Android: Tìm hiểu về Android KeyStore
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
I. Android KeyStore là gì?
Theo như google định nghĩa thì :
Android KeyStore là một hệ thống cho phép bạn lưu trữ các khoá mã hoá trong một "thùng chứa" làm cho việc trích xuất khoá từ thiết bị trở lên khó khăn hơn. Khi các khoá nằm trong keyStore, chúng có thể được sử dụng cho các hoạt động mã hoá mà những gì dùng để mã hoá, giả mã là non-exportable.
Nếu đoạn dịch lủng củng của mình ở trên khiến bạn không hiểu gì cả thì đây là nguyên văn của google:
The Android Keystore system lets you store cryptographic keys in a container to make it more difficult to extract from the device. Once keys are in the keystore, they can be used for cryptographic operations with the key material remaining non-exportable.
Nói chung là bạn có thể dùng Android Keystore để mã hoá những dữ liệu nhạy cảm như password, token, ... .Một ứng dụng chỉ có thể chỉnh sửa, lưu trữ và lấy lại các khoá của nó. Để sử dụng Android Keystore đầu tiên bạn cần tạo một cặp khoá private/public. Public key được dùng để mã hoá các dữ liệu, private key được dùng để giả mã dữ liệu đó khi cần.
Ông bà ta hay nói học nên đi đôi với hành. Do đó mình xin trình bày cách dùng Android KeyStore theo ứng dụng dưới đây. Ứng dụng đơn giản chỉ là mã hoá và giải mã đoạn text được nhập vào.
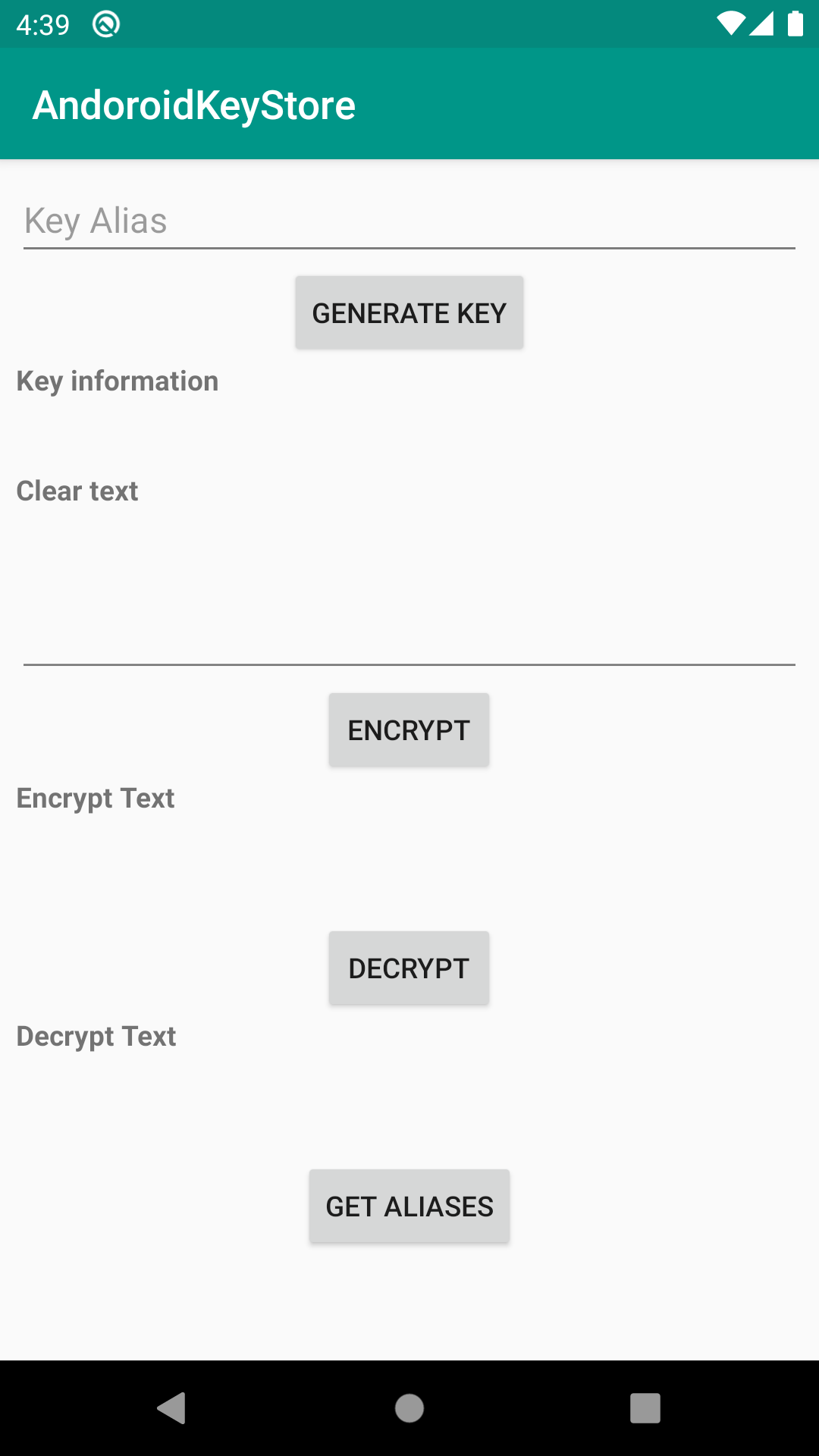
II. Tạo đối tượng keyStore
Đầu tiên ta cần khai báo một đối tượng KeyStore:
private fun initKeyStore() {
try {
keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("AndroidKeyStore")
keyStore.load(null)
} catch (e: Exception) {
Log.d(TAG, e.message.toString());
}
}
- KeyStore.getInstance("AndroidKeyStore") trả về một keystore có keystore type là "AndroidKeyStore". Bạn có thể tìm hiểu về các loại keystore khác ở đây.
- Trước khi keystore có thế được truy cập, nó cần phải được load. load(null) là để tạo một keystore trống.
III. Tạo khoá
Bước tiếp theo là tạo khoá.
private fun createKey(alias: String) {
try {
if (!keyStore.containsAlias(alias)) {
val keyPairGenerator =
KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(KeyProperties.KEY_ALGORITHM_RSA, "AndroidKeyStore")
val parameterSpec = KeyGenParameterSpec.Builder(
alias,
KeyProperties.PURPOSE_ENCRYPT or KeyProperties.PURPOSE_DECRYPT
)
.setEncryptionPaddings(KeyProperties.ENCRYPTION_PADDING_RSA_PKCS1)
.setDigests(KeyProperties.DIGEST_SHA1)
.build()
keyPairGenerator.initialize(parameterSpec)
keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair()
} else Toast.makeText(this, "Alias exist!!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} catch (e: Exception) {
Log.d(TAG, e.message.toString())
}
}
Mỗi khoá trong keystore được định danh bằng một chuỗi "alisa", do đó alias phải là duy nhất.
Đoạn code trên tiên hành tạo một cặp khoá: public và private với mục đích để mã hoá và giải mã. Thuật toán dùng cho quá trình tạo khoá là RSA.
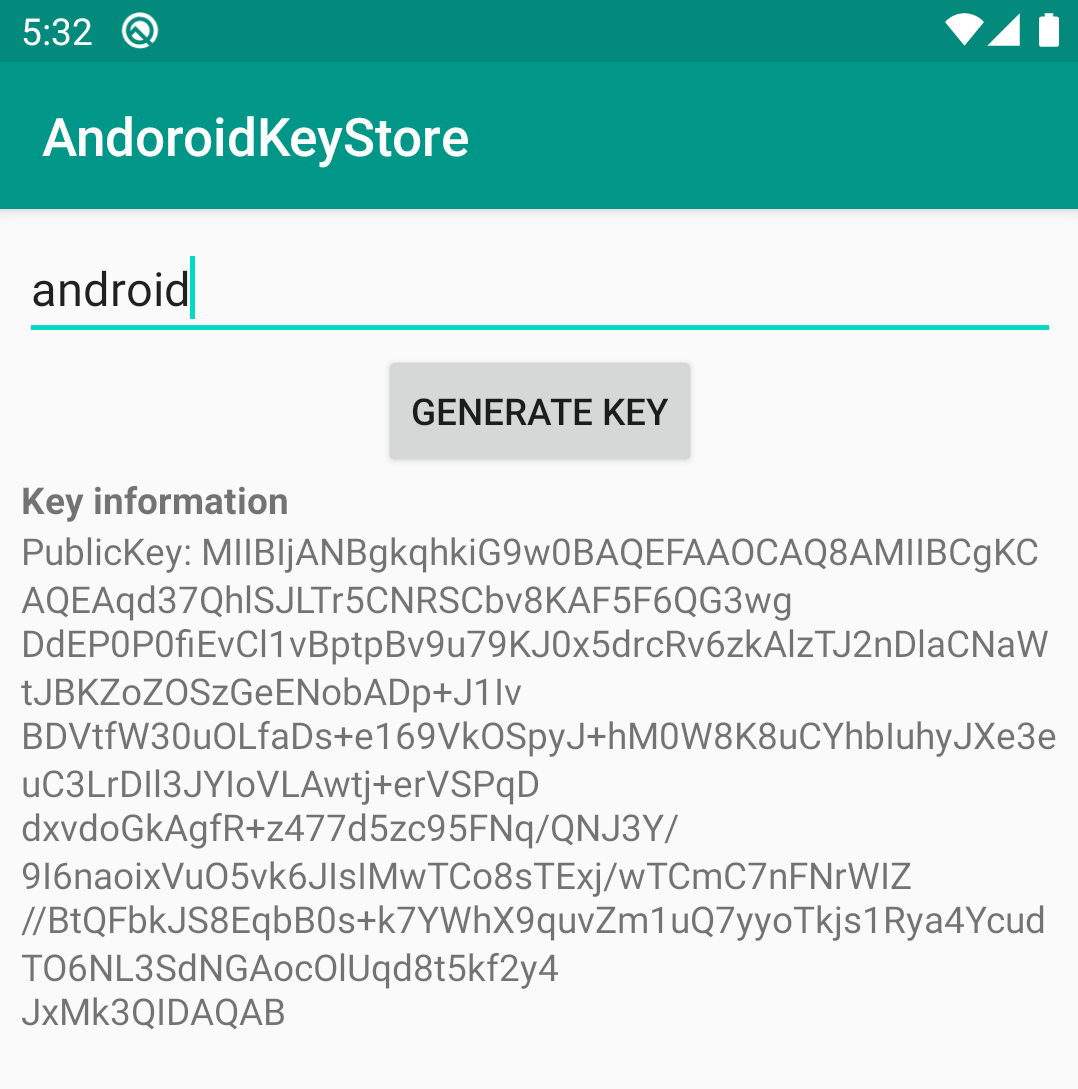
Cặp đã khoá được tạo và lưu vào KeyStore. Để lấy khoá từ trong keystore bạn làm như sau:
private fun getKeyInfo(alias: String) {
val privateKey: PrivateKey =
(keyStore.getEntry(alias, null) as KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry).privateKey
val cert = keyStore.getCertificate(alias)
val publicKey = cert.publicKey
val publicKeyBytes: ByteArray = Base64.encode(publicKey.encoded, Base64.DEFAULT)
val pubKeyString = String(publicKeyBytes)
Log.d(TAG, "------------>${pubKeyString} --- $")
// val privateKeyBytes: ByteArray = Base64.encode(privateKey.encoded, Base64.DEFAULT)
// val priKeyString = String(privateKeyBytes)
// Log.d(TAG, "------------>${priKeyString}")
}
Do cơ chế bảo mật của Android key Store bạn chỉ có thể hiển thị public key. Với private key khi gọi privateKey.encoded sẽ trả về null.
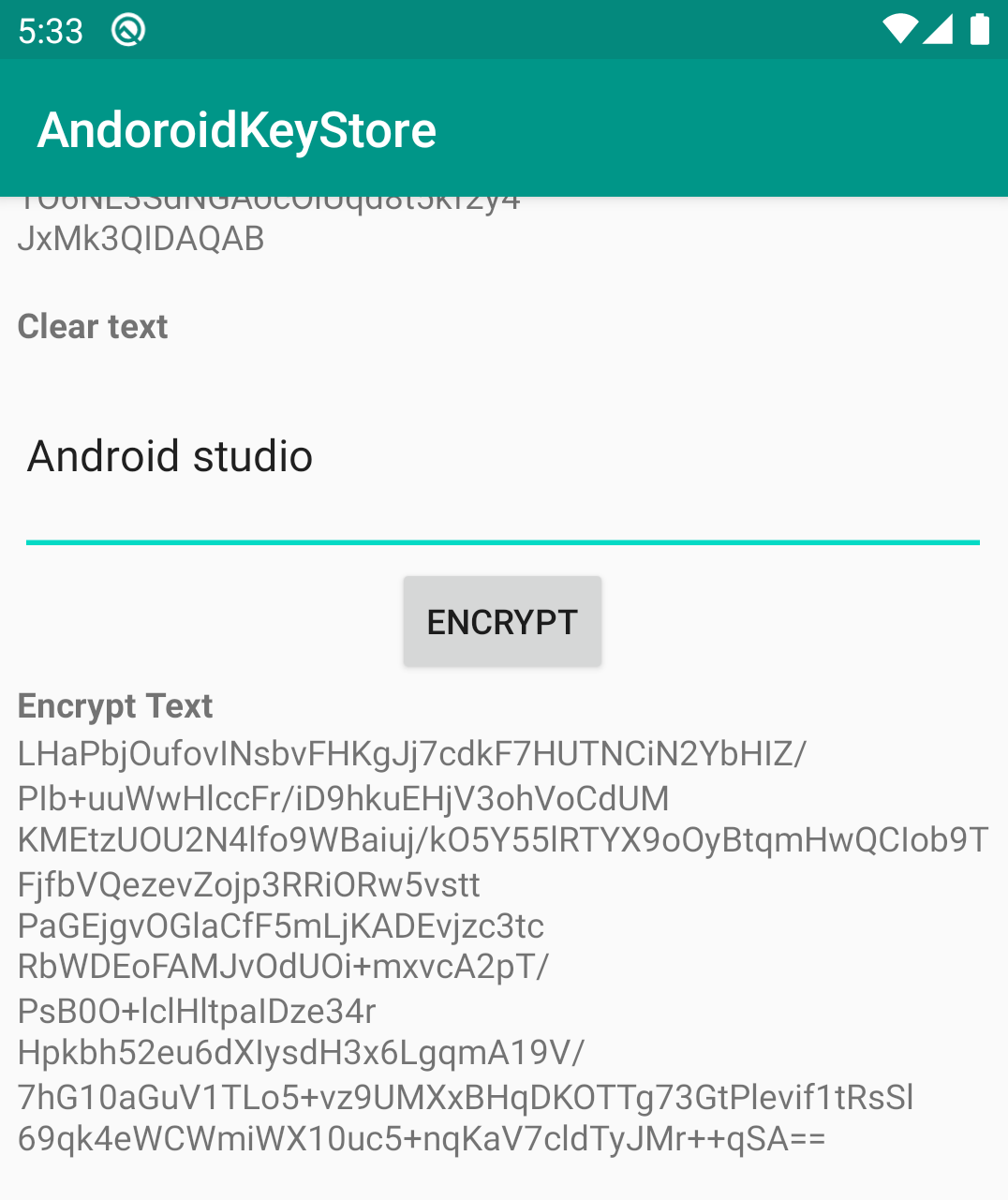
IV. Mã hoã
Tiếp theo ta sẽ tiến hành mã hoá một đoạn text với public key đã được tạo ở trên.
private fun encryptString(clearText: String, alias: String) {
val publicKey = keyStore.getCertificate(alias).publicKey
val cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding")
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey)
val cipherText = cipher.doFinal(clearText.toByteArray(Charsets.UTF_8))
textEncrypt.text = Base64.encodeToString(cipherText, Base64.DEFAULT)
}
- Cipher là một class hỗ trợ việc mã hoá và giả mã. Để tạo một đối tượng Cipher ta gọi Cipher.getInstance(), phương thức này yêu cầu truyền vào một transformation. Tranfomation là một chuỗi mô tả hoạt động (hoặc tập hợp các hoạt động) sẽ được thực hiện trên input đã cho, để tạo ra output. Một transformation có dạng "algorithm" hoặc "algorithm/mode/padding". Xem thêm
- cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey): cipher này sẽ dùng "publicKey" để mã hoá dữ liệu.
- Ta cần chuyển String sang dạng bytes trước khi thực hiện mã hoá.
- Encode về string để hiển thị đoạn text đã được mã hoá.
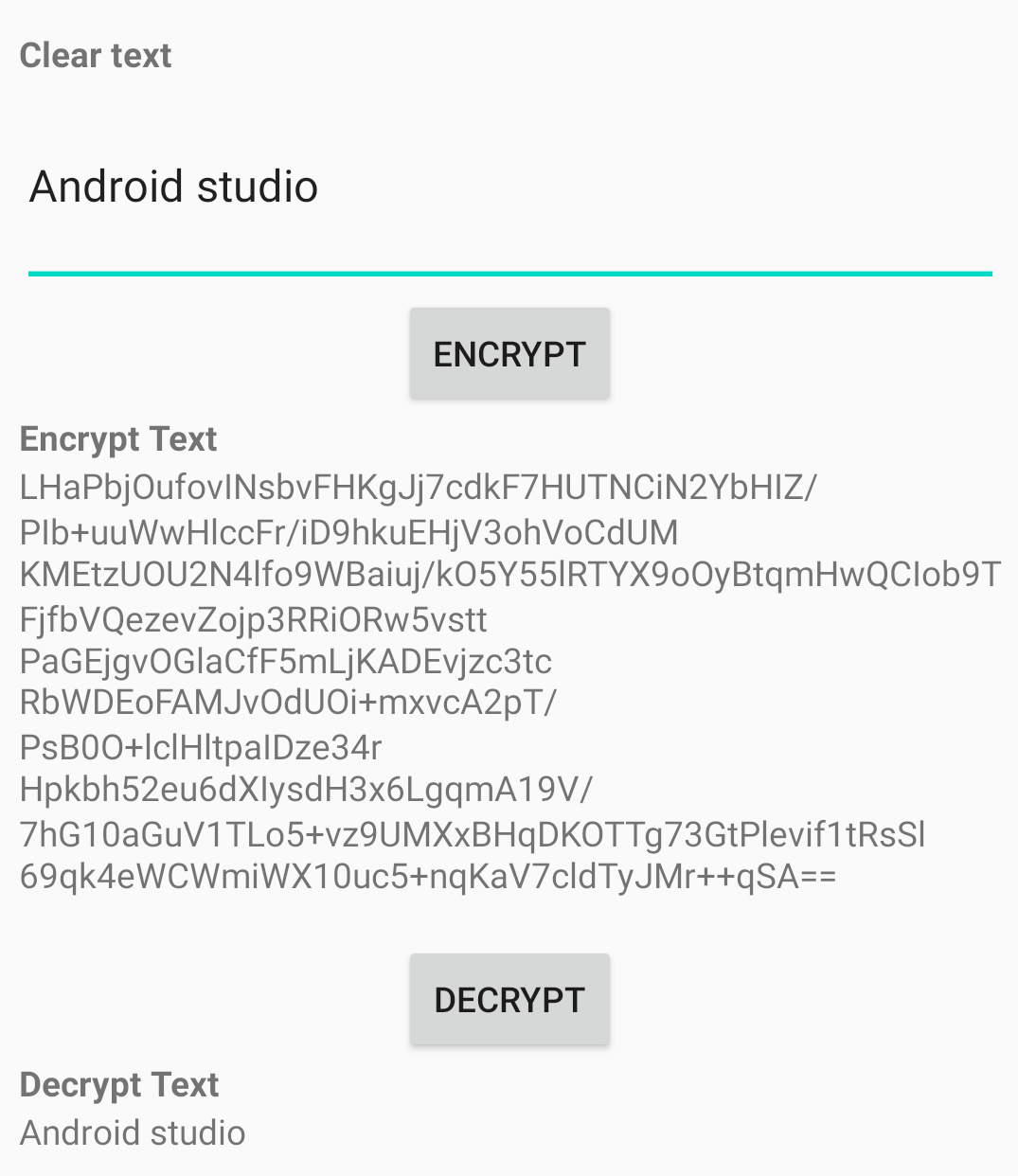
V. Giải mã
Giải đoạn text thu được ở trên với private key:
private fun decryptString(cipherText: String, alias: String) {
val privateKeyEntry = keyStore.getEntry(alias, null) as KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry
val privateKey = privateKeyEntry.privateKey
val cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding")
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey)
val decryptText = cipher.doFinal(Base64.decode(cipherText, Base64.DEFAULT))
textDecrypt.text = String(decryptText)
}
- Tranfomation khi giả mã cần giống mã hoá, ở đây là "RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding"
- cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey): cipher sẽ dùng "privateKey" để giải mã dữ liệu.
VI. Một số function khác của keystore
- Lấy tất cả các alias mà ứng dụng đã lưu:
private fun getAliases() {
var aliasesString = ""
val aliases = keyStore.aliases()
while (aliases.hasMoreElements()) {
aliasesString += "${aliases.nextElement()}, "
}
textAliases.text = aliasesString
}
- Xoá key:
private fun deleteKey(alias: String) {
keyStore.deleteEntry(alias)
}
Bạn có thể xem qua Source code của bài viết ở đây.
Bài viết được tham khảo trên medium và google doc.
All rights reserved