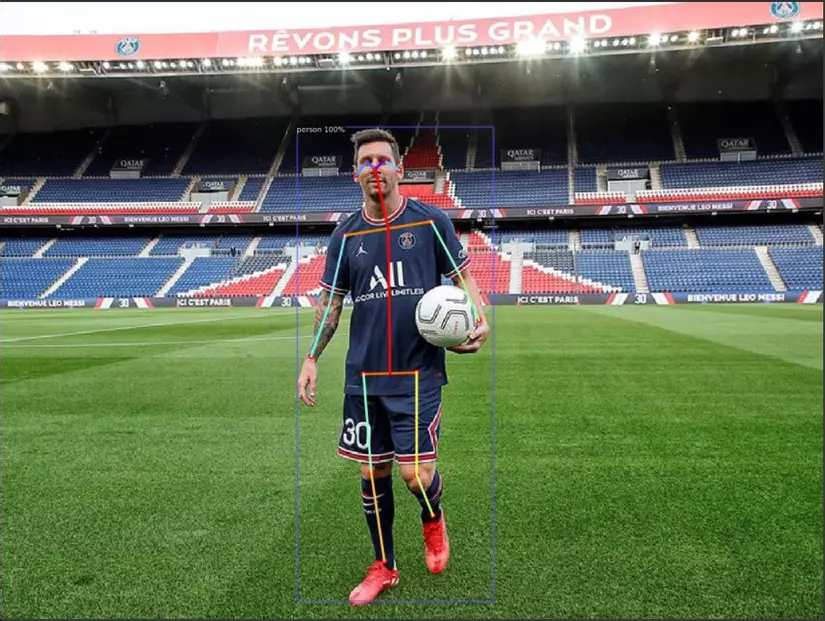
Nhận diện hành động người qua Detectron2 và LSTM
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Lời mở đầu
Chào các bạn, hôm nay mình có đọc qua bài toán phân loại hành động người của tác giả Tô Đức Thắng: https://viblo.asia/p/human-pose-classification-with-cnn-and-lstm-1VgZvJb7ZAw thì thấy sử dụng mô hình CNN kết hợp với LSTM.
Dữ liệu đầu vào ở đây là 1 video có label tương ứng là một hành động nào đó. Các video này sẽ được chuyển đổi thành chuỗi frame dạng ảnh đưa vào CNN để trích xuất dữ liệu. Bài viết cũng có đề cập đến việc dùng các điểm trên cơ thể người (pose keypoints) làm đầu vào nhưng do giới hạn độ dài và chủ đề nên tác giả cũng chưa đi sâu.
Vì vậy hôm nay tôi giới thiệu các bạn một bài viết của tác giả Bibin Sebastian: https://learnopencv.com/human-action-recognition-using-detectron2-and-lstm/ miêu tả phương thức dùng các điểm detect bởi Detectron2 đưa vào mạng LSTM để phân biệt các hành động của con người. Okay! Let's go
Detectron2
Detectron2 là một nền tảng mã nguồn mở của Facebook AI dùng để object detection, dense pose, segmentation, ... code bằng PyTorch.
Ở đây tác giả bài viết dùng pre-trained model R50-FPN trong mục pose estimation của Detectron2 model zoo. Mô hình này huấn luyện với bộ dữ liệu COCO bao gồm 200k ảnh và 200k người, được dán nhãn với các điểm trên cơ thể. Đầu ra của mô hình là 17 điểm với mỗi một người xuất hiện trong ảnh.
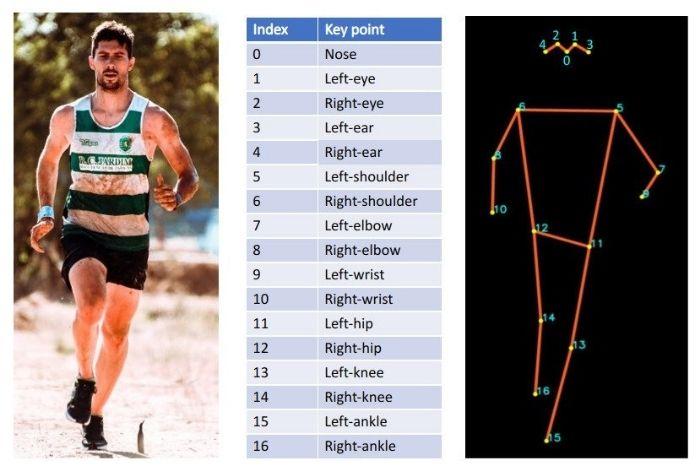
Về thuật toán đánh giá các điểm trên cơ thể người, tôi sẽ giới thiệu với các bạn trong các bài viết sau.
LSTM
Bản nâng cấp của RNN, tôi cũng sẽ không đi sâu vào mạng này bởi có nhiều bài viết giới thiệu mạng LSTM rồi. Mô hình RNN có cấu trúc như sau
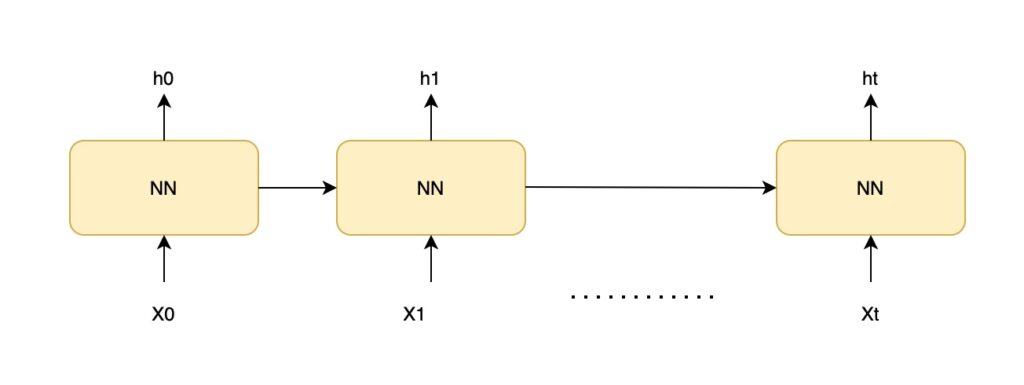
- X0 -> Xt là đầu vào, h0 -> ht là kết quả dự đoán
- Mỗi lần dự đoán ở thời điểm t (ht) phụ thuộc vào kết quả dự đoán của cái trước (ht-1) và đầu vào hiện tại Xt
Trong bài viết này LSTM được dùng để phân loại hành động của một chuỗi pose keypoints trong một video.
Dataset
Bộ dữ liệu huấn luyện mô hình LSTM được dùng ở đây: https://github.com/stuarteiffert/RNN-for-Human-Activity-Recognition-using-2D-Pose-Input
Bộ này cũng được dùng trong repo Openpose https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/openpose và là 1 nhánh con của bộ dữ liệu Berkeley Multimodal Human Action Database (MHAD) https://tele-immersion.citris-uc.org/berkeley_mhad
Bộ này bao gồm 6 hành động:
- Jumping
- Jumping_jacks
- Boxing
- Waving_2hands
- Waving_1hand
- Clappinng_hands

Giải pháp cho việc nhận diện hành động
Để phân loại hành động người, chúng ta cần định vị được các điểm trên cơ thể người ở từng frame, sau đó phân tích chuyển động của người đấy theo thời gian.
Bước đầu sử dụng Detectron2 để xác định 17 điểm trên cơ thể sau khi quan sát từng frame của 1 video.
Bước 2 là phân tích chuyển động của người theo thời gian và dự đoán bằng mô hình LSTM. Video có bao nhiêu frame thì có bấy nhiêu cái 17 điểm, đưa vào mạng LSTM để phân loại hành động.
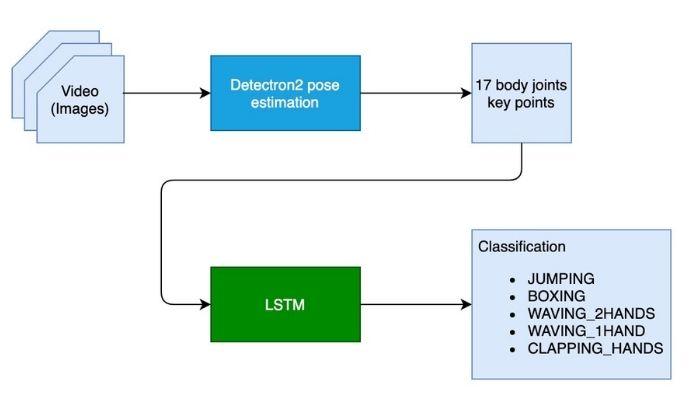
Huấn luyện mô hình
- Dùng pre-trained mô hình ‘R50-FPN’ để xác định 17 điểm
- Implement LSTM bằng PyTorch Lightning để phân loại hành động dựa trên 17 điểm
Đầu vào của LSTM là chuỗi keypoints ( 17 điểm / frame ) và nhãn của nó. Lấy 32 frames nối tiếp nhau làm 1 sample, 32 frame ở đây làm bội số của 2 ( nhị phân ), thuận lợi cho việc huấn luyện. Ta sẽ có một array với size 32x34 ( 17 điểm, mỗi điểm bao gồm x, y => 17x2 = 34 giá trị )
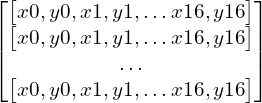
Pose Estimation with Detectron2
Cài đặt pytorch và detectron2
pip install pyyaml==5.1
pip install torch==1.9.0+cu102 torchvision==0.10.0+cu102 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.htmlhttps://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/cu102/torch1.9/index.html
pip install detectron2 -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/cu102/torch1.9/index.html
Kiểm tra phiên bản torch
import torch, torchvision
print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())
Khởi tạo cấu hình detectron2
# obtain detectron2's default config
cfg = get_cfg()
# load the pre trained model from Detectron2 model zoo
cfg.merge_from_file(model_zoo.get_config_file("COCO-Keypoints/keypoint_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml"))
# set confidence threshold for this model
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.5
# load model weights
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = model_zoo.get_checkpoint_url("COCO-Keypoints/keypoint_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml")
# create the predictor for pose estimation using the config
pose_detector = DefaultPredictor(cfg)
Test với 1 ảnh bất kỳ
im = cv2.imread("./messi_tirm.jpg")
cv2_imshow(im)
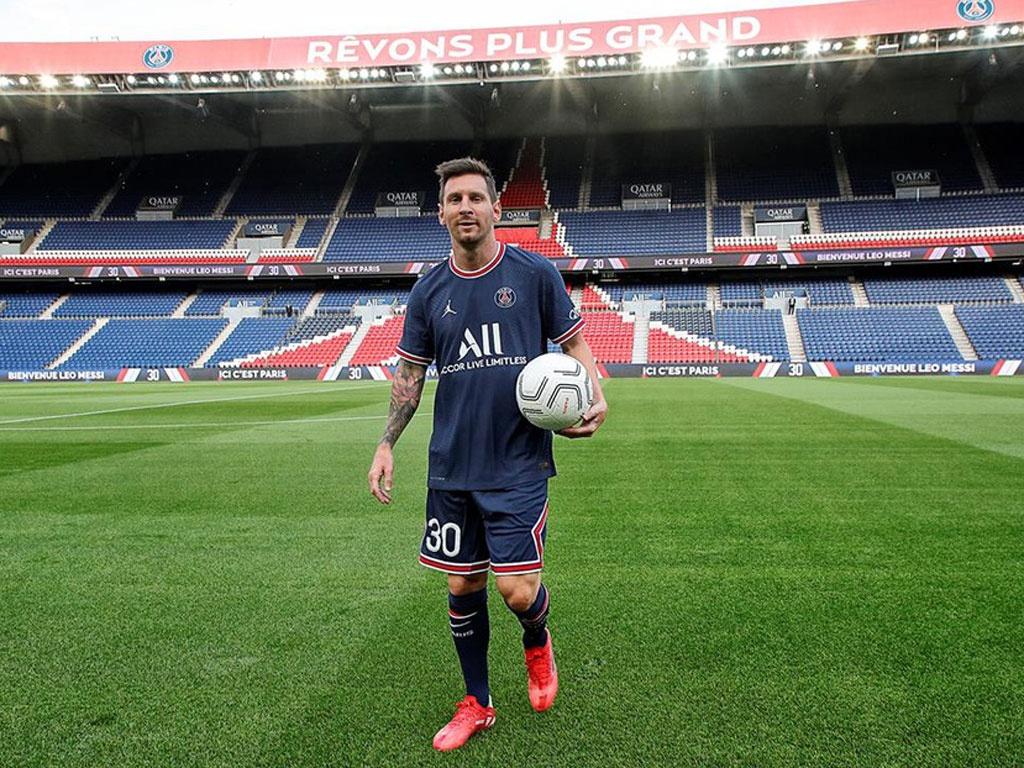

Output keypoints có dạng sau
outputs = pose_detector(im)
pers = outputs["instances"].pred_keypoints
kp_parts = MetadataCatalog.get(cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN[0]).keypoint_names
for p in pers:
for i in range(0, len(p)):
kp = p[i].cpu()
print('%s: (%f, %f)'%(kp_parts[i], kp[0], kp[1]))
nose: (465.678833, 208.531189)
left_eye: (477.176758, 197.984818)
right_eye: (454.180878, 199.902344)
left_ear: (495.381805, 209.489944)
right_ear: (442.682953, 216.201279)
left_shoulder: (535.624512, 273.726959)
right_shoulder: (428.310547, 290.984680)
left_elbow: (572.992859, 343.716553)
right_elbow: (409.147308, 375.355652)
left_wrist: (595.030518, 397.407166)
right_wrist: (386.151489, 441.510193)
left_hip: (517.419495, 461.644196)
right_hip: (451.306427, 463.561707)
left_knee: (517.419495, 589.159424)
right_knee: (460.888000, 586.283203)
left_ankle: (537.540894, 639.015015)
right_ankle: (477.176758, 695.581970)
Visualize
v = Visualizer(im[:, :, ::-1], MetadataCatalog.get(cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN[0]), scale=1.2)
out = v.draw_instance_predictions(outputs["instances"].to("cpu"))
cv2_imshow(out.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])
LSTM
Cài đặt pytorch lightning
pip install pytorch-lightning
Khởi tạo mô hình LSTM bằng pytorch lightning với hidden dimension (hidden_dim) là 50. Tối ưu bằng Adam Optimizer, điều chỉnh learning rate bằng ReduceLROnPlateau dựa trên giá trị của val_loss
import os
import torch
import torchmetrics
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import pytorch_lightning as pl
# We have 6 output action classes.
TOT_ACTION_CLASSES = 6
#lstm classifier definition
class ActionClassificationLSTM(pl.LightningModule):
# initialise method
def __init__(self, input_features, hidden_dim, learning_rate=0.001):
super().__init__()
# save hyperparameters
self.save_hyperparameters()
# The LSTM takes word embeddings as inputs, and outputs hidden states
# with dimensionality hidden_dim.
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_features, hidden_dim, batch_first=True)
# The linear layer that maps from hidden state space to classes
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, TOT_ACTION_CLASSES)
def forward(self, x):
# invoke lstm layer
lstm_out, (ht, ct) = self.lstm(x)
# invoke linear layer
return self.linear(ht[-1])
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# get data and labels from batch
x, y = batch
# reduce dimension
y = torch.squeeze(y)
# convert to long
y = y.long()
# get prediction
y_pred = self(x)
# calculate loss
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_pred, y)
# get probability score using softmax
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# calculate accuracy
acc = torchmetrics.functional.accuracy(pred, y)
dic = {
'batch_train_loss': loss,
'batch_train_acc': acc
}
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar or any other operations
self.log('batch_train_loss', loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('batch_train_acc', acc, prog_bar=True)
#return loss and dict
return {'loss': loss, 'result': dic}
def training_epoch_end(self, training_step_outputs):
# calculate average training loss end of the epoch
avg_train_loss = torch.tensor([x['result']['batch_train_loss'] for x in training_step_outputs]).mean()
# calculate average training accuracy end of the epoch
avg_train_acc = torch.tensor([x['result']['batch_train_acc'] for x in training_step_outputs]).mean()
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('train_loss', avg_train_loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('train_acc', avg_train_acc, prog_bar=True)
def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# get data and labels from batch
x, y = batch
# reduce dimension
y = torch.squeeze(y)
# convert to long
y = y.long()
# get prediction
y_pred = self(x)
# calculate loss
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_pred, y)
# get probability score using softmax
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# calculate accuracy
acc = torchmetrics.functional.accuracy(pred, y)
dic = {
'batch_val_loss': loss,
'batch_val_acc': acc
}
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('batch_val_loss', loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('batch_val_acc', acc, prog_bar=True)
#return dict
return dic
def validation_epoch_end(self, validation_step_outputs):
# calculate average validation loss end of the epoch
avg_val_loss = torch.tensor([x['batch_val_loss']
for x in validation_step_outputs]).mean()
# calculate average validation accuracy end of the epoch
avg_val_acc = torch.tensor([x['batch_val_acc']
for x in validation_step_outputs]).mean()
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('val_loss', avg_val_loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('val_acc', avg_val_acc, prog_bar=True)
def configure_optimizers(self):
# adam optimiser
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.hparams.learning_rate)
# learning rate reducer scheduler
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.5, patience=10, min_lr=1e-15, verbose=True)
# scheduler reduces learning rate based on the value of val_loss metric
return {"optimizer": optimizer,
"lr_scheduler": {"scheduler": scheduler, "interval": "epoch", "frequency": 1, "monitor": "val_loss"}}
Inference
Pipeline này bao gồm 2 mô hình: Detectron2 và LSTM
- Đầu vào: 1video, quan sát từng frame bằng opencv. Detectron2 dự đoán 17 điểm ở mỗi frame
- 17 điểm này sẽ được nối vào một buffer có size là 32 => ta có được 1 array có size là 32, 34
- Sau đó đưa vào mô hình LSTM đã huấn luyện để nhận diện hành động
- Hành động được nhận diện được dán nhãn trên video và hiển thị kết quả
Tốc độ inference: Detectron2: 0.14s/frame, LSTM: 0.002s/frame => 6 frame/s by inference pipeline.
Để tăng tốc độ inference, tác giả bài viết gợi ý dùng các giải pháp
- Dùng Pruning và Quantization làm giảm dung lượng mô hình, giảm số lượng param
- Skip frame, giả sử 1 video có FPS là 30, thì cứ xử lý frame thứ 5 mỗi giây do hành động của người không thay đổi nhiều trong 1s
- Multi threading: tạo nhiều thread, thêm các frames vào queue, xử lý song song.
# how many frames to skip while inferencing
# configuring a higher value will result in better FPS (frames per rate), but accuracy might get impacted
SKIP_FRAME_COUNT = 0
# analyse the video
def analyse_video(pose_detector, lstm_classifier, video_path):
# open the video
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# width of image frame
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
# height of image frame
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# frames per second of the input video
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# total number of frames in the video
tot_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
# video output codec
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
# extract the file name from video path
file_name = ntpath.basename(video_path)
# video writer
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter('res_{}'.format(
file_name), fourcc, 30, (width, height))
# counter
counter = 0
# buffer to keep the output of detectron2 pose estimation
buffer_window = []
# start time
start = time.time()
label = None
# iterate through the video
while True:
# read the frame
ret, frame = cap.read()
# return if end of the video
if ret == False:
break
# make a copy of the frame
img = frame.copy()
if(counter % (SKIP_FRAME_COUNT+1) == 0):
# predict pose estimation on the frame
outputs = pose_detector(frame)
# filter the outputs with a good confidence score
persons, pIndicies = filter_persons(outputs)
if len(persons) >= 1:
# pick only pose estimation results of the first person.
# actually, we expect only one person to be present in the video.
p = persons[0]
# draw the body joints on the person body
draw_keypoints(p, img)
# input feature array for lstm
features = []
# add pose estimate results to the feature array
for i, row in enumerate(p):
features.append(row[0])
features.append(row[1])
# append the feature array into the buffer
# not that max buffer size is 32 and buffer_window operates in a sliding window fashion
if len(buffer_window) < WINDOW_SIZE:
buffer_window.append(features)
else:
# convert input to tensor
model_input = torch.Tensor(np.array(buffer_window, dtype=np.float32))
# add extra dimension
model_input = torch.unsqueeze(model_input, dim=0)
# predict the action class using lstm
y_pred = lstm_classifier(model_input)
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred_index = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# pop the first value from buffer_window and add the new entry in FIFO fashion, to have a sliding window of size 32.
buffer_window.pop(0)
buffer_window.append(features)
label = LABELS[pred_index.numpy()[0]]
#print("Label detected ", label)
# add predicted label into the frame
If label is not None:
cv2.putText(img, 'Action: {}'.format(label),
(int(width-400), height-50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.9, (102, 255, 255), 2)
# increment counter
counter += 1
# write the frame into the result video
vid_writer.write(img)
# compute the completion percentage
percentage = int(counter*100/tot_frames)
# return the completion percentage
yield "data:" + str(percentage) + "\n\n"
analyze_done = time.time()
print("Video processing finished in ", analyze_done - start)
Lời kết
Bài viết đến đây là kết thúc, full source code các bạn có thể tìm được ở link này https://github.com/spmallick/learnopencv/tree/master/Human-Action-Recognition-Using-Detectron2-And-Lstm
Rất cám ơn tác giả Bibin Sebastian vì bài viết mang lại cho mình một số gợi ý trong công việc 
References
https://learnopencv.com/human-action-recognition-using-detectron2-and-lstm/#detectron2
All rights reserved
