Communicate between 2 Fragments in a Activity
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Chắc hẳn các dev Android đi phỏng vấn thường gặp câu hỏi như là "Làm sao để có thể giao tiếp giữa 2 Fragment trong cùng 1 Activity? ". Mình thì thường dùng 1 trong 2 cách mà mình sẽ trình bày chi tiết trong bài viết này, đó là sử dụng Callback và ViewModel.
Mình có đề bài đơn giản như sau: Có 1 Activity chứa đồng thời 2 Fragmen A và B, Fragment A để send data gồm 1 EditText và 1 Button, Fragment B có 1 TextView, làm thế nào để khi click vào Button bên A sẽ hiển thị nội dung trong EditText bên B. Cùng sử dụng 2 cách trên để giải quyết đề bài này nhé.
1. Sử dụng Callback
Đây là cách khá phổ biến và quen thuộc, chúng ta sẽ sử dụng 1 callback để truyền data từ A sang B. Fragment A sẽ có đối tượng callback, khi click button Send sẽ gọi method sendText() trong Callback. Chúng ta sẽ implement callback đó trong activity chứa cả 2 Fragment. Để dễ hình dung hơn, các bạn tham khảo đoạn code sau:
Các file xml:
activity_main
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/send_fragment_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#E8F1F1"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/receive_fragment_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:background="#E8EBF5"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
fragment_send
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="16dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_send"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:hint="Type to send"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_send"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="send"/>
</LinearLayout>
fragment_receive
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="32dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_receive"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp" />
</LinearLayout>
SendFagment
public class SendFragment extends Fragment {
private static SendFragment instance;
private SendTextListener sendTextListener;
public static SendFragment getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SendFragment();
}
return instance;
}
public void setSendTextListener(SendTextListener sendTextListener) {
this.sendTextListener = sendTextListener;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_send, container, false);
initView(view);
return view;
}
public void initView(View view) {
final EditText editText = view.findViewById(R.id.edit_send);
Button button = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_send);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sendTextListener.sendText(editText.getText().toString());
}
});
}
}
ReceivedFragment
public class ReceivedFragment extends Fragment {
private static ReceivedFragment instance;
private TextView textReceived;
public static ReceivedFragment getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ReceivedFragment();
}
return instance;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_receive, container, false);
textReceived = view.findViewById(R.id.text_receive);
return view;
}
public void getText(String text) {
textReceived.setText(text);
}
}
SendTextListenner
public interface SendTextListener {
void sendText(String text);
}
MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SendTextListener{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().add(R.id.send_fragment_container, SendFragment.getInstance()).commit();
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().add(R.id.receive_fragment_container, ReceivedFragment.getInstance()).commit();
SendFragment.getInstance().setSendTextListener(this);
}
@Override
public void sendText(String text) {
ReceivedFragment.getInstance().getText(text);
}
}
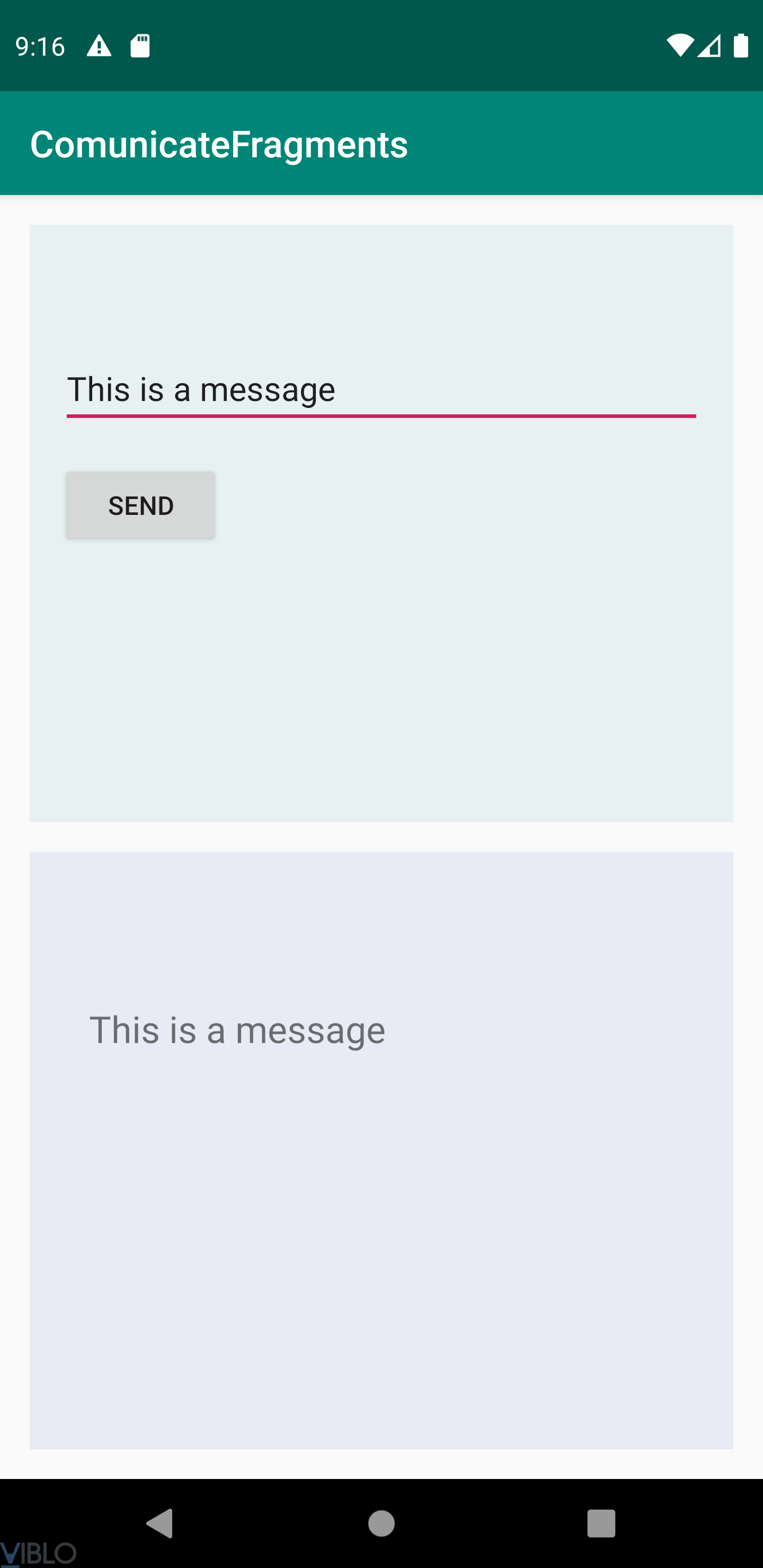
Kết quả sẽ được như sau, khi nhập vào Edittext nội dung "This is a message" và click button Send, sẽ hiển thị lên TextView của Fragment B
2. Sử dụng ViewModel
Mình giới thiệu qua 1 chút về ViewModel. ViewModel là một class được thiết kế để lưu trữ và quản lý các dữ liệu trong một lifecycle riêng, nó cho phép dữ liệu được bảo toàn ngay cả khi màn hình bị xoay. Trong cách 1 trên, khi bạn xoay màn hình dẫn đến Configuration change, Activity của bạn sẽ được khởi tạo lại, dẫn đến dữ liệu bị mất, nội dung TextView trong Fragment B cũng sẽ được reset lại thành rỗng. Còn với sử dụng ViewModel, do dữ liệu được lưu trữ trong 1 lifecycle riêng và không phụ thuộc vào vòng đời của Activity hay Fragment (trong trường hợp xoay màn hình) nên dữ liệu vẫn được giữ nguyên, vậy nên khi bạn xoay màn hình thì dữ liệu vẫn giữ nguyên.
Nói qua thế thôi, tiếp theo là cách giao tiếp giữa 2 Fragments qua ViewModel. Đầu tiên mình sẽ tạo 1 class kế thừa ViewModel, có 1 thuộc tính kiểu MutableLiveData (các bạn có thể tự tìm hiểu thêm về LiveData, bài viết này dài rồi nên mình không giới thiệu nữa).
SendTextViewModel
public class SendTextViewModel extends ViewModel {
public MutableLiveData<String> text = new MutableLiveData<>();
public MutableLiveData<String> getText() {
return text;
}
}
Fragment B sẽ đăng kí lắng nghe sự thay đổi giá trị của thuộc tính "text" trong ViewModel để khi thay đổi giá trị của thuộc tính "text" trong Fragment A, Fragment B sẽ biết được sự thay đổi của thuộc tính đó và cập nhật lên giao diện. Các bạn có thể tham khảo đoạn code ở dưới để dễ hiểu hơn.
SendFragment
public class SendFragment extends Fragment {
private static SendFragment instance;
private SendTextViewModel viewmodel;
public static SendFragment getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SendFragment();
}
return instance;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_send, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
initView(view);
}
public void initView(View view) {
final EditText editText = view.findViewById(R.id.edit_send);
viewmodel = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(SendTextViewModel.class);
Button button = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_send);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
viewmodel.getText().postValue(editText.getText().toString());
}
});
}
ReceivedFragment
public class ReceivedFragment extends Fragment {
private static ReceivedFragment instance;
private TextView textReceived;
private SendTextViewModel viewmodel;
public static ReceivedFragment getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ReceivedFragment();
}
return instance;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_receive, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
viewmodel = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(SendTextViewModel.class);
textReceived = view.findViewById(R.id.text_receive);
viewmodel.getText().observe(this, new Observer<String>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(String s) {
textReceived.setText(s);
}
});
}
}
Và tất nhiên kết quả cũng giống như cách 1 nhưng cách này khá ngắn gọn và được bonus thêm trường hợp bảo toàn được dữ liệu khi xoay màn hình.
3. Tổng kết
Mình đã trình bày xong 2 cách mình thường dùng để giải quyết câu hỏi đã nêu ra ở đầu bài viết. Các bạn dùng những cách nào khác thì comment ở dưới để chúng ta tìm hiểu và áp dụng nhé.
Link github tại đây.
All rights reserved