[FuelPHP] Validate dữ liệu
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 7 năm
Validate (kiểm tra hay xác thực) dữ liệu đầu vào từ phía người dùng là vô cùng quan trọng của một ứng dụng để loại bỏ đi các nguy cơ tấn công vào hệ thống đồng thời chuẩn hóa dữ liệu để lưu vào database (DB). Đối với Laravel, công việc này thực hiện đơn giản với lớp Validator hoặc các Request đã được cung cấp sẵn. Trong bài viết chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu validate với FuelPHP, không hỗ trợ quá chi tiết như Laravel 
1. Validation Class
FuelPHP cung cấp cho bạn lớp Validation để phục vụ xác thực dữ liệu. Các hàm của nó hỗ trợ bao gồm
Tạo đối tượng gán với view để xác thực: forge()
// Use default
$val = Validation::forge();
// ... or name it
$val = Validation::forge('my_validation');
Thiết lập các rule (giống laravel)
Sử dụng 2 phương thức add_rules (add từng rule một cho từng trường) hoặc add_field (add nhiều rules cho một trường luôn)
$val = Validation::forge('my_validation');
// Add a field for username, give it the label "Your username" and make it required
$val->add('username', 'Your username')->add_rule('required');
// Now add another field for password, and require it to contain at least 3 and at most 10 characters
$val->add('password', 'Your password')->add_rule('required')
->add_rule('min_length', 3)
->add_rule('max_length', 10);
// Hoặc
// The same fields as the example above
$val = Validation::forge('my_validation');
$val->add_field('username', 'Your username', 'required');
$val->add_field('password', 'Your password', 'required|min_length[3]|max_length[10]');
Các methods kết quả trả về của việc kiểm tra
1.1 run()
Validate thành công hay không (không quan tâm lỗi chi tiết):
// run validation on just post
if ($val->run())
{
// process your stuff when validation succeeds
}
else
{
// validation failed
}
1.2. error()
Lấy về các lỗi nếu xác thực không đúng
// get an array of validation errors as field => error pairs
$errors = $val->error();
1.3. validated()
Lấy về các giá trị đã xác thực thành công (để old request như laravel)
// get an array of successfully validated fields => value pairs
$vars = $val->validated();
1.4. input()
Lấy về tất cả các giá trị từ request trước khi chúng được validate
// get an array of the input that was validated, this merged the post & input given to run()
$input = $val->input();
1.5. set_message()
Tùy chỉnh thông báo lỗi khi validate không thành công
// change the error message for a specific validation object
$val->set_message('required', 'The field :label is required.');
// or change the message for a specific field, no matter the actual error
echo $val->error('username')->get_message('The field :label must be filled out before auth is attempted.');
// Outputs "The field Your username must be filled out before auth is attempted." when validation for username
// failed, or nothing when not yet validated or validation succeeded.
1.5. Hết rồi :v.
Như vậy chỉ có một số hàm, nhớ rất ít. Một chú ý nhỏ là mình chưa tìm ra cách xác thực giá trị đã tồn tại trong DB hay chưa (rule unique trong laravel), vì vậy nếu muốn xác thực duy nhất, bạn phải tự làm tay)
2. Xây dựng ứng dụng: Xác thực dữ liệu khi đăng nhập
Như vậy Fuel chỉ có 2 methods (add_rule, add_field) thiết lập rules, 4 methods (run, error, validated, input) nhận giá trị trả về từ validate. Dễ nhớ quá nhể. Thiết lập thử một pha xác thực như Laravel thôi
2.1. Tạo view: 2 trường username và password
<form method="post" action="/login/login">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Username:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="email" placeholder="Enter username" name="username">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="pwd">Password:</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="pwd" placeholder="Enter password" name="password">
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label><input type="checkbox" name="remember"> Remember me</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary"> Login </button>
<br> <br>
<p> I don't have an account <a href="/login/register"> Register </a> </p>
</form>
2.2. Xây dựng rule
Mình sẽ tách phần rule ra làm một hàm riêng trong controller login.php
// validater login
private function _vali()
{
$vali = Validation::forge();
$vali->add_field('username', 'Your username', 'required');
$vali->add_field('password', 'Your password', 'required|min_length[3]|max_length[10]');
return $vali;
}
2.3. Kiểm tra dữ liệu thôi
Hàm này xử lý dữ liệu khi ấn button login. Mình viết tất cả trong 1 controller cho chạy được đã chứ chưa có theo pattern design nào đâu :3 nên có thể hơi khó đọc code
public function post_login()
{
$vali = $this->_vali();
$check_vali = $vali->run();
// was the login form posted?
if (\Input::method() == 'POST') {
if ($check_vali) {
// check the credentials.
if (\Auth::instance()->login(\Input::param('username'), \Input::param('password'))) {
// did the user want to be remembered?
if (\Input::param('remember', false)) {
// create the remember-me cookie
\Auth::remember_me();
} else {
// delete the remember-me cookie if present
\Auth::dont_remember_me();
}
// logged in, go back to the page the user came from, or the
// application dashboard if no previous page can be detected
\Response::redirect_back('/');
} else {
// login failed, show an error message
//\Messages::error(__('login.failure'));
$errorMessage = 'Username or password not right!';
$data = [
'errorMessage' => $errorMessage,
];
return Response::forge(View::forge('login/index')->set($data));
}
} else {
$errors = $vali->error();
$oldRequest = $vali->validated();
$data = [
'errors' => $errors,
'oldRequest' => $oldRequest,
];
return Response::forge(View::forge('login/index')->set($data));
}
}
// display the login page
return \View::forge('login/index');
}
Bỏ qua các đoạn checklogin, check remember me mà hãy tập trung vào các đoạn kiểm tra dữ liệu
- Biến
$valichứa các rule của các trường (username và password) - Biến
$check_valilà kết quả trả về của việc kiểm tra này (true or false) - Nếu
$check_valivà true, tất nhiên kiểm tra dữ liệu thành công rồi mới xử lý tiếp chứ, kiểm tra thông tin đăng nhập username, password xem có đúng không
- Chú ý đoạn xử lý code nếu kiểm tra không đúng.
$errors = $vali->error();
$oldRequest = $vali->validated();
$data = [
'errors' => $errors,
'oldRequest' => $oldRequest,
];
return Response::forge(View::forge('login/index')->set($data));
-
Mình đang lấy về 2 giá trị
$errors(lỗi chưa thoả mãn rules) và$oldRequest(Các giá trị đã thỏa mãn rules để làm chức năng old request như Laravel) -
Sau khi có lỗi và các trường thành công rồi, sang view xử lý nốt thôi cho nó hiện ra

<!-- Hiển thị các lỗi kiểm tra không hợp lệ -->
<?php if (!empty($errors)): ?>
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<?php foreach ($errors as $error): ?>
<li> <?php echo $error ?> </li>
<?php endforeach;?>
</div>
<?php endif; ?>
<form method="post" action="/login/login">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Username:</label>
<!-- Hiển thị giá trị cũ người dùng đã điền -->
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="email" placeholder="Enter username" name="username"
value=<?php echo !empty($oldRequest['username']) ? $oldRequest['username'] : '' ?>>
<!-- Hiển thị lỗi chi tiết cho từng trường nếu trường đó không pass việc validate) -->
<?php if (!empty($errors['username'])): ?>
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<?php echo $errors['username'] ?>
</div>
<?php endif; ?>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="pwd">Password:</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="pwd" placeholder="Enter password" name="password">
<!-- Hiển thị lỗi chi tiết cho từng trường nếu trường đó không pass việc validate) -->
<?php if (!empty($errors['password'])): ?>
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<?php echo $errors['password'] ?>
</div>
<?php endif; ?>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label><input type="checkbox" name="remember"> Remember me</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary"> Login </button>
<br> <br>
<p> I don't have an account <a href="/login/register"> Register </a> </p>
</form>
Mình đang để hiện lỗi tổng thể và hiện lỗi chi tiết cho từng trường. Tùy ứng dụng yêu cầu mà bạn muốn để như thế nào thì tùy các bạn =)). Tận hưởng thôi
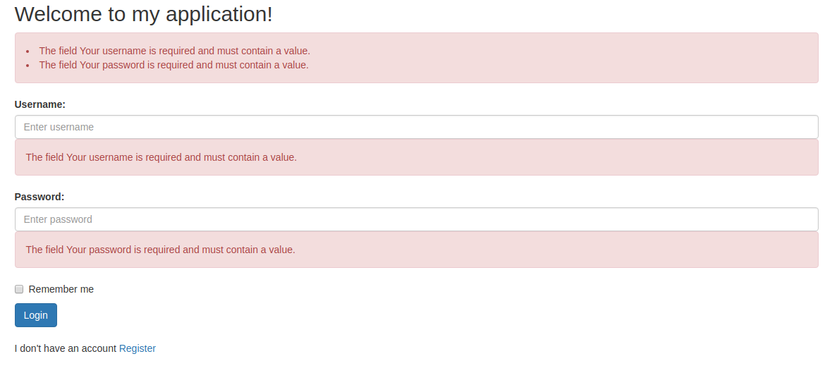
2.4. Hiển thị thông báo lỗi validate theo ý bạn
Sử dụng hàm set_message để hiển thị thông báo lỗi. Khá đơn giản
// change the error message for a specific validation object
$val->set_message('required', 'The field :label is required.');
// or change the message for a specific field, no matter the actual error
echo $val->error('username')->get_message('The field :label must be filled out before auth is attempted.');
// Outputs "The field Your username must be filled out before auth is attempted." when validation for username
// failed, or nothing when not yet validated or validation succeeded.
2.5. Kiểm tra unique hoặc các kiểm tra liên quan đến Database
private function _validation_unique_username($username)
{
$exists = DB::select(DB::expr('COUNT(*) as total_count'))->from('users')
->where('username', '=', $username)->execute()->get('total_count');
return (bool) !$exists;
}
Tài liệu tham khảo
- Validation: https://fuelphp.com/docs/classes/validation/validation.html
- Validation Errors: https://fuelphp.com/docs/classes/validation/errors.html
- Link github project: https://github.com/minhnv2306/authencation_fuelphp
All rights reserved