Interpreter Design Pattern - Trợ thủ đắc lực của Developers
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
1. Giới thiệu
- Interpreter là một mẫu thiết kế thuộc nhóm hành vi (Behavioral Pattern).
- Interpreter Pattern giúp người lập trình có thể “xây dựng” những đối tượng “động” bằng cách đọc mô tả về đối tượng rồi sau đó “xây dựng” đối tượng đúng theo mô tả đó.
- Ví dụ, viết một chương trình cho phép người dùng nhập vào dòng lệnh (command) theo một cấu trúc xác định do ta quy định sẵn, chương trình sẽ nhận dạng Command dựa vào cấu trúc của nó và trả về kết quả phù hợp
2. Kiến trúc
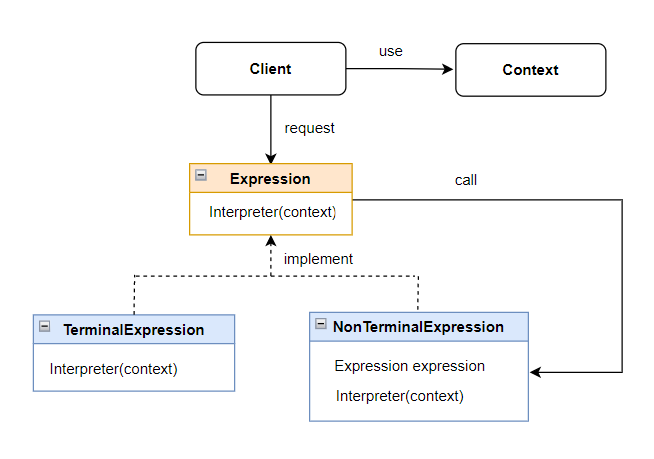
Các thành phần trong mô hình:
- AbstractionExpression: Khai báo một giao diện cho việc thực hiện một thao tác.
- TerminalExpression: Cài đặt một thao tác thông dịch liên kết với những ký pháp đầu cuối, đóng vai trò một thể nghiệm được yêu cầu cho mọi ký pháp đầu cuối trong câu.
- NonterminalExpression: Có thể chứa TerminalExpression bên trong và cũng có thể chứa một NonterminalExpression khác. Nó đóng vai trò như là “ngữ pháp” của ngôn ngữ đặc tả.
- Context: Là đối tượng thông tin để thực hiện thông dịch. Đối tượng này là toàn cục đối với quá trình thông dịch (dùng chung giữa các node).
3. Ưu & nhược điểm
Ưu điểm
- Giảm sự phục thuộc giữa abstraction và implementation (loose coupling).
- Giảm số lượng những lớp con không cần thiết.
- Code sẽ gọn gàn hơn và kích thước ứng dụng sẽ nhỏ hơn.
- Dễ bảo trì hơn.
- Dễ dàng mở rộng về sau.
- Cho phép ẩn các chi tiết implement từ client.
Nhược điểm
- Ngôn ngữ đặc tả được xây dựng đòi hỏi phải có cấu trúc ngữ pháp đơn giản.
- Hiệu suất không đảm bảo
4. Khi nào thì sử dụng
Sử dụng Interpreter Patern khi chúng ta muốn:
- Bộ ngữ pháp đơn giản. Pattern này cần xác định ít nhất một lớp cho mỗi quy tắc trong ngữ pháp. Do đó ngữ pháp có chứa nhiều quy tắc có thể khó quản lý và bảo trì.
- Không quan tâm nhiều về hiệu suất. Do bộ ngữ pháp được phân tích trong cấu trúc phân cấp (cây) nên hiệu suất không được đảm bảo.
- Interpreter Pattern thường được sử dụng trong trình biên dịch (compiler), định nghĩa các bộ ngữ pháp, rule, trình phân tích SQL, XML, …
5. Source code minh họa với C#
Bài toán: thực hiện chương trình để diễn giải thương hiệu, loại và số kiểu máy bay từ tên kiểu dịch vụ của nó.
Step 1: Tạo Context
class Context
{
private string ac_model = "";
private bool isAircraft = false;
public Context(string _ac_model)
{
this.ac_model = _ac_model;
}
public string getModel()
{
return this.ac_model;
}
public int getLenght()
{
return this.ac_model.Length;
}
public string getLastChar()
{
return this.ac_model[this.ac_model.Length - 1].ToString();
}
public string getFirstChar()
{
return this.ac_model[0].ToString();
}
public void setIsAircraft(bool _isAircraft)
{
this.isAircraft = _isAircraft;
}
public bool getIsAircraft()
{
return this.isAircraft;
}
}
Step 2: Tạo AbstractionExpression
interface Expression
{
void InterpretContext(Context context);
}
Step 3: Tạo NonterminalExpression
class CheckExpression : Expression
{
public void InterpretContext(Context context)
{
//We assume tthe aircraft models only start with A or B and contains 4 or 5 chars.
string ac_model = context.getModel();
if (ac_model.StartsWith("A") || ac_model.StartsWith("B"))
{
if (ac_model.Length == 4 || ac_model.Length == 5)
{
context.setIsAircraft(true);
Console.WriteLine(ac_model + " is an aircraft...");
}
else
{
context.setIsAircraft(false);
Console.WriteLine(ac_model + " is not aircraft...");
}
}
else
{
context.setIsAircraft(false);
Console.WriteLine(ac_model + " is not aircraft...");
}
}
}
Step 4: Tạo TerminalExpression
class BrandExpression : Expression
{
public void InterpretContext(Context context)
{
if (context.getIsAircraft() == true)
{
if (context.getFirstChar().Equals("A"))
Console.WriteLine("Brand is Airbus");
else if (context.getFirstChar().Equals("B"))
Console.WriteLine("Brand is Boeing");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Brand could not be interpreted");
}
}
class ModelExpression : Expression
{
public void InterpretContext(Context context)
{
if (context.getIsAircraft() == true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Model is : " + context.getModel().Substring(1, 3));
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Model could not be interpreted");
}
}
class TypeExpression : Expression
{
public void InterpretContext(Context context)
{
if (context.getIsAircraft() == true)
{
string ac_model = context.getModel();
if (context.getLenght() == 5 && context.getLastChar().Equals("F"))//F-> Freighter
{
Console.WriteLine("Aircraft type is Cargo/Freighter");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Aircraft type is Passenger Transportation");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Type could not be interpreted");
}
}
Step 5: Tạo Client
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Title = "Interpreter Design Pattern Example - TheCodeprogram";
List<Context> lstAircrafts = new List<Context>();
List<Expression> lstExpressions = new List<Expression>();
lstAircrafts.Add(new Context("A330"));
lstAircrafts.Add(new Context("A330F"));
lstAircrafts.Add(new Context("B777"));
lstAircrafts.Add(new Context("B777F"));
lstAircrafts.Add(new Context("TheCode"));
lstExpressions.Add(new CheckExpression());
lstExpressions.Add(new BrandExpression());
lstExpressions.Add(new ModelExpression());
lstExpressions.Add(new TypeExpression());
for (int ac_index = 0; ac_index < lstAircrafts.Count; ac_index++)
{
for (int exp_index = 0; exp_index < lstExpressions.Count; exp_index++)
{
lstExpressions[exp_index].InterpretContext(lstAircrafts[ac_index]);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
6. Design Pattern liên quan
- Cây cú pháp trừu tượng là một thể nghiệm trong mẫu Composite.
- Interpreter thường sử dụng một Iterator để duyệt cấu trúc.
- Visitor có thể được sử dụng để duy trì hành vi trên mỗi nút trong cây cú pháp trừu tượng của lớp.
Bài viết của mình đến đây là kết thúc, cảm ơn các bạn đã theo dõi. Nếu các bạn thấy có ích có thể khám phá thêm Series Design Patterns - Trợ thủ đắc lực của Developers của mình!!
Tài liệu tham khảo
[1] Refactoring.Guru. https://refactoring.guru/design-patterns
[2] Design Patterns for Dummies, Steve Holzner, PhD
[3] Head First, Eric Freeman
[4] Gang of Four Design Patterns 4.0
[5] Dive into Design Pattern
All rights reserved