AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional - Identity Federation - AWS Organizations
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Introduction
A quick note about AWS Organizations. This post is a quick note from the course Ultimate AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional by Stephane Maarek. The only purpose of this post is a summary, if you want detailed learning, please buy a course by Stephane Maarek.
AWS Organizations
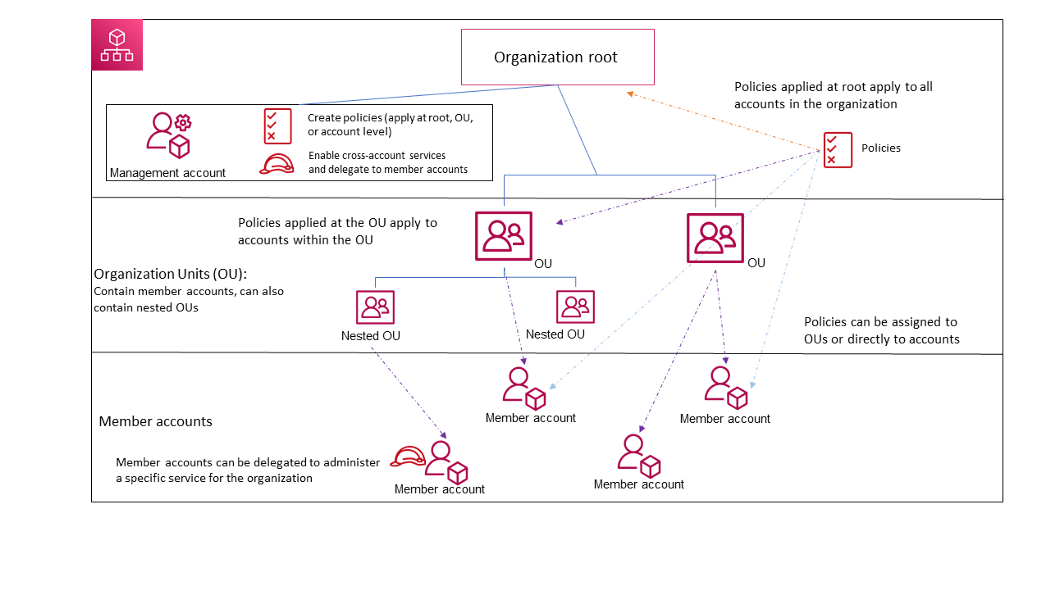
AWS Organizations is an account management service that lets you manage multiple AWS accounts in an organization. You can create member accounts and invite existing accounts to join your organization, organize those accounts into groups and attach policy-based controls.
AWS Organizations can organize the accounts in a hierarchy, with a root at the top and organizational units nested under the root.
Root
The parent container for all the accounts for your organization. If you apply a policy to the root, it applies to all organizational units (OUs) and accounts in the organization.
Management Account
The root contains our management account, which is an account that will be used for all administration purposes:
- Create accounts in the organization.
- Invite other existing accounts to the organization.
- Remove accounts from the organization.
- Manage invitations.
- Apply policies to entities (roots, OUs, or accounts) within the organization.
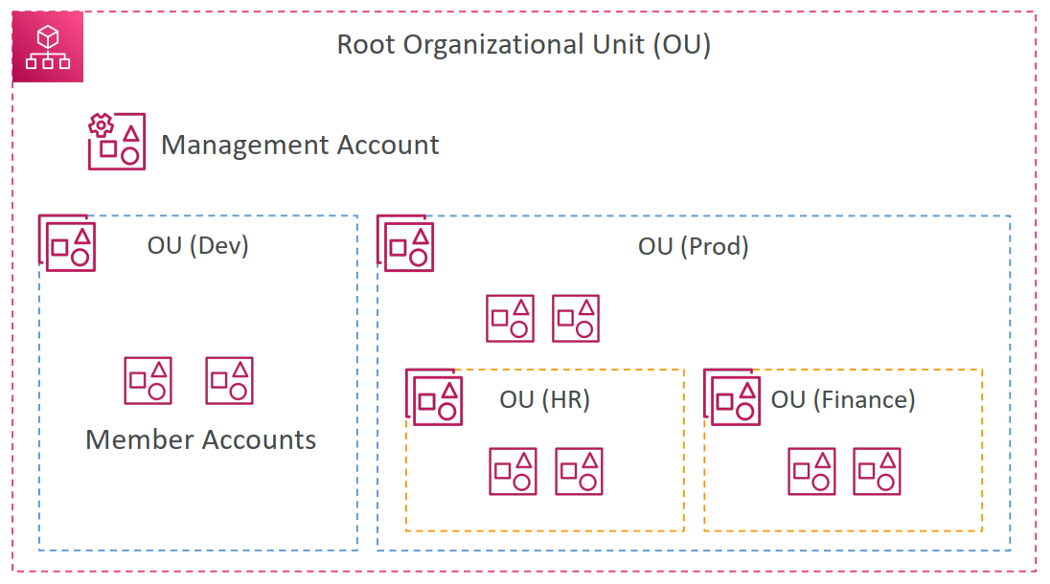
Organizational Unit (OU)
A container for accounts within a root. An OU also can contain other OUs, enabling you to create a hierarchy that resembles an upside-down tree with a root at the top.
When you attach a policy to one of the OU, it flows down and affects all the nested OUs.
Member accounts
A member account is the AWS account. An account can be a member of only one organization at a time. You can attach a policy to an account to apply controls to only that one account.
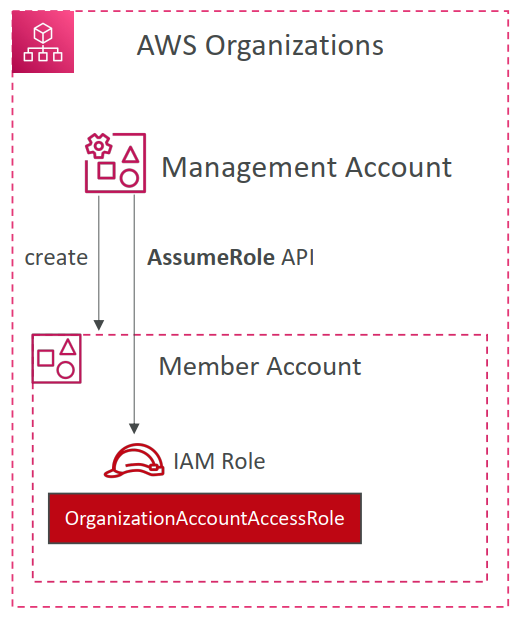
Organization Account Access Role
When you create a member account using the AWS Organizations console, AWS Organizations automatically creates an IAM role named OrganizationAccountAccessRole in the account. This role has full administrative permissions in the member account.
However, member accounts that you invite to join your organization do not automatically get an administrator role created. You have to do this manually, see Creating the OrganizationAccountAccessRole in an invited member.
Multi Account Strategies
Create accounts per department, per cost center, per dev/test/prod, based on regulatory restrictions (using SCP), for better resource isolation (ex: VPC), to have separate per-account service limits, isolated account for logging.
Use tagging standards for billing purposes.
Enable CloudTrail on all accounts, and send logs to the central S3 account.
Send CloudWatch Logs to the central logging account.
Strategy to create an account for security.
For example.
- We have a business unit type of OU that manage account per department.
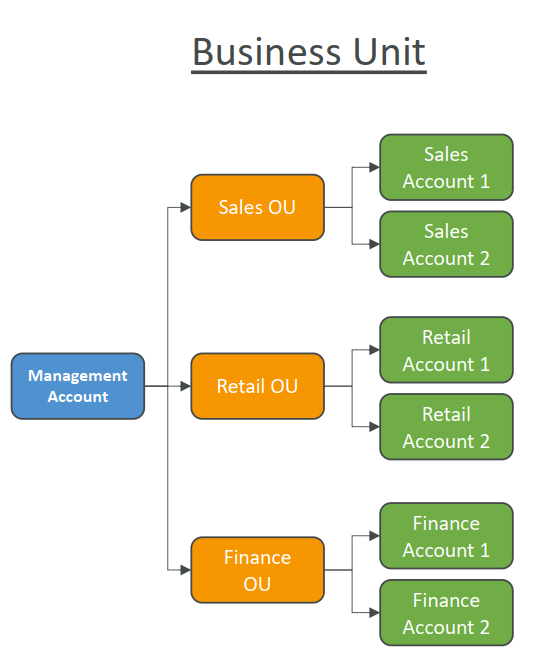
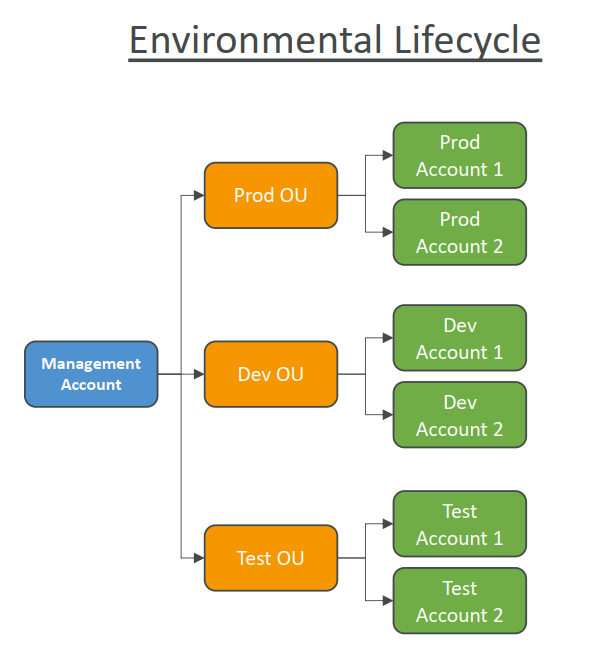
- We have an env unit type of OU that manage account per environment.
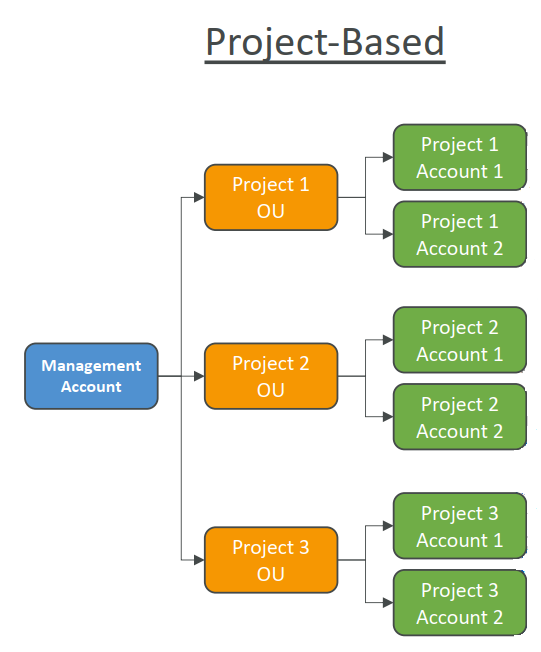
- We have a project unit type of OU that manage account per project.
Feature Modes
There are two feature modes of AWS Organization you need to know for the example.
Consolidated billing features:
- Consolidated Billing across all accounts — single payment method.
- Pricing benefits from aggregated usage (volume discount for EC2, S3…).
All Features (Default):
- Includes consolidated billing features, SCP.
- Invited accounts must approve enabling all features.
- Ability to apply an SCP to prevent member accounts from leaving the org.
- Can’t switch back to Consolidated Billing Features only.
Reserved Instances in AWS Organizations
For billing purposes, the consolidated billing feature of AWS Organizations treats all the accounts in the organization as one account.
This means that all accounts in the organization can receive the hourly cost the benefit of Reserved Instances that are purchased by any other account.
The payer account (Management account) of an organization can turn off Reserved Instance (RI) discount and Savings Plans discount sharing for any accounts in that organization, including the payer account.
This means that RIs and Savings Plans discounts aren’t shared among any accounts that have sharing turned off.
To share an RI or Savings Plans discount with an account, both accounts must have sharing turned on.
End
End note about AWS Organizations.
All rights reserved