are responsible for maintaining the state of the cluster Every worker node consists of the following components:
- Kubelet
- Container Runtime (Docker)
These components are responsible for deploying and running the application containers.
All request to create/update/delete objects in kubernetes must be done through api-server. Client can talk to api-server in two ways.
- kubectl a command line interface tool
- Custom program by calling REST api endpoints
These relationship can be described with the following diagram
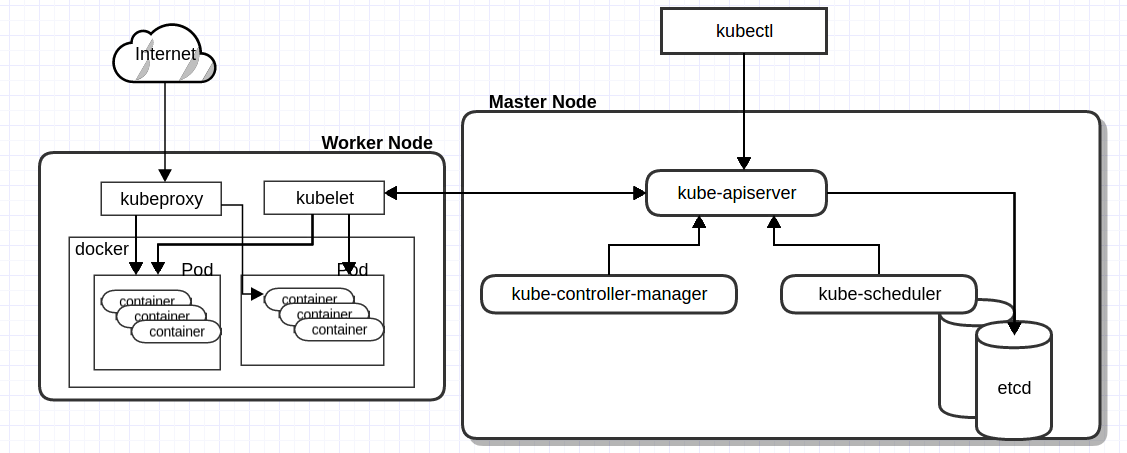
Master Node
Core component that responsible for managing worker nodes, make global decisions about the cluster, detect and respond to cluster events.
API Server
This is a central place to all other components. It's job is to validate object information before saving it into etcd. Mostly client communicate to api server through kubectl or REST api. API server won't create/update/delete object when it received a request instead it pass that request to Controller Manager to handle that.
Controller Manager
Responsible for noticing and responding when nodes go down, maintaining pods, replication controller and spin up pods to fufill the desired object state for every replicas.
Scheduler
Allocate what node the pods needs to be created, registers with Api Server for any newly created object/resource, checks whether the worker node has desired capacity or not, figuring out the node the scheduler will just update the resource specification and send it API Server. API Server will then update that object information and store them into etcd and notify kubelet.
Etcd
Open Source distributed key-value store used to store object, cluster, status & metadata that used in kubernetes. When working with complex system and application infrastructure, it is a good idea to have a backup so that you don't loose all your object data.
Worker Node
A machine (virtual or physical) that runs our software. Inside a worker node there is a process called kubelet that manage pods which in turn run one or more containers
Kubelet
The main contact point of each node within a cluster group is done through a kubelet service. Kubelet communicates with the master to identify which commands require to be executed and the work to be carried out. The kubelet service is also responsible for maintaining the state of work worker node. It registers the node it is running with the API Server. It monitor the API Server for Pods that are scheduled to the node, and then it will start the pod's containers by instructing to docker engine.
Kubelet Proxy
A network interface that makes services available to external parties. The process forwards requests to appropriate containers and handles load balancing at a primitive level. Generally, it ensures that the network is predictable and isolated
Pod
A pod is the smallest unit of Kubernetes in the object model that can be created or deployed. In simple terms, a pod represents a running process on a cluster.
A pod consists of an application container, storage resources, a network IP and options that govern how the containers should execute. A pod constitutes a unit of deployment which might consist of either a single container or a small number of containers that are tightly coupled.
Container Runtime
Software that is responsible for running containers. Kubernetes support any runtime that implemented CRI Interface as well as existing technologies such as docker, containerd, cri-o, rktlet.
What's Next?
In this post we've mostly learn about the architecture of kubernetes and how each component works together. In the next post we will learn how to define create/update/delete objects, make deployment and snitch together a working example.
All rights reserved