Create an example API by SpringBoot framework
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Lời mở đầu
Bài viết này mình sẽ hướng dẫn cho mấy bạn lần đầu viết API bằng java, sử dụng framework SpringBoot. Trước tiên ta định nghĩa API là gì.
API viết tắt của Application Program Interface, được hiểu là giao diện lập trình ứng dụng. Là phần mềm để các ứng dụng giao tiếp với nhau (Website, Mobile,..)
Qua đó ta cũng có thể hiểu nôm na là nó cũng có thể đáp ứng được các chức năng cơ bản của 1 ứng dụng là xem, thêm, sửa, xóa. Người ta hay gọi là CRUD (viết tắt của Create, Read, Update, Delete) Bài viết này mình sẽ tạo một ứng dụng mẫu cơ bản bằng java với Spring Boot, JPA, Hibernate, và MySQL.
Bắt đầu
Tạo project
- Mở eclipse lên. Chọn File -> New -> Spring Starter Project
Sẽ hiển thị giao diện như sau:

Các bạn đổi tên project theo ý muốn. Sau đó ấn Next. Tiếp theo ta chọn các gói dependencies: MySQL Driver, Spring Dat JPA, Spring Boot Actuator, Spring Boot DevTools, Spring Web.
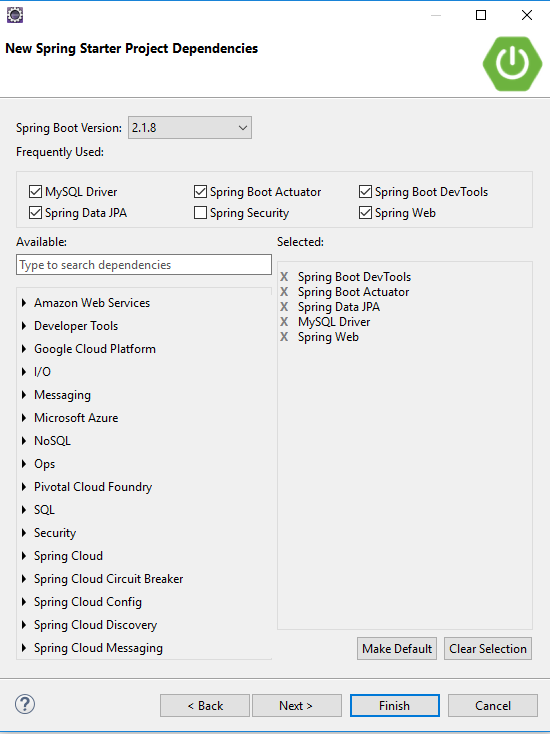
Rồi ấn Finish.
Cấu hình database
Vào file application.properties (thư mục scr/main/resources)
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database_name?useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql = true
Tạo entity class
Entity class này giống như các class được mapping với các table trên database
Ví dụ ta tạo 1 class Student với các thuộc tính: mssv, name, birthday, khoa
1 class Khoa với các thuộc tính: id, name.
Ta tạo package com.demo.entities. Rồi tạo các class Student và Khoa tương ứng như sau:
@Entity
@Table(name = "sinhvien")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long mssv;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "birthday")
private String birthday;
@Column(name = "gender")
private int gender;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "khoa_id")
private Khoa khoa;
//Các hàm dựng getter, setter
@Entity
@Table(name = "khoa")
public class Khoa {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column
private String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="khoa")
private Set<Student> listSV = new HashSet<>();
//Các hàm dựng getter, setter
Anotation: @Id, @GeneratedValue là chỉ định cho trường mssv là khóa chính. @Column là chỉnh định cột.
@ManyToOne là chỉ mối quan hệ giữa bảng sinhvien và bảng khoa là 1-n. Tức là 1 sinh viên thuộc về 1 khoa, 1 khoa có nhiều sinh viên.
Vậy là ta đã có các class rồi. Tiếp theo ta sẽ tạo 1 package JPA để các đối tượng tương tác tới database
Tạo JPA repository
Tạo package com.demo.repositories, rồi tạo các repository tương ứng như sau:
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> {
//Get list student of khoa
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM sinhvien WHERE khoa_id = :k_id", nativeQuery = true)
List<Student> getStudentKhoa(@Param("k_id") long khoa_id);
}
@Repository
public interface KhoaRepository extends JpaRepository<Khoa, Long> {
}
Long là kiểu dữ liệu của khóa chính.
Tạo Services
Các service sẽ tạo các method để xử lí và trả về kết quả cho các request.
Để cho dễ hiểu thì ví dụ: Bạn muốn lấy danh sách tất cả các sinh viên. Thì service sẽ lấy tất cả các đối tượng sinh viên nhờ các JPA Repository.
Tạo package com.demo.services, rồi tạo các interface service tương ứng như sau:
public interface StudentService {
//Get all students
public List<Student> getAllStudent();
//Get student by id
public Student getStudent(long id);
//Create new student
public Student addStudent(Student student);
//Update student
public Student updateStudent(Student student);
//Delete student
public boolean delStudent(long id);
//Get list student of Khoa
public List<Student> getStudentOfKhoa(long khoa_id);
}
public interface KhoaService {
//Get all khoa
public List<Khoa> getAllKhoa();
}
Tạo các implements để thực thi các interface service
Tạo package com.demo.services.impl
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Override
public List<Student> getAllStudent() {
List<Student> listStudent = studentRepository.findAll();
return listStudent;
}
@Override
public Student getStudent(long id) {
Student student = studentRepository.getOne(id);
return student;
}
@Override
public Student addStudent(Student student) {
return studentRepository.save(student);
}
@Override
public Student updateStudent(Student student) {
student = studentRepository.save(student);
return student;
}
@Override
public boolean delStudent(long id) {
Student student = studentRepository.getOne(id);
if (student != null) {
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public List<Student> getStudentOfKhoa(long khoa_id) {
List<Student> listStd = studentRepository.getStudentKhoa(khoa_id);
return listStd;
}
}
@Service
public class KhoaServiceImpl implements KhoaService {
@Autowired
private KhoaRepository khoaRepository;
@Override
public List<Khoa> getAllKhoa() {
List<Khoa> listKhoa = khoaRepository.findAll();
return listKhoa;
}
}
Vậy là ta đã có các service rồi. Bây giờ tạo các Rest Controller nữa là xong.
Tạo Rest Controller
Các rest controller sẽ xử lí các request và trả về dữ liệu dưới dạng JSON.
Như các chức năng đã đề cập ở trên thì bây giờ ta sẽ viết rest controller để xử lí các chức năng Xem, Thêm, Sửa, Xóa tương ứng với 4 method request: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE.
Ta tạo package com.demo.controllers rồi tạo các controller tương ứng cho Student và Khoa.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("student/all")
public ResponseEntity<List<Student>> getAll(){
List<Student> listStudent = studentService.getAllStudent();
return new ResponseEntity<List<Student>>(listStudent, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@GetMapping("student/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<?> getStudent(@PathVariable("id") long id){
if (studentService.getStudent(id) == null) {
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Not Found Student ID: " + id);
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
} else {
Student std = studentService.getStudent(id);
return new ResponseEntity<Student>(std, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
@GetMapping("student/khoa/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<?> getStudentOfKhoa(@PathVariable("id") long id){
List<Student> listStd = studentService.getStudentOfKhoa(id);
if (listStd.size() > 0) {
return new ResponseEntity<List<Student>>(listStd, HttpStatus.OK);
}else {
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Not Found Student of Khoa: " + id);
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
//Add new student
@PostMapping("student/add")
public ResponseEntity<?> addStudent(@RequestBody Student std){
Student dataStd = studentService.addStudent(std);
if (dataStd != null) {
return new ResponseEntity<Student>(dataStd, HttpStatus.OK);
}
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Can not create student ");
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@PutMapping("student/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<?> updateStudent(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestBody Student std){
Student dataStd = studentService.getStudent(id);
if (dataStd == null) {
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Not found student id: "+ id);
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
} else {
dataStd.setName(std.getName());
dataStd.setBirthday(std.getBirthday());
dataStd.setGender(std.getGender());
studentService.updateStudent(dataStd);
return new ResponseEntity<Student>(dataStd, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
@DeleteMapping("student/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<?> deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") long id){
Student dataStd = studentService.getStudent(id);
if (dataStd == null) {
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Not found student id: "+ id);
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
} else {
studentService.delStudent(id);
APIMessages apiErr = new APIMessages("Deleted student id: "+ id);
return new ResponseEntity<APIMessages>(apiErr, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
}
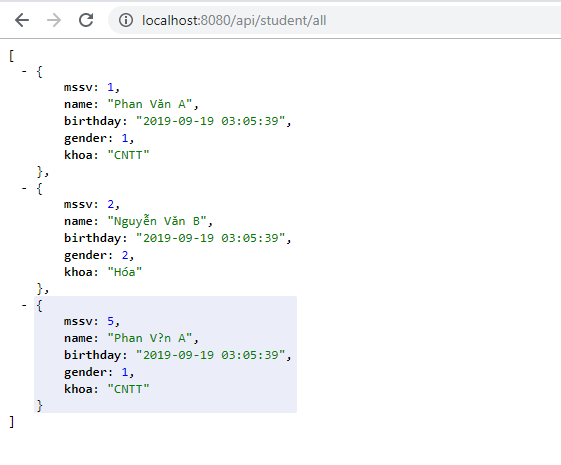
Để test kết quả, ta gửi request tới các đường dẫn tương ứng. Các bạn có thể sử dụng Postman để kiểm tra kết quả.
Ví du lấy tất cả sinh viên: localhost:8080/api/student/all
Tổng kết
Hi vọng bài viết có thể giúp anh em lần đầu tiếp xúc với API bằng java. Hãy comment ở bài viết nếu có gì thắc mắc mình sẽ nhiệt tình giải đáp.
All rights reserved