Defect Density? How to Calculate The Defect Density in Software Products
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
By detecting defects and errors during the early stages of software development one can ensure the quality, performance, scalability, features, security, as well as other important elements of the software. Moreover, by conducting defect detection software developers can validate whether the application is being built as per the demands of the client and make all the necessary changes if required. To ensure that the product’s effectiveness is apt and correct, software engineers use defect density, which is a metric that states, “The more defects in the software, the lower the quality is”.
What is Meant by Defect Density?
Defect Density is the number of defects confirmed in software/module during a specific period of operation or development divided by the size of the software/module. It enables one to decide if a piece of software is ready to be released.
Defect density is counted per thousand lines of code also known as KLOC.
How do you Calculate Defect Density?
The defect density could be defined as the value of the total defects, which are known to the size of the software product calculated:
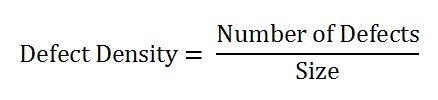
There is no fixed standard for defect density, however, studies suggest that one Defect per 1000 lines of codes (LOC), which is generally considered as a sign of good project quality. This standard of defect density is also known as KLOC.
Defect density, therefore, is a measure showing the ratio of defects against the size of a development (number of defects/size), in which the size is typically expressed in terms of Function Points (FP), Impact points or other ‘points’ measures.
Hence, following are the steps for calculating defect density:
- Collect the raw material, i.e., testers will require the total number of defects detected while developing the software product.
- Calculate the average number of defects/ Functional area or Line of Code (LOC).
Defect Density Example
1. For example: For a particular test cycle there are 30 defects in 5 modules or components. Therefore, the density will be:
Total no. of defects/ KLOC.
30/15 = 0.5
Hence, the density is 1 defect for every 2 KLOC
2. Suppose, you have 3 modules integrated into your software product. Each module has the following number of bugs discovered-
- Module 1 = 10 bugs
- Module 2 = 20 bugs
- Module 3 = 10 bugs Total bugs = 10+20+10 =40
The total line of code for each module is
- Module 1 = 1000 LOC
- Module 2 = 1500 LOC
- Module 3 = 500 LOC Total Line of Code = 1000+1500+500 = 3000
Defect Density is calculated as:
Defect Density = 40/3000 = 0.013333 defects/loc = 13.333 defects/KLOC
Standard for defect density
However, there is no fixed standard for bug density, studies suggest that one Defect per thousand lines of code is generally considered as a sign of good project quality.
Uses of Defect Density:
Defect density is a recognised industry standard and it uses are numerous. It is a process of calculating the number of defects per development, which helps software engineers in determining the areas that are weak as well as that require rigorous testing.
Defect density is also used to compare subsequent releases of a product, to track the impact of defect reduction and quality improvement activities. Moreover, through this technique, one can compare differences between products or product lines. Other uses of defect density are:
- Predict the remaining defects when compared to the expected defect density.
- Determine if the amount of testing is sufficient.
- Establish a database of standard defect densities.
- Conveys the progress, productivity and quality of the product.
- It provides information regarding the product, which helps in deciding whether it is fit for use or not.
- As a module with high defect density requires mending and work, defect density helps in identifying them and promotes call for action.
Factors that affect the defect density metrics
- Code complexity
- The type of defects taken into account for the calculation
- Time duration which is considered for Defect density calculation
- Developer or Tester skills
Advantages of defect density
- It helps to measure the testing effectiveness
- It helps to differentiate defects in components/software modules
- It is useful in identifying the areas for correction or improvement
- It is useful in pointing towards high-risk components
- It helps in identifying the training needs to various resources
- It can be helpful in estimating the testing and rework due to bugs
- It can estimate the remaining defects in the software
- Before the release, we can determine whether our testing is sufficient
- We can ensure a database with a standard defect density
Conclusion:
The above discussion reflects the importance as well as the benefit of using defect density during the process of software development. Though defect density is considered insignificant and unnecessary by several software engineer, it is one of the best way to judge the areas that are highly affected by bugs and errors.
Reference:
https://www.professionalqa.com
https://www.guru99.com
All rights reserved