Giao tiếp giữa các Fragment
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Giao tiếp giữa các Fragment
Để có thể tái sử dụng các Fragment, bạn nên xây dựng các Fragment là hoàn toàn độc lập về dữ liệu cũng như là giao diện. Khi đã xác định được các Fragment có thể tái sử dụng, bạn có thể gắn chúng với 1 Activity hoặc Fragment khác và kết nối chúng với logic của ứng dụng.
Để phản ứng với các sự kiện bên ngoài (có thể là từ thao tác người dùng, dữ liệu từ service trả lên...) hoặc chia sẻ thông tin trạng thái của Fragment hiện tại bạn thường cần có những kênh giao tiếp (interface, public function...) giữa các Fragment với nhau hoặc giữa Fragment với Activity chứa nó. Nhưng để các Fragment được khép kín thì bạn không nên để Fragment có thể giao tiếp trực tiếp với Activity hoặc các Fragment khác. Nếu để các liên kết trức tiếp đó thì sẽ tạo thêm nhiều rằng buộc và kiến việc mở rộng cũng như tái sử dụng càng ngày càng khó khăn khi ứng dụng của bạn thêm nhiều chức năng mới.
Fragment có cung cấp cho lập trình viên 2 tùy chọn để thiết lập giao tiếp là Shared ViewModel và Fragment Result API. Để chia sẻ dữ liệu với các Fragment khác mà không chung FragmentManager bạn nên sử dụng Shared ViewModel, còn các Fragment có chung FragmentManager mà các bạn muốn gửi và nhận sữ liệu 1 lần thông qua "Bundle" thì các bạn nên sử dụng Fragment Result API.
Các phần dưới đây, mình sẽ giới thiệu với các bạn 2 các sử dụng Shared ViewModel và Fragment Result API để chuyển tiếp dữ liệu giữa các Fragment với nhau.
1. Share data using a ViewModel
Sử dụng Share ViewModel là 1 lựa chọn lý tưởng để giúp bạn chuyển tiếp dữ liệu giữa nhiều Fragment hoặc các Fragment có chung Host Acticity. Để đọc hiểu thêm về ViewModel các bạn có thể tham khảo tại đây
1.1 Share data with the host activity
Trong 1 số trường hợp mà bạn muốn chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa nhiều Fragment có chung host activity nhưng lại khác FragmentManager thì các bạn có thể dụng ShareViewModel mà vòng đời của ViewModel phụ thuộc vào vòng đời của Activity.
Định nghĩa file ItemViewModel
// Kotlin Code
class ItemViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val mutableSelectedItem = MutableLiveData<Item>()
val selectedItem: LiveData<Item> get() = mutableSelectedItem
fun selectItem(item: Item) {
mutableSelectedItem.value = item
}
}
Trong đoạn code trên, dữ liệu sẽ được chứa trong MutableLiveData. LiveData là 1 kiểu dữ liệu mà chỉ có thể đọc chứ không thế thay đổi được giá trị của nó, dữ liệu kiểu MutableLiveData thì giúp chung ta thay đổi được giá trị mà nó chứa. Ở đây mình đặt biến MutableLiveData là private và cung cấp biến LiveData để các class bên ngoài có thể đọc và lắng nghe sự thay đổi. Cách viết như này nhằm đảm bảo dữ liệu chỉ có thể được thay đổi trong nội bộ class ItemViewModel.
Cả Fragment và Activity có thể truy cập tới shared instance of a ViewModel với vòng đời phụ thuộc vào vòng đời của Activity thông qua ViewModelProvider. ViewModelProvider sẽ quản lý việc khỏi tạo ViewModel hoặc truy xuất nó nếu nó đã tồn tại.
// Kotlin Code
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the activity-ktx
// artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope
private val viewModel: ItemViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
viewModel.selectedItem.observe(this, Observer { item ->
// Perform an action with the latest item data
})
}
}
class ListFragment : Fragment() {
// Using the activityViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the
// fragment-ktx artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope
private val viewModel: ItemViewModel by activityViewModels()
// Called when the item is clicked
fun onItemClicked(item: Item) {
// Set a new item
viewModel.selectItem(item)
}
}
1.2 Share data between fragments
Quay trở lại với bài toán nhiều Fragment cần trao đổi dữ liệu với nhau. Nếu các Fragmetn đó cùng nằm chung trên 1 Activity thì các bạn vẫn có thể sử dụng tốt ShareViewModel cho trường hợp này.
Ở ví dự dưới đây chúng ta sẽ có 2 Framgent. 1 Fragment cho phép hiển thị 1 danh sách, 1 Fragment cho phép người dùng áp dụng các bộ lọc lên các danh sách đó. Nếu 2 Fragment này được thêm vào 2 Page của ViewPager trong đó 1 Fragment cho phép dụng bộ lọc đang được hiển thị còn Fragment hiển thị danh sách đang được ẩn đi thì việc viết 1 liên kết trực tiếp giữa 2 Fragment này khá là khó khăn và việc viết liên kết như thế sẽ không đảm bảo tính độc lập của các Fragment.
Trong trường hợp này thì các bạn có thể khởi tạo 1 ViewModel với Scope là Activtiy chứa 2 Fragment đó thực hiện việc chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các Fragment thông qua ViewModel đó.
// Kotlin code
class ListViewModel : ViewModel() {
val filters = MutableLiveData<Set<Filter>>()
private val originalList: LiveData<List<Item>>() = ...
val filteredList: LiveData<List<Item>> = ...
fun addFilter(filter: Filter) { ... }
fun removeFilter(filter: Filter) { ... }
}
class ListFragment : Fragment() {
// Using the activityViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the
// fragment-ktx artifact to retrieve the ViewModel in the activity scope
private val viewModel: ListViewModel by activityViewModels()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { list ->
// Update the list UI
}
}
}
class FilterFragment : Fragment() {
private val viewModel: ListViewModel by activityViewModels()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
viewModel.filters.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { set ->
// Update the selected filters UI
}
}
fun onFilterSelected(filter: Filter) = viewModel.addFilter(filter)
fun onFilterDeselected(filter: Filter) = viewModel.removeFilter(filter)
}
1.3 Share data between a parent and child fragment
Khi bạn làm việc với 1 Fragment mà trong nó chứa nhiều Fragment con nhỏ hơn và bạn cần chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa Fragment cha bên ngoài và các Fragment con thì trong trường hợp này ShareViewModel cũng là 1 giải pháp tốt.
// Kotlin code
class ListFragment: Fragment() {
// Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx
// artifact to retrieve the ViewModel
private val viewModel: ListViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { list ->
// Update the list UI
}
}
}
class ChildFragment: Fragment() {
// Using the viewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx
// artifact to retrieve the ViewModel using the parent fragment's scope
private val viewModel: ListViewModel by viewModels({requireParentFragment()})
...
}
1.3 Share data between use Navigation Graph
Nếu bạn đang sử dụng thư viện Navigation library bạn có thể sử dụng ViewModel với vòng đời là vòng đời của NavBackStackEntry thực hiện việc chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các Fragment bên trong chúng.
// Kotlin code
class ListFragment: Fragment() {
// Using the navGraphViewModels() Kotlin property delegate from the fragment-ktx
// artifact to retrieve the ViewModel using the NavBackStackEntry scope
// R.id.list_fragment == the destination id of the ListFragment destination
private val viewModel: ListViewModel by navGraphViewModels(R.id.list_fragment)
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
viewModel.filteredList.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer { item ->
// Update the list UI
}
}
}
Để đọc hiểu thêm về phạm vi của ViewModel sử dụng trong NavBackStackEntry các bạn có thể tham khảo thêm ở đây.
2. Get results using the Fragment Result API
Trong 1 vài trường hợp bạn chỉ muốn chuyển dữ liệu 1 lần giữa các Framgent và dữ liệu đó sẽ không cần lưu lại để tái sử dụng. Bắt đầu từ Fragment 1.3.0-alpha04 các FragmentManager đều được implements FragmentResultOwner. Việc này khiến cho FragmentManager có thể hoạt động như 1 trung tâm chứa và chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các Fragment mà nó quản lý. Thay đổi này cho phép các Fragment mà được quản lý bởi chung 1 FragmentManager có thể thiết lập các giao tiếp với nhau thông qua hàm Callback được định nghĩ trong FragmentManager mà không cần tạo các liên kết trực tiếp với nhau.
2.1 Pass results between fragments
Để chuyển tiếp dữ liệu giữa FragmentB tới FragmentA trước tiên hay viết 1 lắng nghe sự kiện thay đổi trong FragmentA.
// Kotlin code
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact
setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { requestKey, bundle ->
// We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported
val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
// Do something with the result
}
}
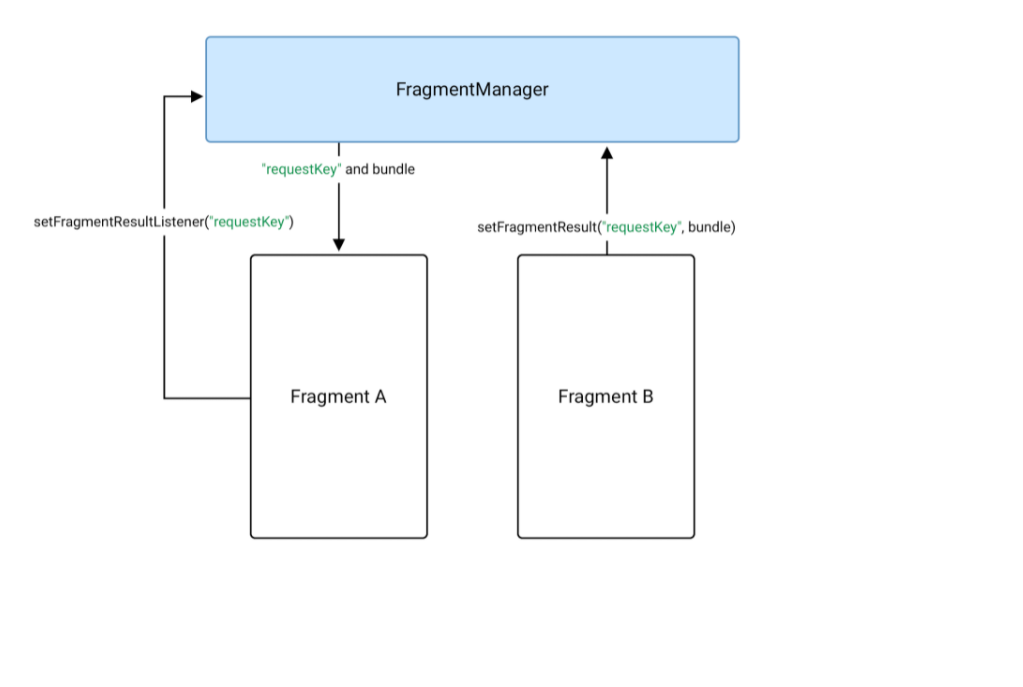
Fragment B gửi dữ liệu tới Fragment A thông qua
FragmentManager
Trên FragmentB bạn hãy gửi dữ liệu thông qua hàm setFragmentResult(). Nhưng phải lưu ý là 2 Fragment A và B đểu được quản lý bởi 1 FragmentManager.
// Kotlin code
button.setOnClickListener {
val result = "result"
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact
setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result))
}
Fragment A nhận kết quả từ Fragment B thông qua listener callback 1 lần khi hàm listener được khai báo trong onCreate
Ở đây bạn chỉ có thể viêt 1 làm lắng nghe duy nhất cho 1 requestKey, nếu ở 1 hàm nào đó bạn viết lại đoạn lắng nghe trên thì đoạn lắng nghe trong hàm onCreate sẽ không nhận được kết quả. Nếu bạn gọi hàm setFragmentResult() nhiều lần với cùng 1 requestKey nhưng với các dữ liệu khác nhau và chưa có Fragment viết hàm nhận dữ liệu từ requestKey đó thì khi 1 dữ liệu mới được truyền vào thông qua setFragmentResult() với requestKey thì dữ liê cũ sẽ được ghi đè bằng dữ liệu mới.
Khi ở Fragment A bạn nhận dữ liệu thông qua listener callback setFragmentResultListener thì hàm onFragmentResult() sẽ được kích hoạt, và dữ liệu tương ứng với requestKey đó sẽ được xóa đi. Việc này có 2 mục đích chính:
- Các Fragment khác sẽ không nhận được kết quả từ
requestKeyđó. Khi mà Fragment đang giữ liên kết vớirequestKeyđó được pop ra khỏi Stack thì Fragment tiếp theo trong Stack có thể đăng ký và nhận dữ liệu. - Khi Fragment B gọi hàm để truyểển dữ liệu sang FramgentA thì dữ liệu sẽ được truyền đi ngay lập tức.
Việc xóa dữ liệu và với mỗi requestKey thì chỉ 1 nơi có thể nhận dữ liệu này cũng đảm bảo tính duy nhất của dữ liệu.
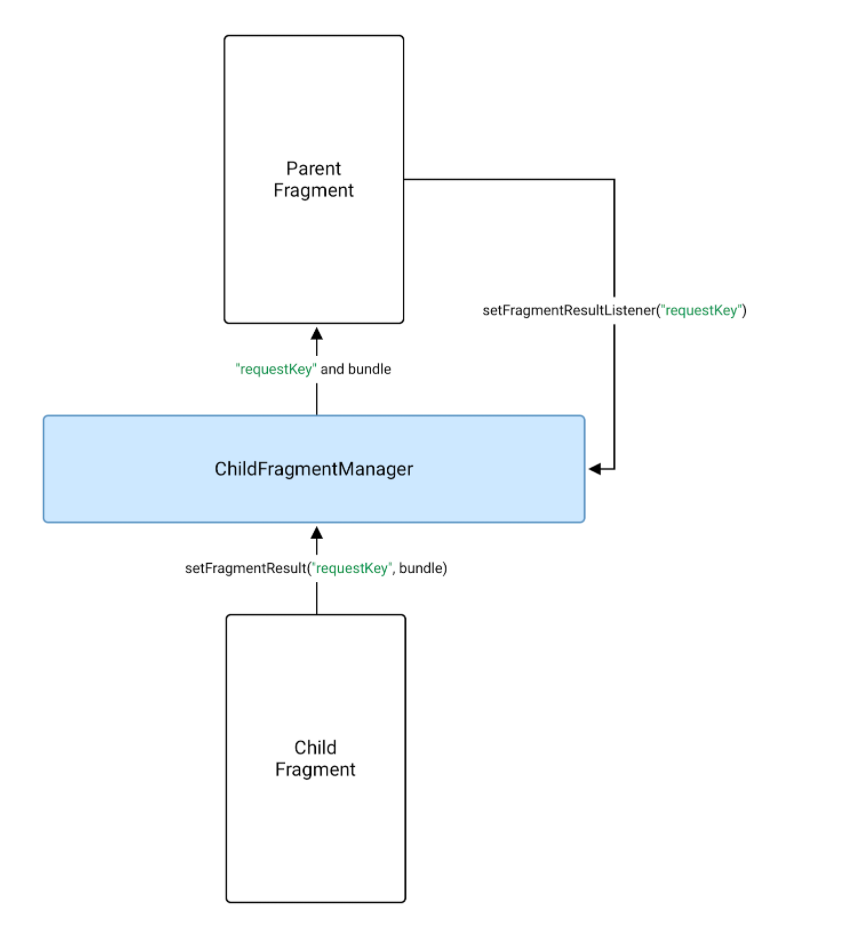
2.2 Pass results between parent and child fragments
Cũng tương tự như trên việc chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa Fragment cha và Fragment con bên trong cũng có thể thực hiên được thông qua Fragment Result API
// Kotlin Code
// Parent Fragment
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// We set the listener on the child fragmentManager
childFragmentManager.setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { key, bundle ->
val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
// Do something with the result
}
}
...
// Child Fragment
button.setOnClickListener {
val result = "result"
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact
setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result))
}
Đây là việc chia sẻ dữ liệu từ Child Fragment -> Parent Fragment
// Kotlin Code
// Parent Fragment
button.setOnClickListener {
val result = "result"
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact
childFragmentManager.setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result))
}
...
// Child Fragment
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setFragmentResultListener("requestKey") { key, bundle ->
val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
// Do something with the result
}
}
Đây là việc chia sẻ dữ liệu từ Parent Fragment -> Child Fragment
Cũng tương tự như vậy. Chúng ta hoàn toàn có thể chia sẻ dữ liệu với Activity chứa Fragment hiện tại thông qua getSupportFragmentManager()
// Kotlin Code
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
supportFragmentManager
.setFragmentResultListener("requestKey", this) { requestKey, bundle ->
// We use a String here, but any type that can be put in a Bundle is supported
val result = bundle.getString("bundleKey")
// Do something with the result
}
}
}
// Fragment
button.setOnClickListener {
val result = "result"
// Use the Kotlin extension in the fragment-ktx artifact
supportFragmentManager.setFragmentResult("requestKey", bundleOf("bundleKey" to result))
}
Qua bài viết trên các bạn cũng nhận thấy việc chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các Framgent cũng khá là đơn giản. Tùy thuộc vào mục đích thiết kế mà các bạn lựa chọn 2 cách trên làm sao cho phù hợp. Mỗi cách có 1 điểm mạnh và điểm yếu riêng của nó.
Shared ViewModelthì tiện nhưng biến dữ liệu được lưu trong ViewModel thì có thể được truy xuất bới bất kỳ Fragment có liên kết với ViewModel chưa dữ liệu đó. Đây cũng chính là điểm mạnh và điểm yếu của phương pháp này.Fragment Result APIthì có vẻ là triển khai khó hơn 1 chút, nhưng nó lại có tính bảo toàn dữ liệu cao, dữ liệu chỉ được truy xuất 1 lần duy nhất bởi 1 Fragment duy nhất đăng ký sự kiện lắng nghe gần nhất.
Việc các bạn thiết kế Fragment càng độc lập và ít phụ thuộc vào các yếu tố bên ngoài bao nhiêu thì khiến cho việc tái sử dụng, mở rộng và bảo trì sau này càng dễ dàng bấy nhiêu. Link bài viết gốc của Google các bạn có thể tham khảo tại đây.
All rights reserved