Deploying .NET Application on Docker & Kubernetes
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Overview
In this Post , We’ll share the Process how you can Develop and Deploy .NET Application using Docker and Kubernetes and Adopt DevOps in existing .NET Applications
Prerequisites
To follow this guide you need
-
Kubernetes - Kubernetes is an open source platform that automates container operations and Minikube is best for testing Kubernetes.
-
Kubectl - Kubectl is command line interface to manage Kubernetes cluster either remotely or locally. To configure kubectl in your machine follow this link.
-
Shared Persistent Storage - Shared Persistent Storage is permanent storage that we can attach to the Kubernetes container so that we don`t lose our data even container died. We will be using GlusterFS as a persistent data store for Kubernetes container applications.
-
.NET Application Source Code - Application Source Code is source code that we want to run inside a kubernetes container.
-
Dockerfile - Dockerfile contains a bunch of commands to build .NET application.
-
Container-Registry - The Container Registry is an online image store for container images.
Below mentioned options are few most popular registries.
-
Private Docker Hub
-
AWS ECR
-
Docker Store
-
Google Container Registry
Create a Dockerfile
The below-mentioned code is sample dockerfile for .NET applications. In which we are using Microsoft .NET 1.1 SDK for .NET Application.
FROM microsoft/dotnet:1.1-sdk
# Setting Home Directory for application
WORKDIR /app
# copy csproj and restore as distinct layers
COPY dotnetapp.csproj .
RUN dotnet restore
# copy and build everything else
COPY . .
RUN dotnet publish -c Release -o out
EXPOSE 2223
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "out/main.dll"]
Building .NET Application Image
The below-mentioned command will build your application container image.
$ docker build -t <name of your application>:<version of application>
Publishing Container Image
Now we publish our .NET application container images to any container registry like Docker Hub, AWS ECR, Google Container Registry, Private Docker Registry.
We are using Azure Container Registry for publishing Container Images.
You also need to Sign Up on Azure Cloud Platform and then create Container Registry using this link.
Now Click The Link to Pull and Push to Azure Container Registry.
Similarly, we can Push or Pull any container image to any of the below-mentioned Container Registry like Docker Hub, AWS ECR, Private Docker Registry, Google Container Registry etc.
Creating Deployment Files for Kubernetes
Deploying application on kubernetes with ease using deployment and service files either in JSON or YAML format.
-
Deployment File
Following Content is for “<name of application>.deployment.yml” file of Python container application.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: <name of application>
namespace: <namespace of Kubernetes>
spec:
replicas: <number of application pods>
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: <name of application>
spec:
containers:
- name: <name of application>
image: <image name >:<version tag>
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
ports:
- containerPort: 2223
-
Service File
Following Content is for “<name of application>.service.yml” file of Python container application.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: <name of application>
name: <name of application>
namespace: <namespace of Kubernetes>
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 2223
selector:
k8s-app: <name of application>
Running .NET Application on Kubernetes
.NET Application Container can be deployed either by kubernetes Dashboard or Kubectl (Command line).
I`m explaining command line that you can use in production Kubernetes cluster.
$ kubectl create -f <name of application>.deployment.yml
$ kubectl create -f <name of application>.service.yml
Now we have successfully deployed .NET Application on Kubernetes.
Verification
We can verify application deployment either by using Kubectl or Kubernetes Dashboard.
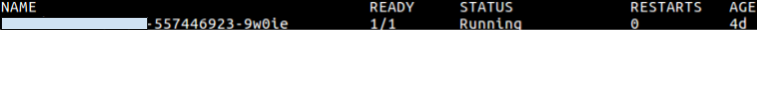
The below-mentioned command will show you running pods of your application with status running/terminated/stop/created.
$ kubectl get po --namespace=<namespace of kubernetes> | grep <application name>
Result of above command
Continue Reading About Deploying .NET Application On Docker & Kubernetes
All rights reserved