Hiểu cách Retrofit làm việc
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Networking là một trong những phần quan trọng nhất của các ứng dụng Android. Ban đầu, chúng ta sử dụng HTTP class để xử lý networking. Theo Thời gian mọi thứ trở nên dễ dàng hơn khiến chúng ta phụ thuộc vào các thư viện. Chúng ta sử dụng nhiều thư viễ để thực hiện công việc nhanh hơn nhưng hầu hết chúng ta không phân thích những hạn chế và nhược điểm của nó. Trươc sử dụng bất kỳ thư viện nào chúng ta cần phân tích ba điều What, Why và How. Một thư viện rất phổ biến để xử lý Networking là Retrofit. Trong bài viết này, hãy phân tích những điều trên và hiểu cách mà Retrofit xử lý các request bên trong nó.
What
Retrofit là một type-safe HTTP client cho Android và Java.
Why
Sử dụng Retrofit làm các tác vụ networking trở nên dêx dàng hơn trong các ứng dụng Android. Vì nó có nhiều tính năng như dễ dàng thêm custom heawder và request types, file uploads, mocking response, v.v giúp chúng ta giảm code thừa trong các ứng dụng và xử lý web service dễ dàng.
How
Để làm việc với Retrofit về cơ bản chúng ta cần 3 class sau:
- Một model class được sử dụng làm Json model.
- Một interface mà định nghĩa HTTP operastion cần phải xử lý.
- Retrofit.Builder clas: Instance sử dụng interface được định nghĩa ở trên và Builder API để cho phép định nghĩa URL endpoin cho HTTP operations. Nó cũng nhận vào converter chúng ta cung cấp để format Response.
Về cơ bản
Để implement retrofit trong các ứng dụng của chúng ta, chúng ta cần theo các bước cơ bản sau:
- Add các dependencies cần thiết trong build.gradle module level
implementation ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.3.0’
implementation ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.3.0’
- Tạo POJO class hoặc data model tương ứng với response
package com.example.retrofit
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName
import java.io.Serializable
data class SampleSharingModel(
@SerializedName("source")
val source: String,
@SerializedName("url")
val url: String?,
@SerializedName("message")
val message: String?)
- Tạo API interface có các phương thức thực hiện các HTTP request. Retrofit cung cấp một list các anotation cho mỗi HTTP method như @GET, @POST, @PUT, @DELETE,@PATCH, v.v.
package com.example.retrofit
import retrofit2.http.*
interface ApiService {
@GET("api/share-data/")
fun getShareData(): Call<SampleSharingModel>
}
- Tạo một Retrofit Builder
// Create a very simple REST adapter which points the API.
val retrofit = Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
- Tạo một instance của service và gọi các phương thức bên trong nó. Bạn có thể làm điều này trong presenter hoặc ViewModel để lấy được các dữ cần thiết.
// Create an instance of our ApiService interface.
val shareService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);
val shareData = shareService.getShareData().execute()
Việc này sẽ lấy dữ liệu từ server và sau đó chúng ta có thể thực hiện các actions mà cần dùng đến chúng. Liệu chúng ta đã hoàn thành hay chưa?. Với quan điểm của một developer bình thường, như thế này đã ổn để áp thực hiện như kì vọng nhưng chúng ta hãy cùng đi sâu hơn và sẽ thấy được nhiều điều khác. Bây giờ chúng ta hãy cùng nhau phân tích điều gì sảy ra sâu bên trong thư viện.
Behind the scenes
Khi chúng ta tạo một instance của service từ dòng này:
val shareService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);
Có một vài ma thuật xảy ra ở đây. Hãy xem nó. Click vào phương thức create chúng ta sẽ đi tới class Retrofit.java và phương thức create sẽ trong như dưới đây
public <T> T create(final Class<T> service) {
Utils.validateServiceInterface(service);
if (validateEagerly) {
eagerlyValidateMethods(service);
}
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(service.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] { service },
new InvocationHandler() {
private final Platform platform = Platform.get();
private final Object[] emptyArgs = new Object[0];
@Override public @Nullable Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method,
@Nullable Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// If the method is a method from Object then defer to normal invocation.
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
if (platform.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return platform.invokeDefaultMethod(method, service, proxy, args);
}
return loadServiceMethod(method).invoke(args != null ? args : emptyArgs);
}
});
}
Việc kiểm tra đầu tiên là interface được cungc ấp có phải alf một interface hợp lệ hay không bằng cách gọi phương thức validateServiceInterface. Nếu không hợp lệ sẽ ném ra ** IllegalArgumentException**
static <T> void validateServiceInterface(Class<T> service) {
if (!service.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("API declarations must be interfaces.");
}
// Prevent API interfaces from extending other interfaces. This not only avoids a bug in
// Android (http://b.android.com/58753) but it forces composition of API declarations which is
// the recommended pattern.
if (service.getInterfaces().length > 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("API interfaces must not extend other interfaces.");
}
}
Bước thứ 2 giống như một chuỗi các phương bắt đầu từ lệnh gọi phương thức eagerlyValidateMethods
private void eagerlyValidateMethods(Class<?> service) {
Platform platform = Platform.get();
for (Method method : service.getDeclaredMethods()) {
if (!platform.isDefaultMethod(method) && !Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
loadServiceMethod(method);
}
}
}
Trong phương thức trên Platform.get() có implementation dưới đây để return platform type. Bạn có thể check full code trong IDE của bạn nếu bạn muốn biết cụ thể hơn.
class Platform {
private static final Platform PLATFORM = findPlatform();
static Platform get() {
return PLATFORM;
}
private static Platform findPlatform() {
try {
Class.forName("android.os.Build");
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT != 0) {
return new Android();
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignored) {
}
try {
Class.forName("java.util.Optional");
return new Java8();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignored) {
}
return new Platform();
}
/* More methods of this class
........
........
.........
*/
}
Sau khi lấy được platform type nó gọi service.getDeclaredMethods() bên trong eagerlyValidateMethods() trả ra một array chứa các Method object phản ánh tất cả các phương thức được khia báo của class hoặc interface đại diện bởi object này, bao gồm cả public, protected, default, access, và private method nhưng không bao gồm các phương thức được kế thừa.
public Method[] getDeclaredMethods() throws SecurityException {
Method[] result = getDeclaredMethodsUnchecked(false);
for (Method m : result) {
// Throw NoClassDefFoundError if types cannot be resolved.
m.getReturnType();
m.getParameterTypes();
}
return result;
}
Duyệt qua tất cả các phần tử chứa trong các method array để xác định request type, method name, Annotations và arguments của mỗi cái được lưu trữ trong map serviceMethodCache như trong code bên dưới:
private final Map<Method, ServiceMethod<?>> serviceMethodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ServiceMethod<?> loadServiceMethod(Method method) {
ServiceMethod<?> result = serviceMethodCache.get(method);
if (result != null) return result;
synchronized (serviceMethodCache) {
result = serviceMethodCache.get(method);
if (result == null) {
result = ServiceMethod.parseAnnotations(this, method);
serviceMethodCache.put(method, result);
}
}
return result;
}
ServiceMethod là một abstract class như sau:
package retrofit2;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import javax.annotation.Nullable;
import static retrofit2.Utils.methodError;
abstract class ServiceMethod<T> {
static <T> ServiceMethod<T> parseAnnotations(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
RequestFactory requestFactory = RequestFactory.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method);
Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(returnType)) {
throw methodError(method,
"Method return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);
}
if (returnType == void.class) {
throw methodError(method, "Service methods cannot return void.");
}
return HttpServiceMethod.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method, requestFactory);
}
abstract @Nullable T invoke(Object[] args);
}
Đến lượt nó gọi final class RequestFactory trong đó Builder method có code như sau:
Builder(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
this.retrofit = retrofit;
this.method = method;
this.methodAnnotations = method.getAnnotations();
this.parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
this.parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();
}
Vì chúng ta không thể đi qua toàn bộ code của framework ở đây, vui lòng check trong IDE của bạn di chuyển qua các phương thức của chúng.
Cuối chúng ta sẽ tới java.lang.reflect để fetch annotation từ AccessibleObject class, getGenericParameterTypes() và getGenericParameterTypes() từ Method class.
Data Flow
Hãy xem data Flow của retrofit:
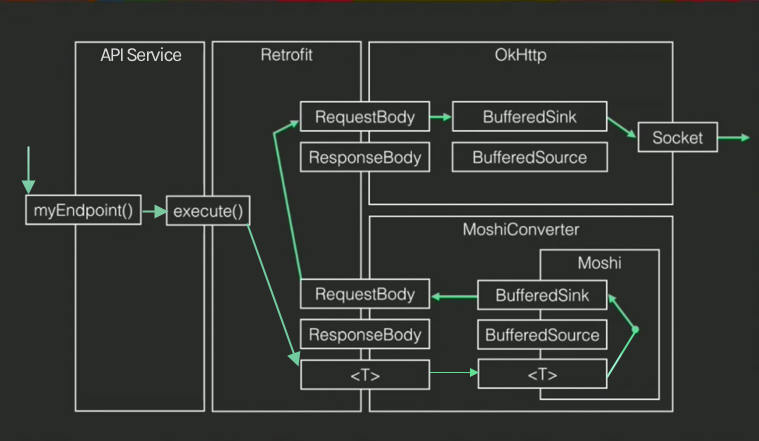
Trong hình trên, chúng ta có thể thấy rằng OkHttp bên dưới Retrofit. OkHttp kết hợp với OkHttp Soket tạo rat HTTP request. Và nó có các types của Okio library được gọi là BufferSink và BufferedSource chúng ta có thể nghĩ chúng như input stream và output stream. Các types đặt ở giữa Retrofit và OkHttp là RequestBody và ResponseBody. Và chúng ta có các converter cho conversions, ở đây chúng ta thấy Moshi converter. Vì Moshi và Okio đều xuất phát từ Square nên 2 thư viện này có thể tương tác được với nhau. Trong Moshi Converter sectiont ở trong ảnh trên, chúng ta cosd thể thấy nó, và nó rất quan trọng bởi vì chúng ta có thể tránh nhiều absstractions ở giữa các layer kahcs nhau. Converter liên lạc với RequestBody và ResponseBody với Retrofit.
Khi chúng ta cọi endpoint Retrofit lấy Object chúng ta đưa vào và đưa nó vào converter. Khi converter nhận các đối tượng đó khi họ muốn gửi nó tới server. Moshi sẽ lấy Object đó và viết nó vào BufferSink, cái mà sẽ được wrap trọng RequestBody và nó cũng chính là type mà Retrofit đưa cho OkHttp và một thứ tương tự cũng được chuyển tới soket bằng BufferSink.
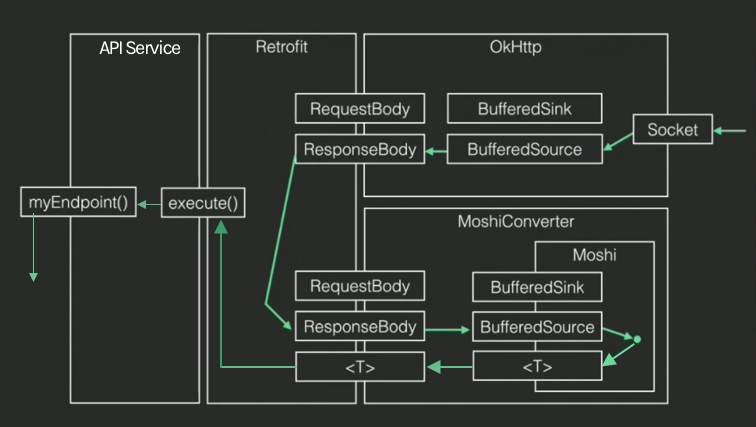
Và tương tự là các đọc từ sockSocketet, OkHttp sẽ wrap nó trong Okio types và cuối cũng thành ResponseBody. Và các converter được đưa trực tiếp cho ResponseBody bới vì Moshi biết cách để giao tiếp với Okio type. Nó lấy dữ liệu từ BuferSource sau đó converter chuyển đổi chúng thành Data Model mà ứng dụng cần.
Kết
Trên đây là bài viết của mình về Retrofit, nếu bài viết có sai sót mong mọi người đã theo dõi.
Tham khảo
https://medium.com/mindorks/understand-how-does-retrofit-work-c9e264131f4a
All rights reserved