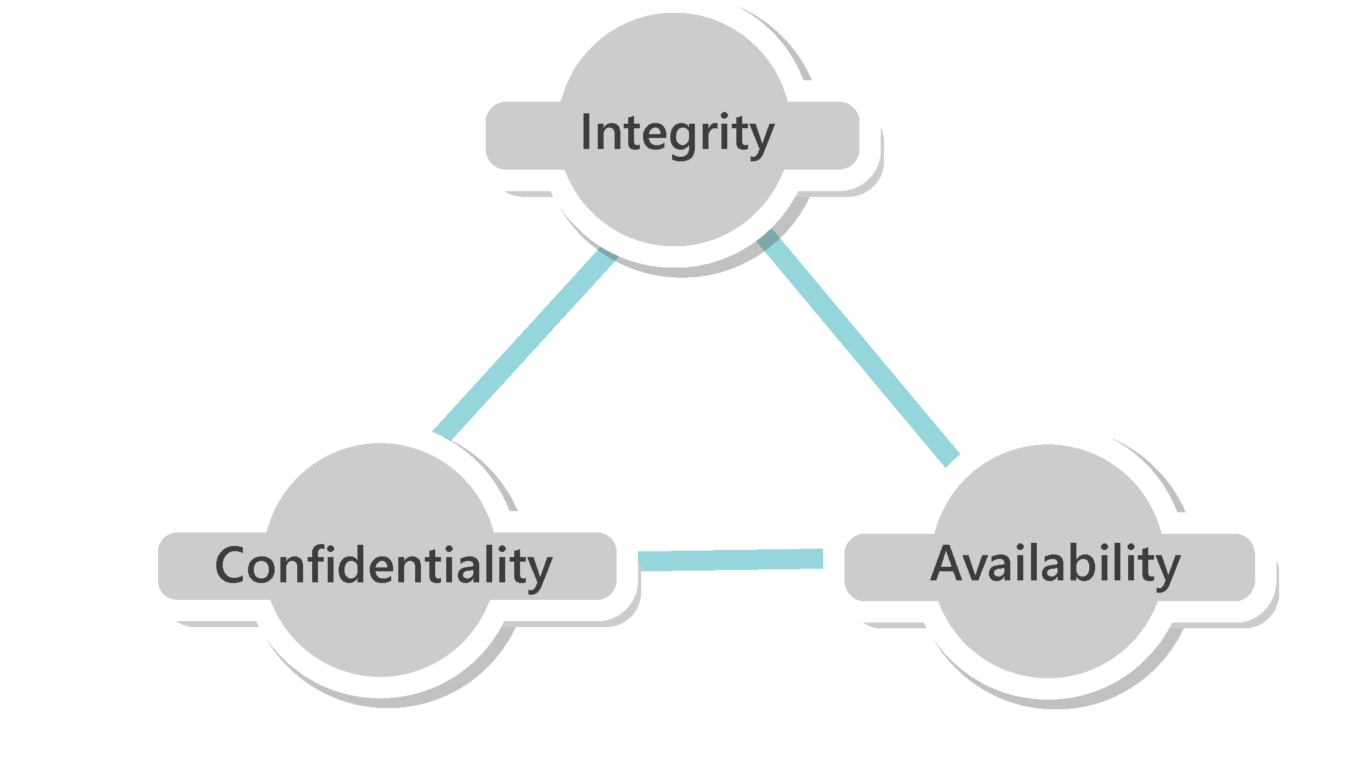
Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability (CIA)
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Confidentiality
Confidentiality refers to protecting information from being accessed by unauthorized parties. In other words, only the people who are authorized to do so can gain access to sensitive data. Imagine your bank records. You should be able to access them, of course, and employees at the bank who are helping you with a transaction should be able to access them, but no one else should. A failure to maintain confidentiality means that someone who shouldn't have access has managed to get it, through intentional behavior or by accident. Such a failure of confidentiality, commonly known as a breach, typically cannot be remedied. Once the secret has been revealed, there's no way to un-reveal it. If your bank records are posted on a public website, everyone can know your bank account number, balance, etc., and that information can't be erased from their minds, papers, computers, and other places. Nearly all the major security incidents reported in the media today involve major losses of confidentiality.
So, in summary, confidentiality means something that is secret and is not supposed to Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessed only by an authorized person and kept away from those not authorized to possess them. Everyone has information which they wish to keep secret. Thus Protecting such information is an important part of information security.
Examples of confidential information:
- Bank account statements
- Personal information
- Credit card numbers
- Trade secrets
- Government documents
In the event that confidentiality is compromised, it might result in unauthorized access to personal information or even complete loss of privacy!
Examples of attacks that affect confidentiality:
- Packet sniffing
- Password cracking
- Dumpster diving
- Wiretapping
- Keylogging
- Phishing
Ways to ensure confidentiality:
- Usernames and passwords
- Two-factor authentication
- Biometric verification
- Security tokens or key fobs
- Data encryption
Integrity
Integrity refers to ensuring the authenticity of information—that information is not altered, and that the source of the information is genuine. Imagine that you have a website and you sell products on that site. Now imagine that an attacker can shop on your web site and maliciously alter the prices of your products, so that they can buy anything for whatever price they choose. That would be a failure of integrity, because your information—in this case, the price of a product—has been altered and you didn't authorize this alteration. Another example of a failure of integrity is when you try to connect to a website and a malicious attacker between you and the website redirects your traffic to a different website. In this case, the site you are directed to is not genuine.
In the context of the information security (InfoSec) world, integrity means that when a sender sends data, the receiver must receive exactly the same data as sent by the sender. Data must not be changed in transit. For example, if someone sends a message “Hello!”, then the receiver must receive “Hello!” That is, it must BE exactly the same data as sent by the sender. Any addition or subtraction of data during transit would mean the integrity has been compromised.
Example attacks that affect Integrity:
- Salami attack
- Data diddling attacks
- Session hijacking
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack
Availability
Availability implies that information is available to the authorized parties whenever required. Unavailability to data and systems can have serious consequences. It is essential to have plans and procedures in place to prevent or mitigate data loss as a result of a disaster. A disaster recovery plan must include unpredictable events such as natural disasters and fire.
A routine backup job is advised in order to prevent or minimize total data loss from such occurrences. Also, extra security equipment or software such as firewalls and proxy servers can guard against downtime and unreachable data due to malicious actions such as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and network intrusions.
Example attacks that affect Availability:
- DoS and DDoS attacks
- SYN flood attacks
- Physical attacks on server infrastructure
Ref:
https://developer.mozilla.org
https://www.testingexcellence.com
All rights reserved