Android Date - Time - Tabs
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Tài liệu này được dịch và làm lại trên slide dạy Android của Đại học Cleveland.
DATE/TIME SELECTION WIDGETS
DATE
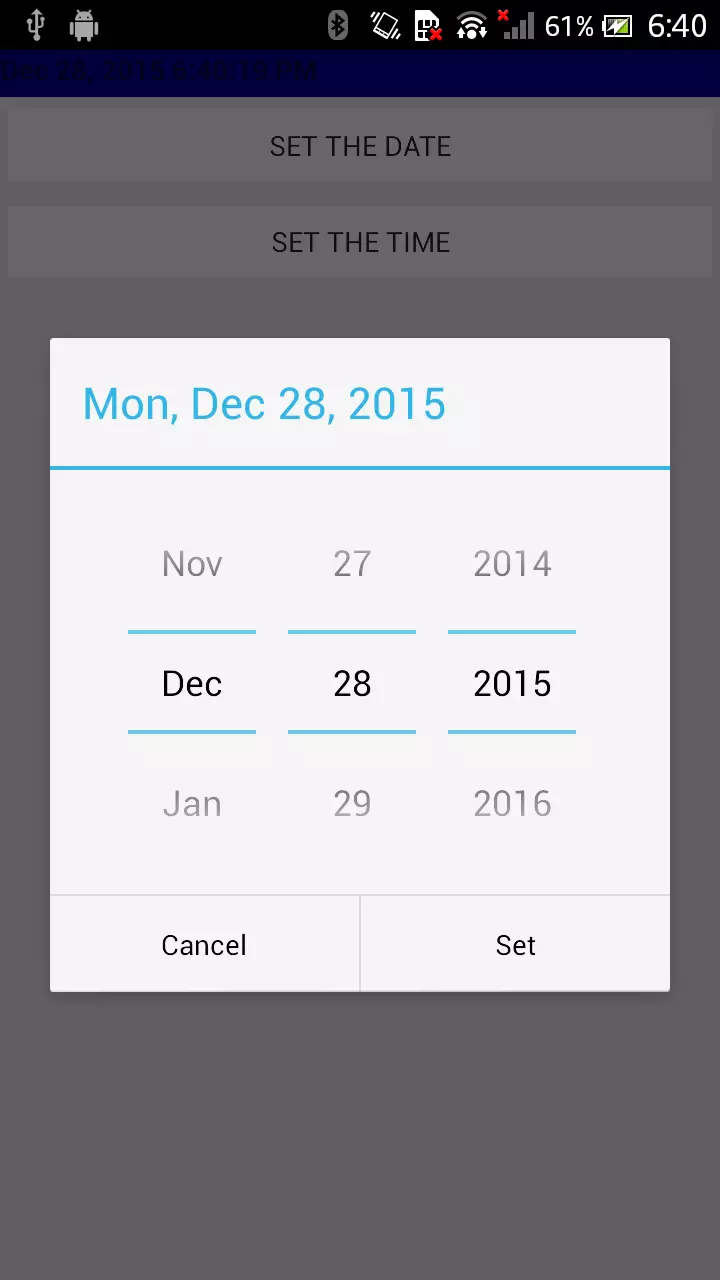
Android hỗ trợ những widget (DatePicker, TimePicker) và những dialog (DatePickerDialog, TimePickerDialog) để hỗ trợ user nhập vào ngày, tháng, năm, thời gian.
DatePicker và DatePickerDialog cho phép bạn đặt 1 ngày thắng năm defaut bắt đầu trước khi user select giá trị.
Giá trị của month sẽ từ 0 là tháng một đến 11 là tháng 12.
Mỗi wigdet sẽ có 1 callback object (OnDateChangedListenter hoặc là OnDateSetListener) để lắng nghe việc user thao tác thay đổi giá trị ngày, tháng năm.
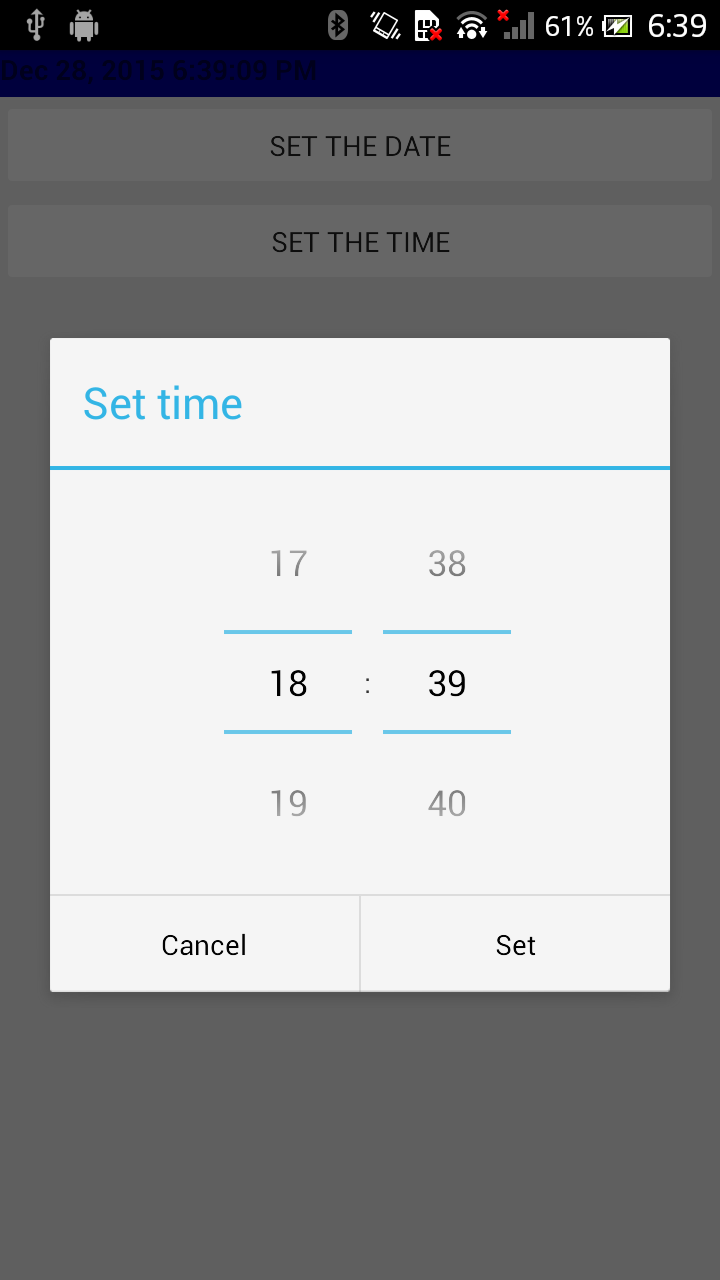
TIME SELECTION
TimePicker và TimePickerDialog sẽ có những thuộc tính như sau :
- cũng cấp các giá trị
hour(từ 0 đến 23),minute(0 đến 59) - selection có thể thuộc
12-hour modehoặc24-hour mode - callback (
OnTimeChangedListenerhoặcOnTimeSetListener)
EXAMPLE
Ở đây sẽ là 1 layout ví dụ cho việc tạo ra 2 button cho phép user có thể setting Date cũng như Time.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/widget28"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/lblDateAndTime"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="47px"
android:background="#ff000099"
android:textStyle="bold"
>
</TextView>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnDate"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Set the Date"
>
</Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnTime"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Set the Time"
>
</Button>
</LinearLayout>

Và đây là đoạn code xử lý trong MainActivity.
package com.example.duongichi.helloworld2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.app.DatePickerDialog;
import android.app.TimePickerDialog;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.DatePicker;
import android.widget.TimePicker;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
DateFormat fmtDateAndTime = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance();
TextView lblDateAndTime;
Calendar myCalendar = Calendar.getInstance();
DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener d = new DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener()
{
public void onDateSet(DatePicker view,
int year, int monthOfYear, int dayOfMonth) {
myCalendar.set(Calendar.YEAR, year);
myCalendar.set(Calendar.MONTH, monthOfYear);
myCalendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, dayOfMonth);
updateLabel();
}
};
TimePickerDialog.OnTimeSetListener t = new TimePickerDialog.OnTimeSetListener()
{
public void onTimeSet(TimePicker view, int hourOfDay, int minute) {
myCalendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, hourOfDay);
myCalendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE, minute);
updateLabel();
}
};
private void updateLabel() {
lblDateAndTime.setText(fmtDateAndTime.format(myCalendar.getTime()));
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
super.onCreate(icicle);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
lblDateAndTime = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.lblDateAndTime);
Button btnDate = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnDate);
btnDate.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
new DatePickerDialog(MainActivity.this, d,
myCalendar.get(Calendar.YEAR),
myCalendar.get(Calendar.MONTH),
myCalendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)).show();
}
});
Button btnTime = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnTime);
btnTime.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
new TimePickerDialog(MainActivity.this, t,
myCalendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY),
myCalendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE), true).show();
}
});
updateLabel();
}
}
Những WIDGET TIME khác##
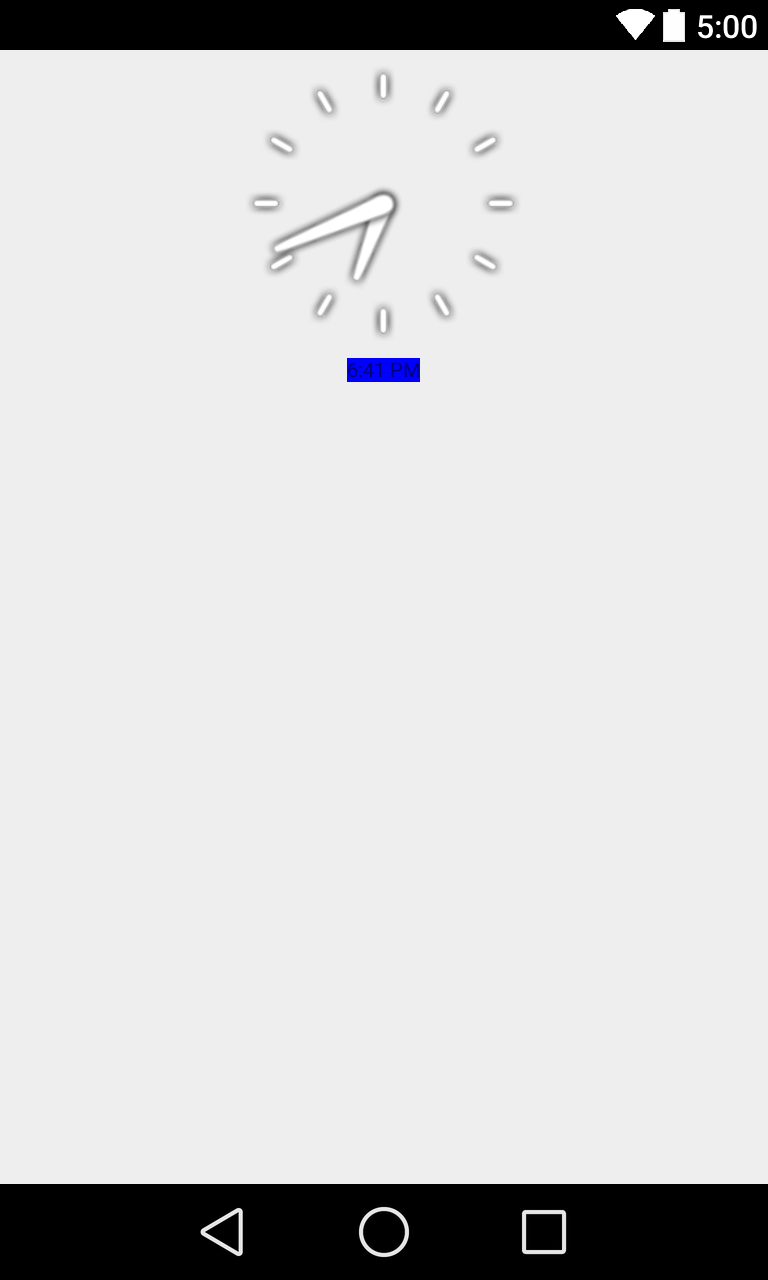
Android cũng cung cấp cho bạn DigitalClock và AnalogClock.
Những clock này sẽ tự động cập nhật time ( tất nhiên là với điều kiện user ko có can thiệp vào)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/widget34"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
>
<DigitalClock
android:id="@+id/digital"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000ff"
android:textSize="20px"
android:layout_below="@+id/analog"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
>
</DigitalClock>
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/analog"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
>
</AnalogClock>
</RelativeLayout>
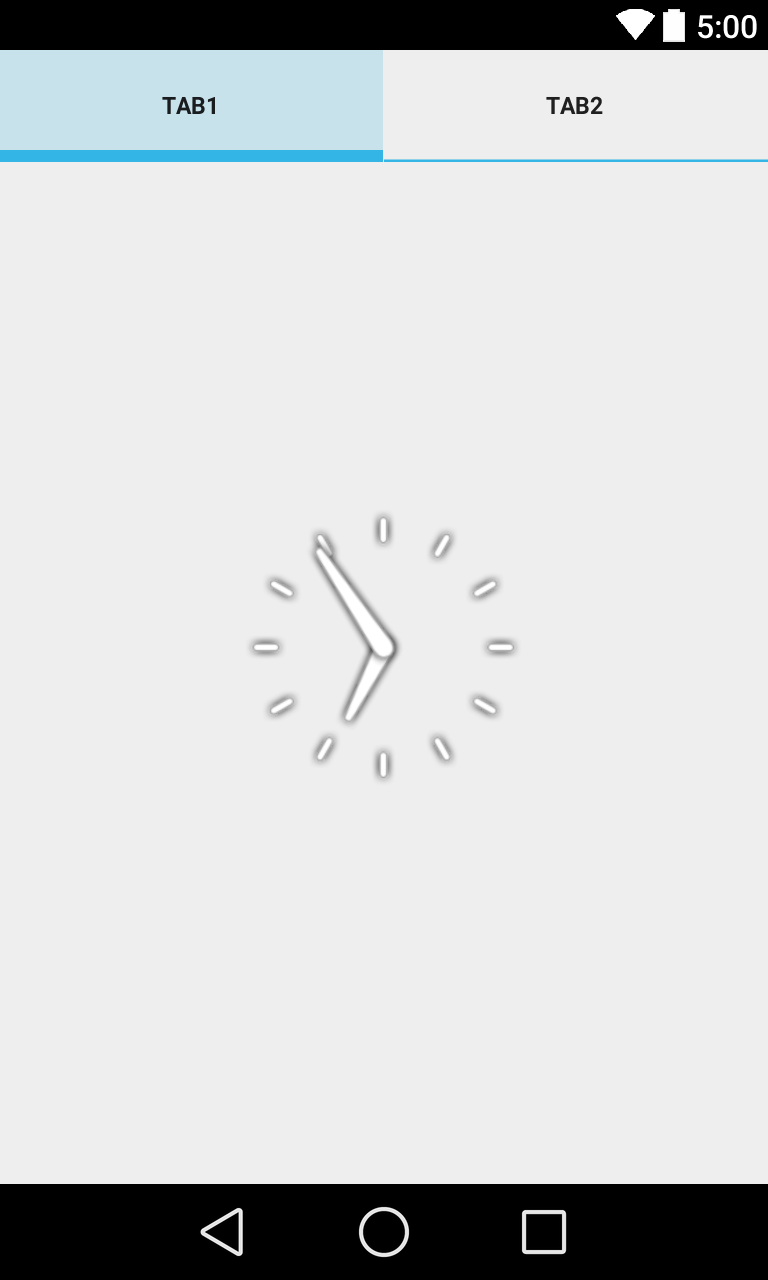
TAB SELECTION WIDGET
Tab SELECTOR
-
Android UIs nên được thiết kế thật đơn giản
-
Khi có quá nhiều thông tin được hiển thị trên 1 app,
Tab Widgetsẽ có thể giúp cho user có thể nhận biết được các phần của thông tin, ngoài ra người thiết kế cũng ko cần thiết phải show hết thông tin ra trên 1 màn hình vào 1 thời điểm.
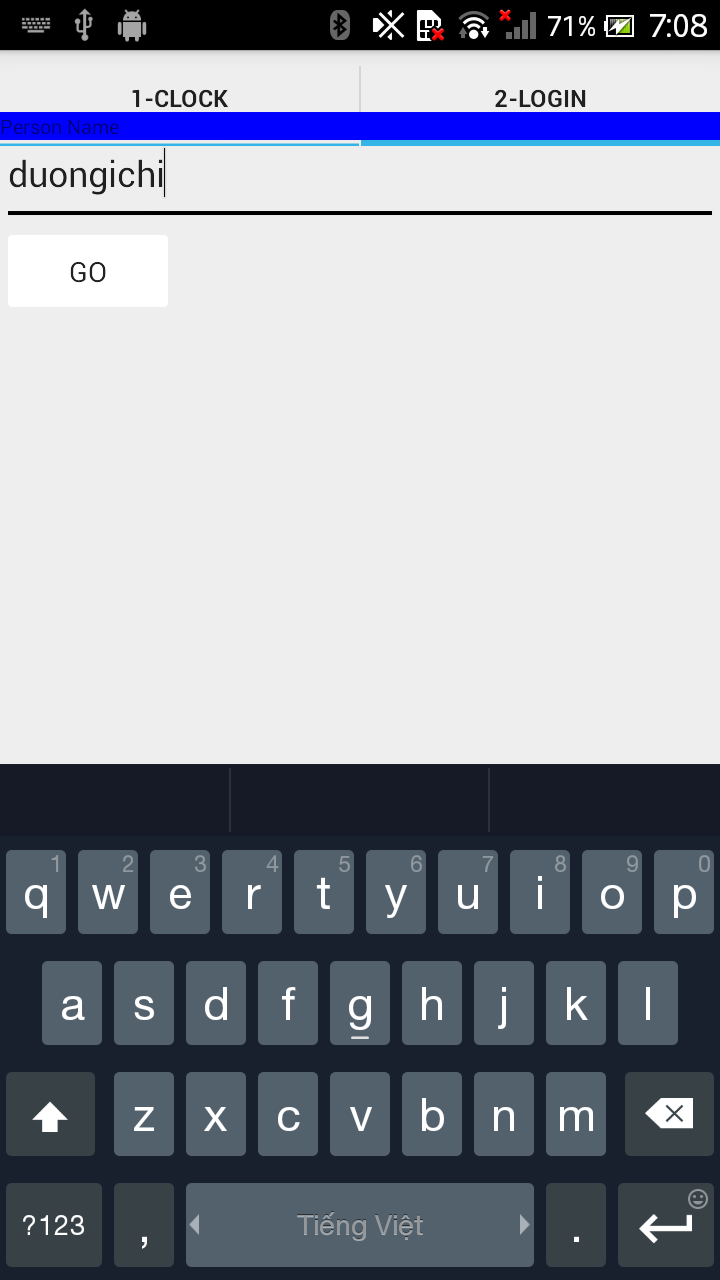
Tabs - Components
Có 1 vài widget và container bạn cần phải sử dụng để tạo thành một view được chia thành nhiều tab con.
-
TabHostlà main container cho các tab nút bấm và tab nội dung -
TabWidgetsẽ thực thi các hàng của tab nút bấm, trong này sẽ chưa các text label và icon. -
FrameLayoutlà container cho các tab nội dung.
Component
Bố trí sẽ là TabHost bao gồm TabWidget và FramgeLayout
Example
Phần PUT HERE FrameLayout1 và PUT HERE FrameLayout2, bạn có thể cho vào những layout cụ thể hoặc có thể sử dụng <include> để refer đến một layout nào đó ngoài và tích hợp nó vào trong xml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TabHost android:id="@+id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TabWidget android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingTop="62px">
<!-- PUT HERE FrameLayout1 -->
<!-- PUT HERE FrameLayout2 -->
</FrameLayout>
</TabHost>
</LinearLayout>
Ở đây mình sẽ thêm vào phần FrameLayout1 là một analog đồng hồ. Và FrameLayout2 sẽ là một label, button và textBox.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TabHost android:id="@+id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TabWidget android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingTop="62px">
<!-- PUT HERE FrameLayout1 -->
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/tab1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
/>
<!-- PUT HERE FrameLayout2 -->
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/caption1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000ff"
android:text="Person Name"
android:textSize="20px"
>
</TextView>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txtPerson"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="txtPerson"
android:textSize="18sp"
>
</EditText>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnGo"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Go"
>
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
</TabHost>
</LinearLayout>

package com.example.duongichi.helloworld2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
super.onCreate(icicle);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TabHost tabs=(TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabhost);
tabs.setup();
TabHost.TabSpec spec;
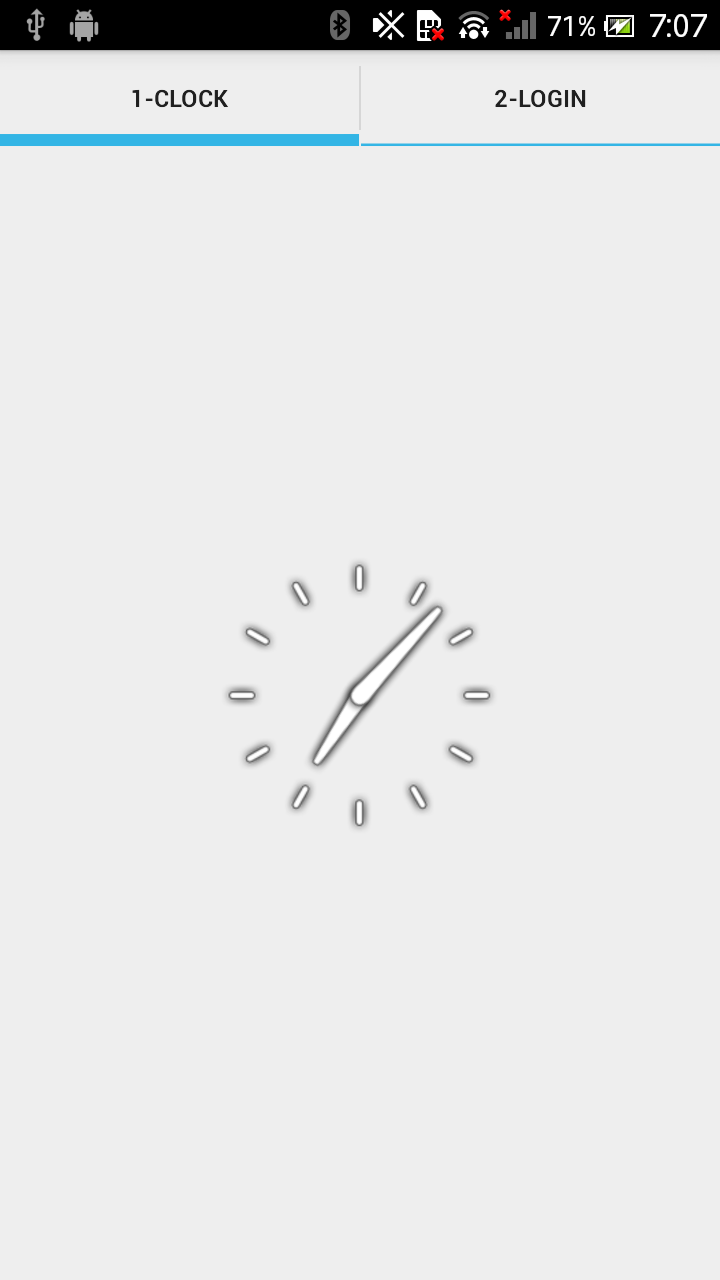
spec =tabs.newTabSpec("tag1");
spec.setContent(R.id.tab1);
spec.setIndicator("1-Clock");
tabs.addTab(spec);
spec=tabs.newTabSpec("tag2");
spec.setContent(R.id.tab2);
spec.setIndicator("2-Login");
tabs.addTab(spec);
tabs.setCurrentTab(0);
Button btnGo = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnGo);
btnGo.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
EditText txtPerson =
(EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtPerson);
String theUser = txtPerson.getText().toString();
txtPerson.setText("Hola " + theUser);
}
});
}
}

Nếu bạn muốn cho hình ảnh icon vào các tab, bạn có thể làm như sau.
spec = tabs.newTabSpec("tag2");
spec.setContent(R.id.tab2);
spec.setIndicator("2-Login",
getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_menu_info_details));
tabs.addTab(spec);
Monitoring
Trong trưởng hợp bạn muốn add thêm 1 listener cho phép bạn có thể xác định được hiện bạn đang ở tab nào. Hãy thêm fragment này vào trong onCreate.
// tabs.setCurrentTab(0);
// you may also use
tabs.setCurrentTabByTag("tag1");
tabs.setOnTabChangedListener(new OnTabChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onTabChanged(String tagId) {
// do something useful with the selected screen
String text = "Im currently in: " + tagId + "\nindex: " + tabs.getCurrentTab();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), text, 1).show();
}
});
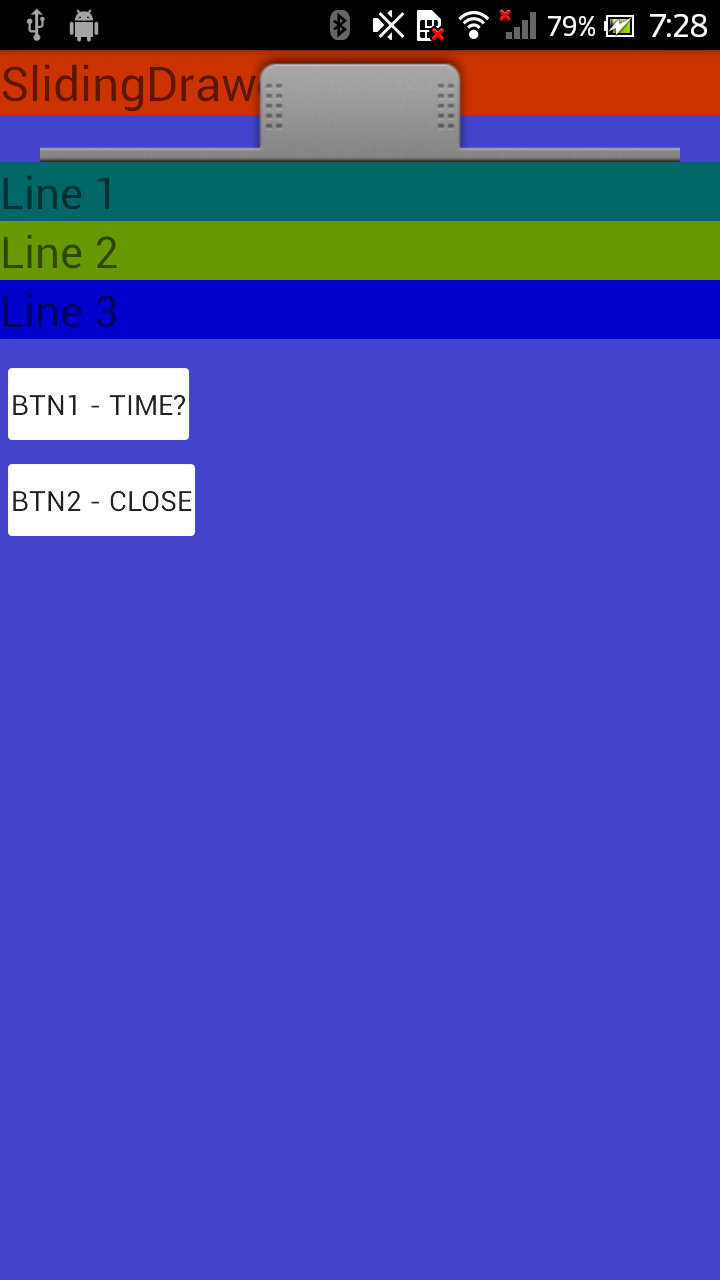
SlidingDrawerWidget
SlidingDrawer
SlidingDrawer sẽ ẩn nội dung khỏi màn hình và cho phép user có thể kéo một handle để tạo nên một màn hình chứa nội dung.
- SlidingDrawercan có thể sử dụng ngang hoặc dọc
- SlidingDrawer sử dụng như một layout overlayinside. Điều này nghĩa là SlidingDrawershould chỉ được sử dụng bên trong một FrameLayout hoặc là RelativeLayout.
- Kích thước của SlidingDrawerdefines sẽ phụ thuộc vào việc nội dung SlidingDrawer cung cấp cho người dùng chiếm ko gian như thế nào cho nên RelativeLayout nên sử dụng
fill_parentcho cả 2 chiều của nó.
Một vài ví dụ về SlidingDrawer là như Launcher cho phép người dùng có thể truy cập vào danh sách các ứng dụng yêu thích được cài đặt trong máy.
Trong XML layout, SlidingDrawer phải định nghĩa id của handle và content :
handlelà một graphic nhỏ để hiển thị một indicate cho phép điều khiển mở đóng nội dungcontentthì sẽ được chứa trong một vài kiều container
Example
Đây là một ví dụ về một SlidingDrawer khá đẹp mình khá ưng ý.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#FF4444CC"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/label0"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffcc3300"
android:text="SlidingDrawer Demo"
android:textSize="24sp" />
<SlidingDrawer
android:id="@+id/drawer"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:handle="@+id/handle"
android:content="@+id/content" >
<ImageView
android:id="@id/handle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/tray_handle_normal"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@id/content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/label1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff006666"
android:text="Line 1"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/label2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff669900"
android:text="Line 2"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/label3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000cc"
android:text="Line 3"
android:textSize="22sp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/filler1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="6sp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="4px"
android:text=" btn1 - time? "
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="4px"
android:text=" btn2 - close "
/>
</LinearLayout>
</SlidingDrawer>
</RelativeLayout>
package com.example.duongichi.helloworld2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btn1;
Button btn2;
TextView label1;
TextView label2;
TextView label3;
SlidingDrawer myDrawer;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myDrawer = (SlidingDrawer)findViewById(R.id.drawer);
btn1 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn2);
label1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.label1);
label2 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.label2);
label3 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.label3);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Date dt = new Date();
String now = dt.toLocaleString();
label1.setText("111 - Hola amigos " + now);
label2.setText("222 - Hola amigos " + now) ;
label3.setText("333 - Hola amigos " + now);
}
});
btn2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
myDrawer.animateClose();
}
});
} //onCreate
} // class

All rights reserved