Sử dụng AI đánh giá sản phẩm trên Lazada(Tiki) dựa trên comment
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Ý tưởng
Hiện nay việc mua bán hàng online đang là xu hướng tất yếu của cuộc sống. Nhưng khi chúng ta mua hàng trên Lazada hay Tiki thì liệu chúng ta có an tâm về sản phẩm đó có đúng chất lượng như họ đã quảng cáo không ? Chúng ta không thể đọc hết tất cả bình luận để đánh giá sản phẩm được. Từ ý tưởng đó , mình tạo ra 1 hệ thống sử dụng AI ( trí tuệ nhân tạo ) để đánh giá sản phẩm trên Lazada , Tiki dựa trên bình luận.Từ đó sẽ đưa ra gợi ý cho người dùng có nên mua sản phẩm đó hay không ? , thống kê các bình luận tiêu cực,....

 Trong hệ thống này sẽ sử dụng các kĩ thuật sau đây :
Trong hệ thống này sẽ sử dụng các kĩ thuật sau đây :
- Kĩ thuật crawl comment trên Lazada (Tiki ) sử dụng BeautifulSoup, Selenium
- Kĩ thuật xử lí dữ liệu
- Model BERT
- Train model
- Predict
Kĩ thuật crawl comment trên Lazada( Tiki) sử dụng BeautifulSoup, Selenium:
1. Use BeautifulSoup :
Thư viện BeautifulSoup là một thư viện của Python cho phép chúng ta lấy dữ liệu từ HTML đơn giản và hiệu quả. Mình sẽ dùng Python 3 và BeautifulSoup 4 để thực hiện việc crawling đơn giản. Trang web được sử dụng là Lazada, việc craw dữ liệu đòi hỏi chúng ta phải biết cấu trúc html của trang web đó.
def load_url(url):
print("Loading url=", url)
page = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(page,"html.parser")
script = soup.find_all("script", attrs={"type": "application/ld+json"})[0]
script = str(script)
script = script.replace("</script>","").replace("<script type=\"application/ld+json\">","")
csvdata = []
for element in json.loads(script)["review"]:
if "reviewBody" in element:
csvdata.append([element["reviewBody"]])
return csvdata
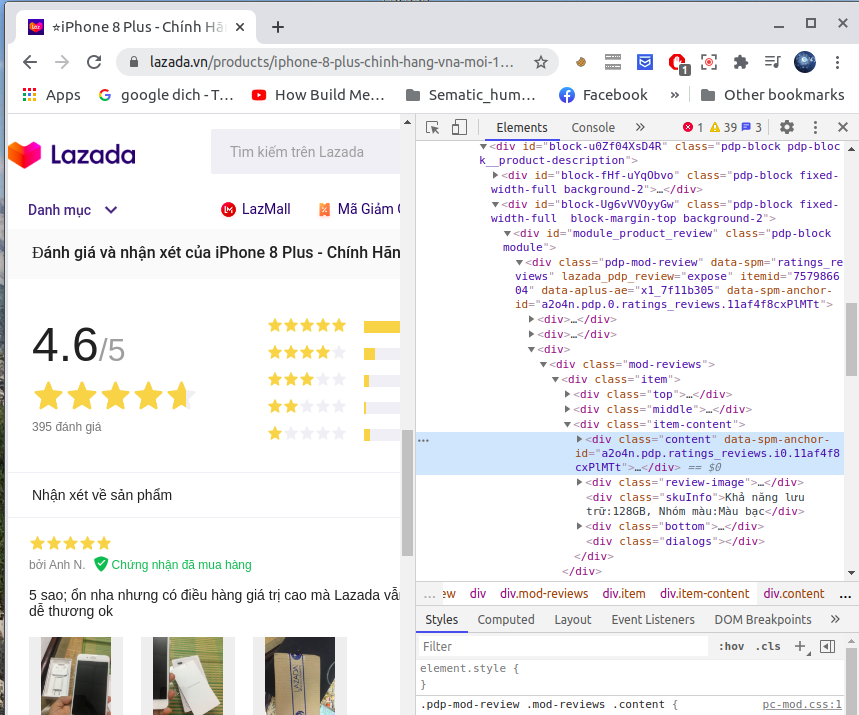
Tuy nhiên việc sử dụng BeautifulSoup chỉ crawl được các trang web tĩnh, không thao tác được trên trang web đó. Ví dụ: ta chỉ crawl được các comment trên url của trang đó thôi mà không thể next sang bình luận của trang khác ( hay comment của Youtobe chỉ load khi cuộn xuống nên không áp dụng được BeautifulSoup). Để khắc phục hạn chế đó ta sẽ sử dụng Selenium.
2. Use Selenium:
Thư viện selenium là 1 thư viện của python cho phép ta mở 1 trình duyệt (chromedriver) và thao tác trên đó luôn. Ở đây mình sẽ crawl comment trên Lazada và Tiki.
def load_url_selenium_lazada(url):
# Selenium
driver=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='/usr/bin/chromedriver')
print("Loading url=", url)
driver.get(url)
list_review = []
# just craw 10 page
x=0
while x<10:
try:
#Get the review details here
WebDriverWait(driver,5).until(EC.visibility_of_all_elements_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR,"div.item")))
except:
print('No has comment')
break
product_reviews = driver.find_elements_by_css_selector("[class='item']")
# Get product review
for product in product_reviews:
review = product.find_element_by_css_selector("[class='content']").text
if (review != "" or review.strip()):
print(review, "\n")
list_review.append(review)
#Check for button next-pagination-item have disable attribute then jump from loop else click on the next button
if len(driver.find_elements_by_css_selector("button.next-pagination-item.next[disabled]"))>0:
break;
else:
button_next=WebDriverWait(driver, 5).until(EC.visibility_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, "button.next-pagination-item.next")))
driver.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", button_next)
print("next page")
time.sleep(2)
x +=1
driver.close()
return list_review
def load_url_selenium_tiki(url):
driver=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='/usr/bin/chromedriver')
print("Loading url=", url)
driver.get(url)
list_review = []
# just craw 10 page
x=0
while x<10:
try:
#Get the review details here
WebDriverWait(driver,5).until(EC.visibility_of_all_elements_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR,"div.review-comment")))
except :
print('Not has comment!')
break
product_reviews = driver.find_elements_by_css_selector("[class='review-comment']")
# Get product review
for product in product_reviews:
review = product.find_element_by_css_selector("[class='review-comment__content']").text
if (review != "" or review.strip()):
print(review, "\n")
list_review.append(review)
#Check for button next-pagination-item have disable attribute then jump from loop else click on the next button
try:
#driver.find_element_by_xpath("//li[@class='btn next']/a").click()
button_next=WebDriverWait(driver, 20).until(EC.visibility_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, "[class = 'btn next']")))
driver.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", button_next)
print("next page")
time.sleep(2)
x +=1
except (TimeoutException, WebDriverException) as e:
print('Load several page!')
break
driver.close()
return list_review
Kĩ thuật xử lí dữ liệu
1. Thu thập dữ liệu comment trên Lazada hoặc Tiki
Chúng ta sẽ sử dụng các kĩ thuật crawl comment như đã trình bày ở trên để thu thập data. Sau đó gán nhãn cho chúng, ví dụ ở đây chỉ có 2 trạng thái comment : tốt-tích cực- trung gian :0, xấu- không tốt- tiêu cực : 1 ( nếu có nhiều hơn 2 trạng thái thì gán 0,1,2 ,3 ,..).
Ở đây mình có chuẩn bị 1 file data gồm 132 comment đã gán nhãn . data.csv
2. Chuẩn hóa data
Chuẩn hóa data ở đây rất đơn giản : xóa đi các dấu câu như ( . ,? * ", ...), xóa đi khoảng trống 2 đầu của comment. Sử dụng regex(Regular Expression)
def standardize_data(row):
# remove stopword
# Remove . ? , at index final
row = re.sub(r"[\.,\?]+$-", "", row)
# Remove all . , " ... in sentences
row = row.replace(",", " ").replace(".", " ") \
.replace(";", " ").replace("“", " ") \
.replace(":", " ").replace("”", " ") \
.replace('"', " ").replace("'", " ") \
.replace("!", " ").replace("?", " ") \
.replace("-", " ").replace("?", " ")
row = row.strip()
return row
2. Word tokenizer
Work tokenizer chuyển 1 câu thành các word có nghĩa ( bao gồm cả từ đơn và từ ghép ). Ví dụ

from underthesea import word_tokenize
# Tokenizer
def tokenizer(row):
return word_tokenize(row, format="text")
Model BERT
1. Kiến trúc model BERT
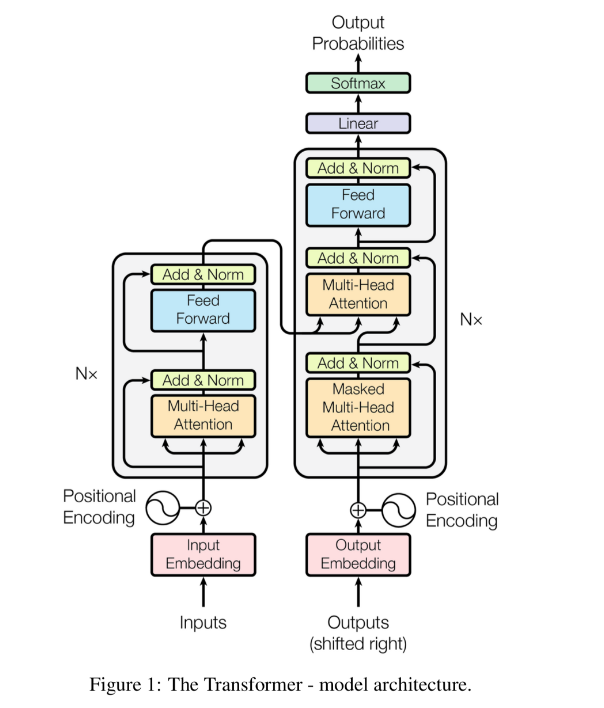
BERT là model hoạt động dựa trên cơ chế attention (chú trọng các đặc trưng ) nó sẽ khắc phục hoàn toàn các nhược điểm của các model như RNN, LSTM,.. ( bị giới hạn bộ nhớ ).
Các bạn có thể đọc tài liệu dưới đây để hiểu rõ về cấu trúc, cách thức hoạt động của model:
- https://phamdinhkhanh.github.io/2020/05/23/BERTModel.html
- https://towardsdatascience.com/bert-explained-state-of-the-art-language-model-for-nlp-f8b21a9b6270
- https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf
Ở series sau mình sẽ ra bài hiểu sâu về kiến trúc model RNN, LSTM, Transformers , BERT,.. so sánh ưu điểm, nhược điểm của mỗi model với nhau.
2. Load data
 Import các thư viện cần thiết :
Import các thư viện cần thiết :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import torch
import transformers
from transformers import BertModel, BertTokenizer
from sklearn.externals import joblib
 Load data
Load data
df = pd.read_csv('data_crawler.csv', delimiter='\t', header=None)
print(df.shape)
# get all rows
# print(df[0])
3. Load pretrain model BERT
'''
Load pretrain model/ tokenizers
'''
model = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
#encode lines
tokenized = df[0].apply((lambda x: tokenizer.encode(x, add_special_tokens = True)))
print('encode',tokenized[1])
# decode
print('decode',tokenizer.decode(tokenized[1]))
4. Fine-tuning model và save model
 Fine-tuning có nghĩa là huấn luyện tiếp trọng số (weights, bias ) của model. Kết quả thu được lưu vào file save_model.pkl
Fine-tuning có nghĩa là huấn luyện tiếp trọng số (weights, bias ) của model. Kết quả thu được lưu vào file save_model.pkl
#get all label
labels = np.zeros(len(df[0]))
for i in range(len(df[0])):
labels[i] = df[0][i][-1]
print('labels shape:', labels.shape)
# get lenght max of tokenized
max_len = 0
for i in tokenized.values:
if len(i) > max_len:
max_len = len(i)
print('max len:', max_len)
# if lenght of tokenized not equal max_len , so padding value 0
padded = np.array([i + [0]*(max_len-len(i)) for i in tokenized.values])
print('padded:', padded[1])
print('len padded:', padded.shape)
#get attention mask ( 0: not has word, 1: has word)
attention_mask = np.where(padded ==0, 0,1)
print('attention mask:', attention_mask[1])
# Convert input to tensor
padded = torch.tensor(padded)
attention_mask = torch.tensor(attention_mask)
# Train model
with torch.no_grad():
last_hidden_states = model(padded, attention_mask =attention_mask)
# print('last hidden states:', last_hidden_states)
features = last_hidden_states[0][:,0,:].numpy()
print('features:', features)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, labels)
cl = LogisticRegression()
cl.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Save model
joblib.dump(cl, 'save_model.pkl')
sc = cl.score(X_test, y_test)
print('score:', sc)
Predict
1 . Nhập đường dẫn url đến của sản phẩm cần đánh giá
Thay đổi url tới sản phẩm cần đánh giá :
predict(url = 'https://www.lazada.vn/products/iphone-8-plus-chinh-hang-vna-moi-100-chua-kich-hoat-chua-qua-su-dung-bao-hanh-12-thang-tai-ttbh-apple-tra-gop-lai-suat-0-qua-the-tin-dung-man-hinh-retina-hd-55-inch-3d-touch-chip-a11-ios11-i757986604-s1985088475.html?spm=a2o4n.searchlistcategory.list.4.46d0bdd5OzWEVE&search=1')
2. Tiền xử lí, word tokenizer
- Chuẩn hóa data, tokenizer:
def standardize_data(row):
# remove stopword
# Remove . ? , at index final
row = re.sub(r"[\.,\?]+$-", "", row)
# Remove all . , " ... in sentences
row = row.replace(",", " ").replace(".", " ") \
.replace(";", " ").replace("“", " ") \
.replace(":", " ").replace("”", " ") \
.replace('"', " ").replace("'", " ") \
.replace("!", " ").replace("?", " ") \
.replace("-", " ").replace("?", " ")
row = row.strip()
return row
# Tokenizer
def tokenizer(row):
return word_tokenize(row, format="text")
def analyze(result):
bad = np.count_nonzero(result)
good = len(result) - bad
print("No of bad and neutral comments = ", bad)
print("No of good comments = ", good)
if good>bad:
return "Good! You can buy it!"
else:
return "Bad! Please check it carefully!"
- Processing data:
def processing_data(data):
# 1. Standardize data
data_frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
print('data frame:', data_frame)
data_frame[0] = data_frame[0].apply(standardize_data)
# 2. Tokenizer
data_frame[0] = data_frame[0].apply(tokenizer)
# 3. Embedding
X_val = data_frame[0]
return X_val
3. Đưa các comment vào model để predict
- Đưa các comment sau khi được xử lí vào model:
def load_pretrainModel(data):
'''
Load pretrain model/ tokenizers
Return : features
'''
model = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
#encode lines
tokenized = data.apply((lambda x: tokenizer.encode(x, add_special_tokens = True)))
# get lenght max of tokenized
max_len = 0
for i in tokenized.values:
if len(i) > max_len:
max_len = len(i)
print('max len:', max_len)
# if lenght of tokenized not equal max_len , so padding value 0
padded = np.array([i + [0]*(max_len-len(i)) for i in tokenized.values])
print('padded:', padded[1])
print('len padded:', padded.shape)
#get attention mask ( 0: not has word, 1: has word)
attention_mask = np.where(padded ==0, 0,1)
print('attention mask:', attention_mask[1])
# Convert input to tensor
padded = torch.tensor(padded)
attention_mask = torch.tensor(attention_mask)
# Load model
with torch.no_grad():
last_hidden_states = model(padded, attention_mask =attention_mask)
# print('last hidden states:', last_hidden_states)
features = last_hidden_states[0][:,0,:].numpy()
print('features:', features)
return features
- Predict:
def predict(url):
# 1. Load URL and print comments
if url== "":
url = "https://tiki.vn/dien-thoai-samsung-galaxy-m31-128gb-6gb-hang-chinh-hang-p58259141.html"
data = load_url_selenium_lazada(url)
# data = load_url_selenium_tiki(url)
data = processing_data(data)
features = load_pretrainModel(data)
# 2. Load weights
model = joblib.load('save_model.pkl')
# 3. Result
result = model.predict(features)
print(result)
print(analyze(result))
4. Kết quả
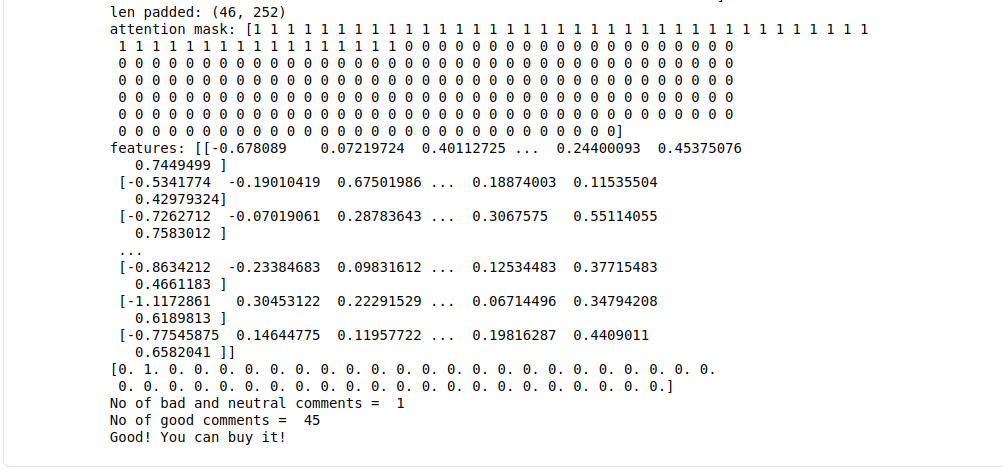
Qua kết quả trên ta thấy có 45 comments tốt về sản phẩm, 1 comment xấu. Nên chúng ta có thể mua nó
Kết luận
Toàn bộ code : https://github.com/trungtruc123/Review_Product_Lazada
Chúng ta có thể sử dụng các model khác như SVM, logistic Regression thay cho BERT. Nhưng độ chính xác của model SVC ~ 0.84, còn model BERT ~ 0.91 ( tại sao lại vậy ? đơn giản vì model BERT kiến trúc phức tạp hơn và sử dụng nhiều trick như attention ,...)
Thông qua project nhỏ này, chúng ta nắm rõ 1 số phương pháp kĩ thuật cơ bản trong xử lí ngôn ngữ tự nhiên, cũng như cách craw dữ liệu trên web, sử dụng model BERT,.... Bên cạnh đó chúng ta có thể áp dụng nhiều hơn 2 trạng thái comment như : bùn, vui, giận dữ, khó chịu , thỏa mãn, thất vọng ,... và viết thành 1 project hoàn chỉnh để làm đề tài tốt nghiệp, luận văn tốt nghiệp,.. Bài viết này còn sơ xài do mình hơi bận, nếu các bạn thấy hay để lại comment mình sẽ ra series 2 hướng dẫn viết hệ thống này một cách hoàn chỉnh.
Cảm ơn các bạn đã tới đây ! Hẹn các bạn trong series 2
Tài liệu tham khảo
All rights reserved