Xây dựng Pipeline Xử lý Tài liệu Thông minh với AWS: S3 → Textract → Comprehend → DynamoDB
Giới thiệu
Trong thế giới số ngày nay, các tổ chức đang chìm ngập trong dữ liệu phi cấu trúc. Tài liệu, hình ảnh và PDF chứa thông tin có giá trị thường không được khai thác do nỗ lực thủ công cần thiết để trích xuất và phân tích chúng. Điều gì sẽ xảy ra nếu chúng ta có thể tự động xử lý những tài liệu này, trích xuất những hiểu biết có ý nghĩa và lưu trữ dữ liệu có cấu trúc để phân tích thêm?
Bài viết blog này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn xây dựng một pipeline xử lý tài liệu thông minh hoàn chỉnh bằng cách sử dụng các dịch vụ AWS. Pipeline của chúng ta sẽ tự động:
- Trích xuất văn bản từ hình ảnh và PDF bằng Amazon Textract
- Phân tích nội dung để tìm thực thể, cụm từ khóa và cảm xúc bằng Amazon Comprehend
- Lưu trữ kết quả có cấu trúc trong DynamoDB để truy vấn và phân tích dễ dàng
- Xử lý tài liệu tự động khi được tải lên S3
Những gì chúng ta đang xây dựng
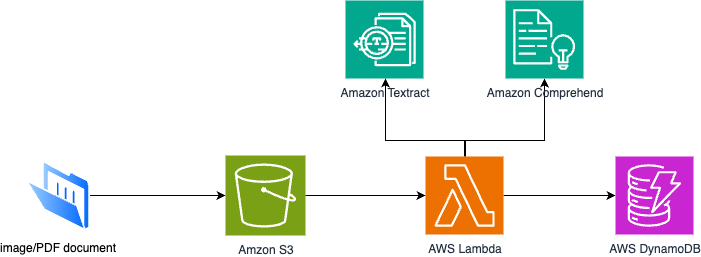
Pipeline của chúng ta tạo ra một luồng liền mạch trong đó:
- Tài liệu được tải lên vào bucket S3 (hình ảnh, PDF, v.v.)
- Hàm Lambda kích hoạt tự động khi có file mới
- Textract trích xuất văn bản và xác định bố cục tài liệu
- Comprehend phân tích văn bản đã trích xuất để tìm hiểu biết
- Kết quả được lưu trữ trong DynamoDB với metadata có cấu trúc
Tổng quan Kiến trúc
Yêu cầu Hệ thống
- Lambda Runtime: Python 3.10
- Memory: 1024 MB (khuyến nghị)
- Timeout: 120 giây
- Environment Variables:
DDB_TABLE: SmartDocResults (mặc định)LANG: en (mặc định)
Triển khai Từng bước
Bước 1: Tạo Bảng DynamoDB
- Điều hướng đến AWS Console → DynamoDB
- Nhấp "Create table"
- Cấu hình:
- Tên bảng:
SmartDocResults - Partition key:
doc_id(String) - Sort key:
paragraph_id(String)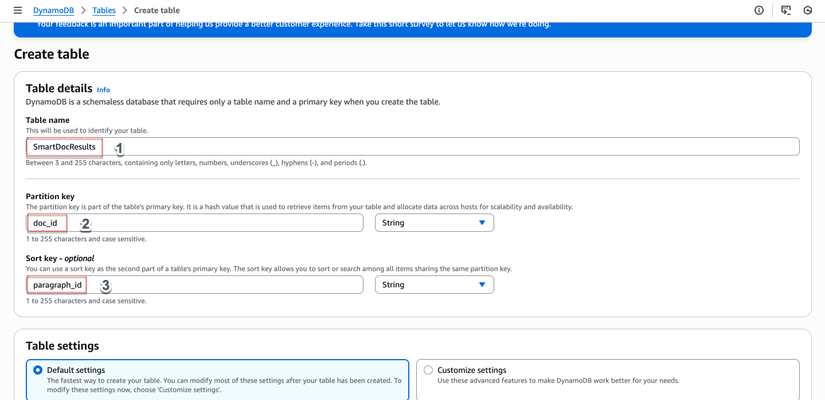
- Tên bảng:
- Nhấp "Create table"
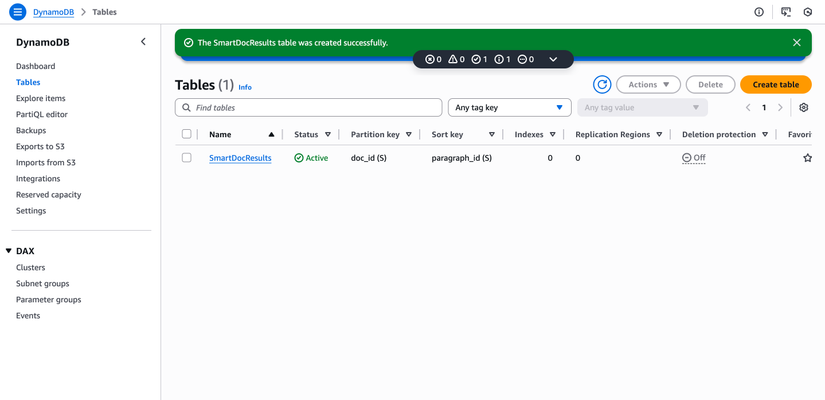
- Đợi trạng thái bảng = "Active"
Bước 2: Tạo Bucket S3
- AWS Console → S3
- Nhấp "Create bucket"
- Cấu hình:
- Tên bucket:
your-smart-doc-bucket(thay đổi thành tên duy nhất) - Region: Chọn region ưa thích của bạn
- Tên bucket:
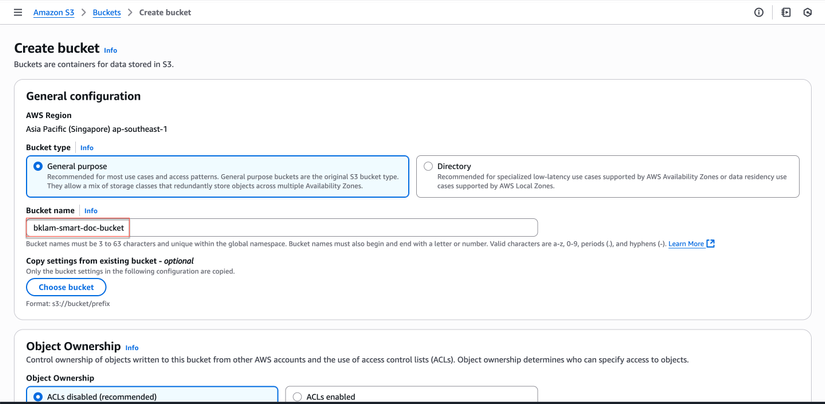
- Nhấp "Create bucket"
- Ghi nhớ tên bucket để sử dụng trong IAM policy
Bước 3: Tạo IAM Policy
- AWS Console → IAM → Policies
- Nhấp "Create policy"
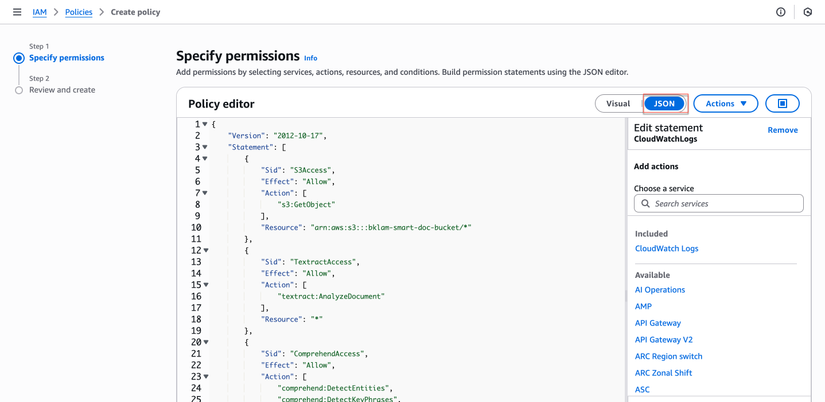
- Chuyển sang tab "JSON"
- Sao chép nội dung từ
iam_policy.jsonvà thay thế placeholders:ACCOUNT_ID: ID tài khoản AWS của bạnREGION: Region của bạn (ví dụ: us-east-1)BUCKET_NAME: Tên bucket S3 từ bước 2
- Nhấp "Next: Tags" → "Next: Review"
- Đặt tên policy:
SmartDocLambdaPolicy
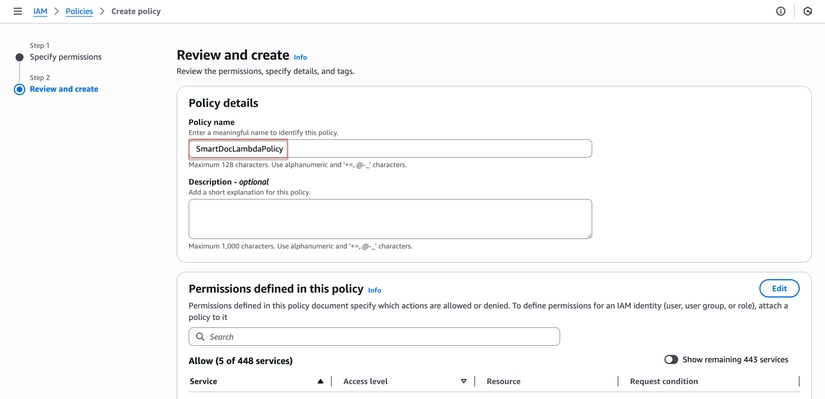
- Nhấp "Create policy"
Least-privilege IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "S3Access",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET_NAME/*"
},
{
"Sid": "TextractAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"textract:AnalyzeDocument"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "ComprehendAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"comprehend:DetectEntities",
"comprehend:DetectKeyPhrases",
"comprehend:DetectSentiment"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "DynamoDBAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:Query",
"dynamodb:Scan"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:REGION:ACCOUNT_ID:table/SmartDocResults"
},
{
"Sid": "CloudWatchLogs",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:REGION:ACCOUNT_ID:*"
}
]
}
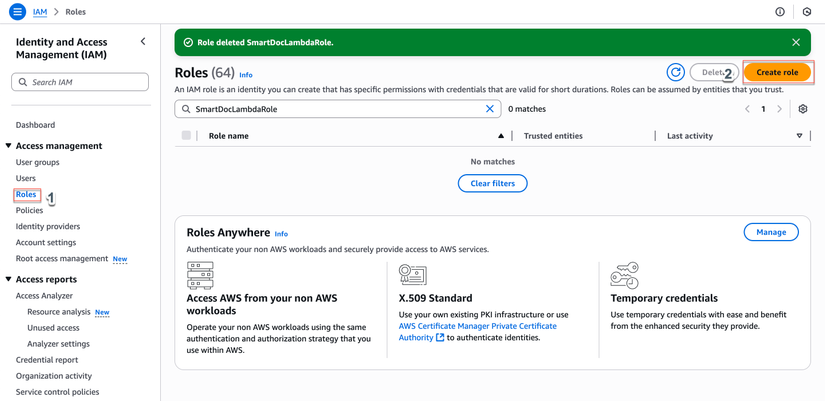
Bước 4: Tạo IAM Role cho Lambda
- AWS Console → IAM → Roles
- Nhấp "Create role"
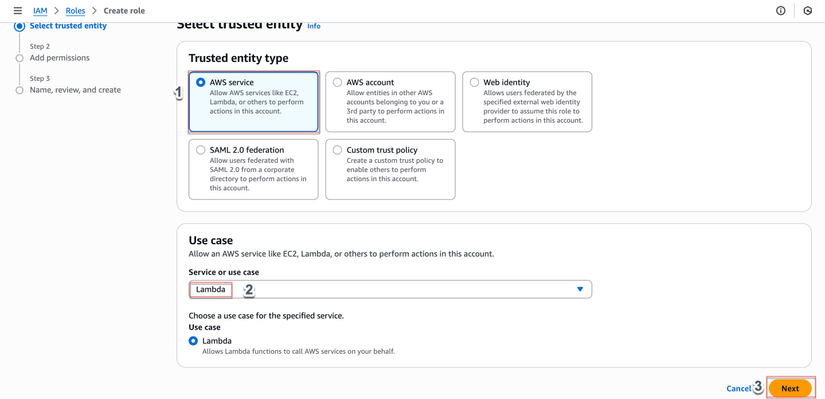
- Chọn "AWS service" → "Lambda"
- Nhấp "Next"
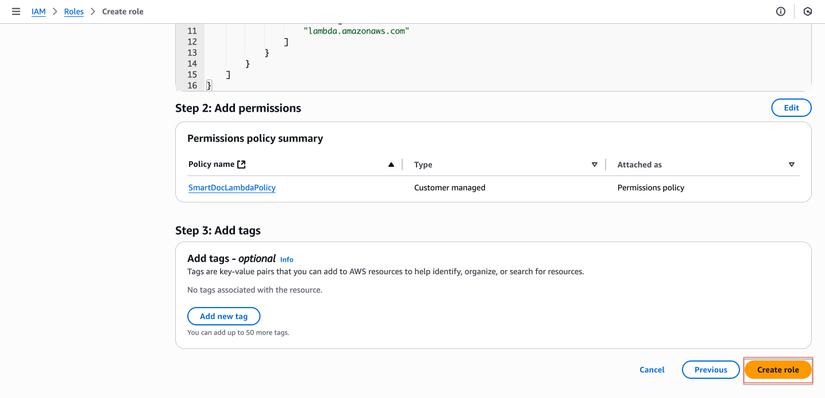
- Trong tab "Permissions":
- Tìm và chọn
SmartDocLambdaPolicyvừa tạo - Check vào policy
- Tìm và chọn
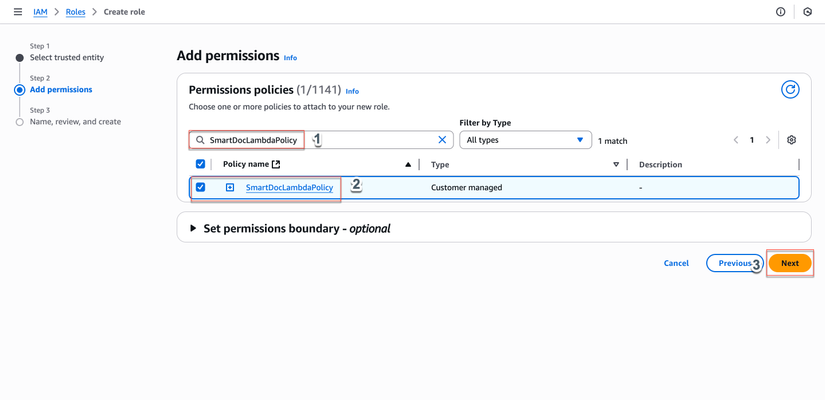
- Nhấp "Next: Tags" → "Next: Review"
- Đặt tên role:
SmartDocLambdaRole
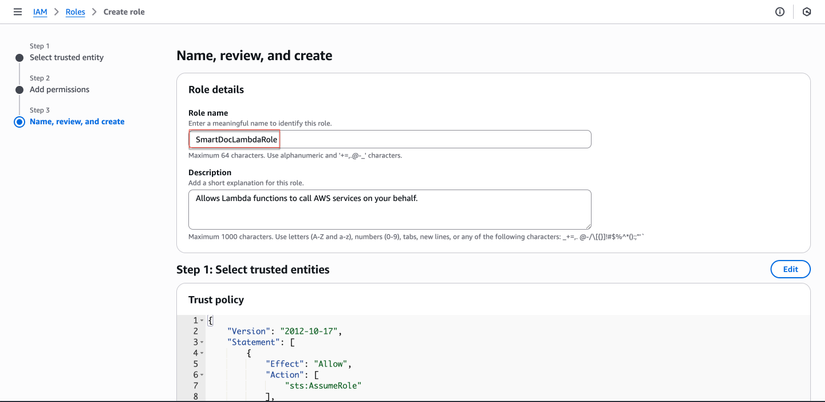
- Nhấp "Create role"
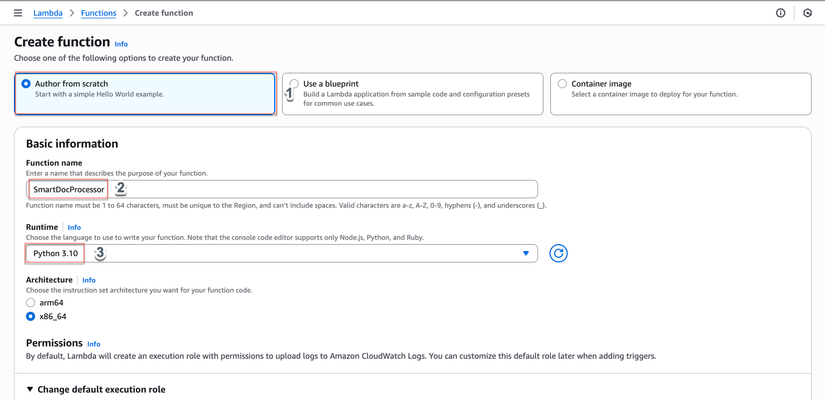
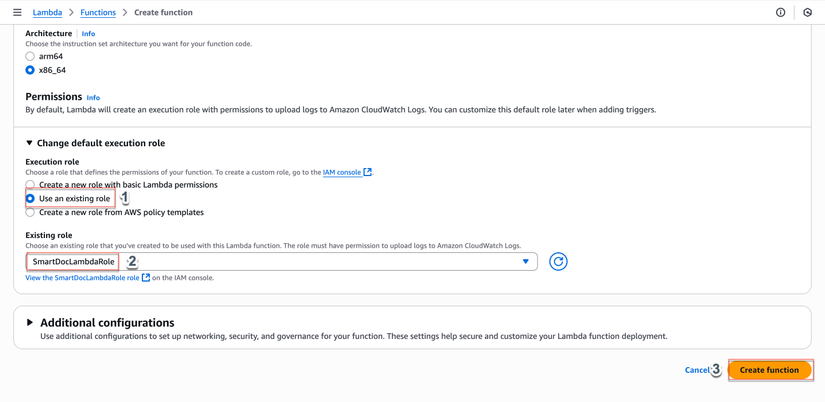
Bước 5: Tạo Hàm Lambda
- AWS Console → Lambda → Functions
- Nhấp "Create function"
- Chọn "Author from scratch"
- Cấu hình:
- Tên hàm:
SmartDocProcessor - Runtime: Python 3.10
- Architecture: x86_64
- Tên hàm:
- Change default execution role:: Chọn "Use an existing role" →
SmartDocLambdaRole
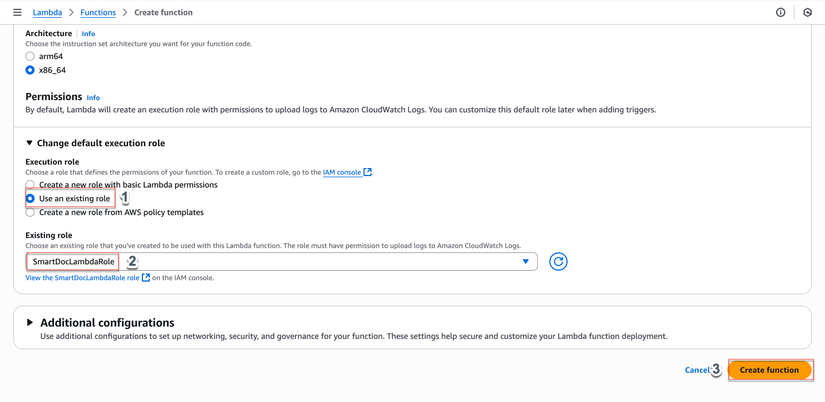
- Nhấp "Create function"
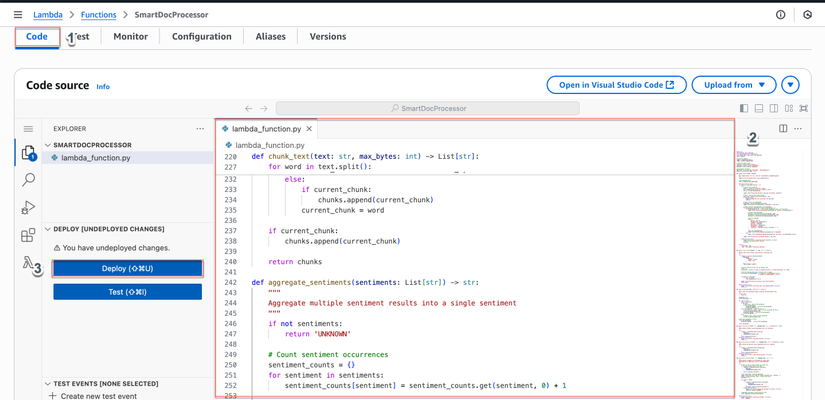
Bước 6: Cấu hình Hàm Lambda
- Trong hàm Lambda, cuộn xuống phần "Code source"
- Xóa code mặc định và dán nội dung từ
lambda_function.py - Nhấp "Deploy"
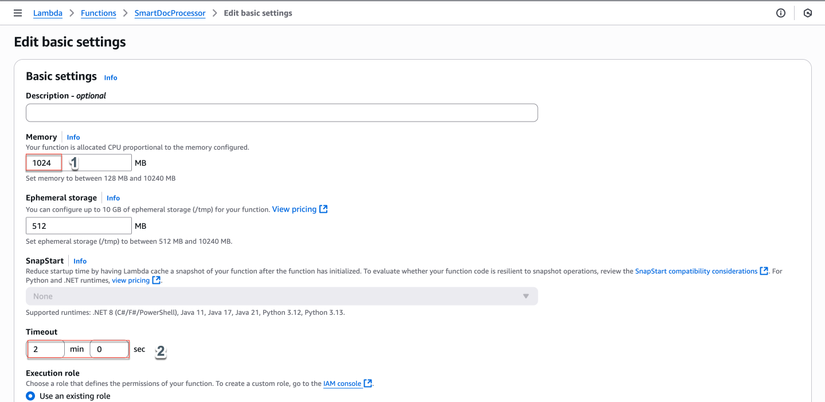
- Cấu hình "Configuration":
- General:
- Memory: 1024 MB
- Timeout: 2 phút
- General:
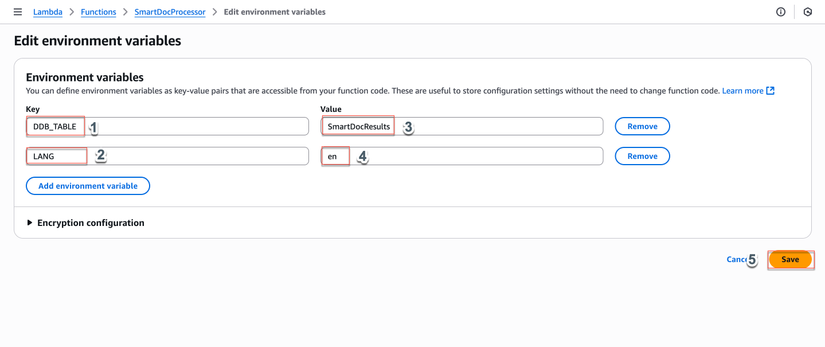
- Environment variables:
DDB_TABLE:SmartDocResultsLANG:en
import json
import boto3
import os
from datetime import datetime
from urllib.parse import unquote_plus
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
import logging
from decimal import Decimal
# Configure logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Initialize AWS clients
textract = boto3.client('textract')
comprehend = boto3.client('comprehend')
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
# Environment variables
DDB_TABLE = os.environ.get('DDB_TABLE', 'SmartDocResults')
LANG = os.environ.get('LANG', 'en')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
"""
Main Lambda handler for S3 → Textract → Comprehend → DynamoDB pipeline
"""
logger.info(f"Processing event: {json.dumps(event)}")
# Get DynamoDB table
table = dynamodb.Table(DDB_TABLE)
# Process each S3 record
for record in event.get('Records', []):
try:
# Extract S3 information
bucket = record['s3']['bucket']['name']
key = unquote_plus(record['s3']['object']['key'])
doc_id = os.path.basename(key)
logger.info(f"Processing document: {doc_id} from bucket: {bucket}")
# Step 1: Extract text using Textract
text_lines = extract_text_from_s3(bucket, key)
if not text_lines:
logger.warning(f"No text extracted from {doc_id}")
continue
# Step 2: Split into paragraphs
paragraphs = split_paragraphs(text_lines)
logger.info(f"Found {len(paragraphs)} paragraphs in {doc_id}")
# Step 3: Process each paragraph with Comprehend
for paragraph_id, paragraph in enumerate(paragraphs, 1):
if len(paragraph) >= 20: # Only process paragraphs with >= 20 characters
logger.info(f"Processing paragraph {paragraph_id} (length: {len(paragraph)})")
# Analyze with Comprehend
entities = detect_entities_safe(paragraph, LANG)
key_phrases = detect_key_phrases_safe(paragraph, LANG)
sentiment = safe_detect_sentiment(paragraph, LANG)
# Convert float values to Decimal for DynamoDB
entities = convert_floats_to_decimal(entities)
key_phrases = convert_floats_to_decimal(key_phrases)
# Save to DynamoDB
item = {
'doc_id': doc_id,
'paragraph_id': str(paragraph_id), # Convert to string
'content': paragraph,
'entities': entities,
'key_phrases': key_phrases,
'sentiment': sentiment,
'created_at': datetime.utcnow().isoformat() + 'Z'
}
table.put_item(Item=item)
logger.info(f"Saved paragraph {paragraph_id} to DynamoDB")
else:
logger.info(f"Skipping paragraph {paragraph_id} (too short: {len(paragraph)} chars)")
logger.info(f"Successfully processed document: {doc_id}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error processing record {record}: {str(e)}")
# Continue processing other records
continue
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Processing completed')
}
def extract_text_from_s3(bucket: str, key: str) -> List[str]:
"""
Extract text from S3 object using Textract synchronous API
"""
try:
response = textract.analyze_document(
Document={
'S3Object': {
'Bucket': bucket,
'Name': key
}
},
FeatureTypes=['LAYOUT']
)
# Extract LINE blocks and sort by reading order
lines = []
line_blocks = [block for block in response['Blocks'] if block['BlockType'] == 'LINE']
# Sort by reading order (top to bottom, left to right)
line_blocks.sort(key=lambda x: (x['Geometry']['BoundingBox']['Top'],
x['Geometry']['BoundingBox']['Left']))
for block in line_blocks:
if 'Text' in block:
lines.append(block['Text'])
logger.info(f"Extracted {len(lines)} lines from document")
return lines
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error extracting text from {bucket}/{key}: {str(e)}")
return []
def split_paragraphs(lines: List[str]) -> List[str]:
"""
Split lines into paragraphs based on spacing and punctuation rules
"""
if not lines:
return []
paragraphs = []
current_paragraph = []
for line in lines:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
# Empty line - end current paragraph
if current_paragraph:
paragraphs.append(' '.join(current_paragraph))
current_paragraph = []
elif line.endswith('.') and len(line) > 1:
# Line ends with period - add to current paragraph and end it
current_paragraph.append(line)
paragraphs.append(' '.join(current_paragraph))
current_paragraph = []
else:
# Regular line - add to current paragraph
current_paragraph.append(line)
# Add final paragraph if exists
if current_paragraph:
paragraphs.append(' '.join(current_paragraph))
return paragraphs
def detect_entities_safe(text: str, language_code: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Safely detect entities using Comprehend with error handling
"""
try:
response = comprehend.detect_entities(
Text=text,
LanguageCode=language_code
)
return response['Entities']
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error detecting entities: {str(e)}")
return []
def detect_key_phrases_safe(text: str, language_code: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Safely detect key phrases using Comprehend with error handling
"""
try:
response = comprehend.detect_key_phrases(
Text=text,
LanguageCode=language_code
)
return response['KeyPhrases']
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error detecting key phrases: {str(e)}")
return []
def safe_detect_sentiment(text: str, language_code: str) -> str:
"""
Safely detect sentiment with chunking for large texts
Comprehend has a 5000 byte limit for DetectSentiment
"""
try:
# Check if text is small enough for single call
if len(text.encode('utf-8')) <= 4500:
response = comprehend.detect_sentiment(
Text=text,
LanguageCode=language_code
)
return response['Sentiment']
# For large texts, chunk and aggregate
logger.info(f"Text too large for single sentiment call, chunking...")
chunks = chunk_text(text, 4000) # Leave some buffer
sentiments = []
for chunk in chunks:
try:
response = comprehend.detect_sentiment(
Text=chunk,
LanguageCode=language_code
)
sentiments.append(response['Sentiment'])
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error detecting sentiment for chunk: {str(e)}")
sentiments.append('UNKNOWN')
# Aggregate sentiments (simple majority vote)
return aggregate_sentiments(sentiments)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error detecting sentiment: {str(e)}")
return 'UNKNOWN'
def chunk_text(text: str, max_bytes: int) -> List[str]:
"""
Split text into chunks that don't exceed max_bytes
"""
chunks = []
current_chunk = ""
for word in text.split():
test_chunk = current_chunk + " " + word if current_chunk else word
if len(test_chunk.encode('utf-8')) <= max_bytes:
current_chunk = test_chunk
else:
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(current_chunk)
current_chunk = word
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(current_chunk)
return chunks
def aggregate_sentiments(sentiments: List[str]) -> str:
"""
Aggregate multiple sentiment results into a single sentiment
"""
if not sentiments:
return 'UNKNOWN'
# Count sentiment occurrences
sentiment_counts = {}
for sentiment in sentiments:
sentiment_counts[sentiment] = sentiment_counts.get(sentiment, 0) + 1
# Return the most common sentiment
return max(sentiment_counts, key=sentiment_counts.get)
def convert_floats_to_decimal(data: Any) -> Any:
"""
Recursively convert float values to Decimal for DynamoDB compatibility
"""
if isinstance(data, dict):
return {key: convert_floats_to_decimal(value) for key, value in data.items()}
elif isinstance(data, list):
return [convert_floats_to_decimal(item) for item in data]
elif isinstance(data, float):
return Decimal(str(data))
else:
return data
Bước 7: Thêm S3 Trigger
- Trong hàm Lambda → "Add trigger"
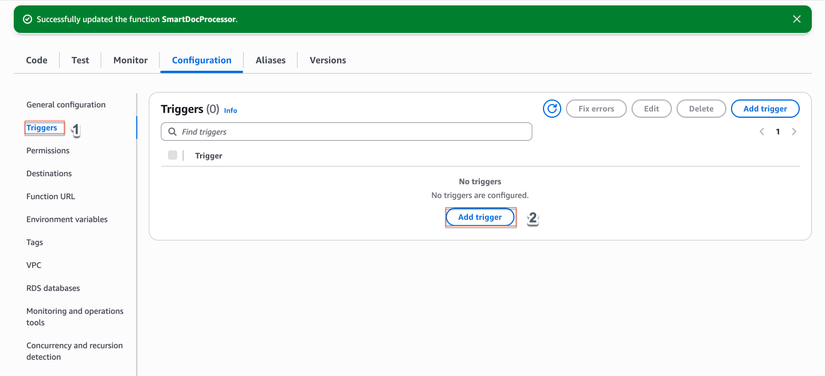
- Chọn "S3"
- Cấu hình:
- Bucket: Chọn bucket đã tạo ở bước 2
- Event type:
All object create events - Prefix: (để trống hoặc thêm đường dẫn thư mục)
- Suffix: (để trống)
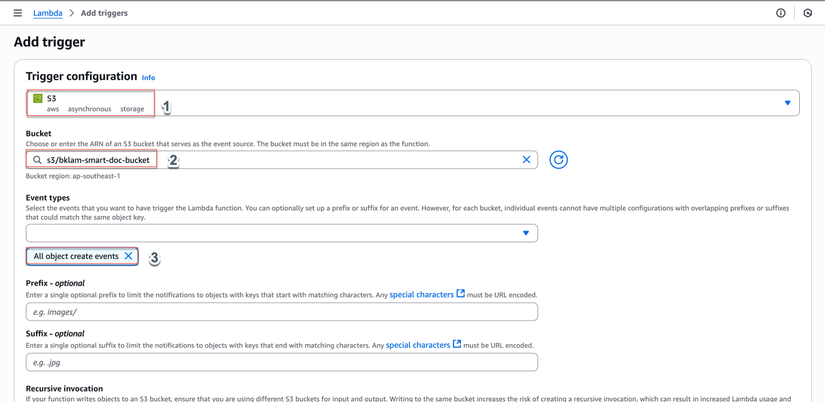
- Check "Recursive invocation" nếu muốn xử lý file trong thư mục con
- Nhấp "Add"
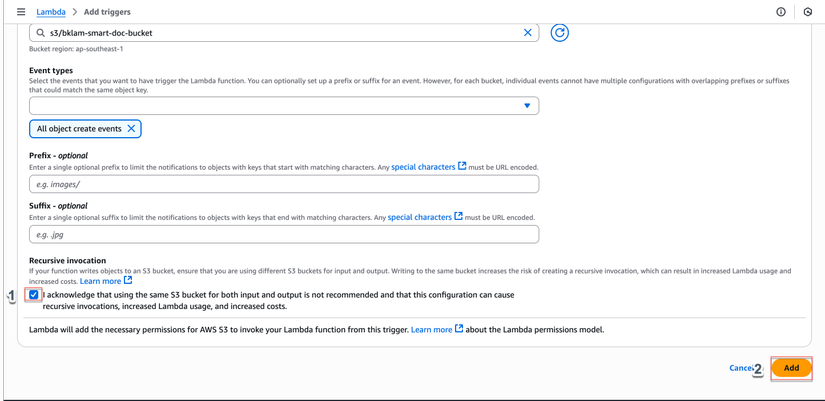
Bước 8: Test với File Mẫu
- Tải lên file test vào bucket S3:
- Loại file hỗ trợ: JPG, PNG, PDF (1 trang)
- Kích thước: < 10MB (giới hạn Textract sync)
- Kiểm tra CloudWatch Logs:
- Hàm Lambda → "Monitor" → "View CloudWatch logs"
- Tìm log group:
/aws/lambda/SmartDocProcessor
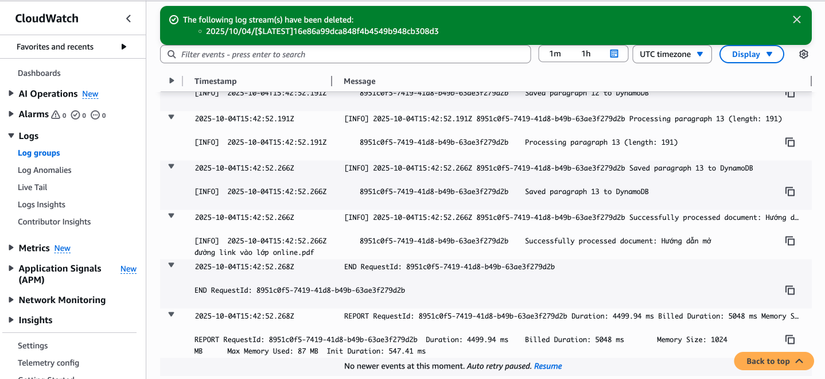
- Kiểm tra DynamoDB:
- DynamoDB → Tables →
SmartDocResults→ "Items" - Xem các item đã tạo
- DynamoDB → Tables →
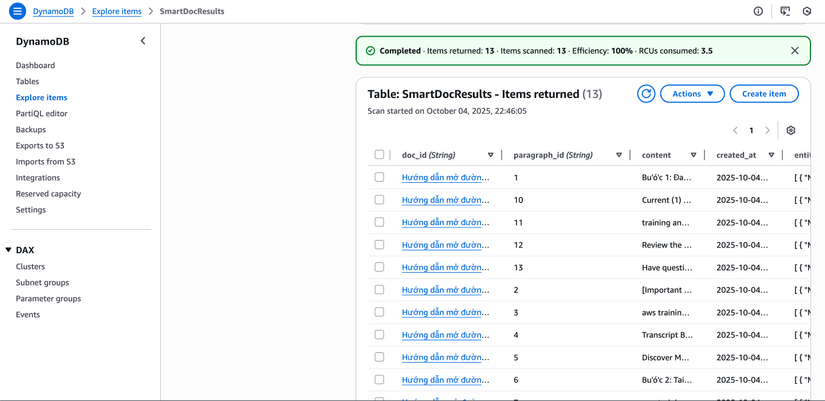
Bước 9: Xác minh Kết quả
Mẫu DynamoDB Item
{
"doc_id": "sample-document.pdf",
"paragraph_id": "1",
"content": "This is the first paragraph of the document with important information.",
"entities": [
{
"Text": "sample-document.pdf",
"Type": "OTHER",
"Score": 0.99
}
],
"key_phrases": [
{
"Text": "important information",
"Score": 0.99
}
],
"sentiment": "POSITIVE",
"created_at": "2024-01-15T10:30:00.000Z"
}
Cách Xác minh
- CloudWatch Logs: Xem log để debug và theo dõi quá trình xử lý
- DynamoDB Console: Xem items với thông tin đầy đủ
- S3 Console: Xác nhận file đã được tải lên
Khắc phục Sự cố
Vấn đề Thường gặp:
- Permission denied: Kiểm tra IAM role có đủ quyền
- Textract error: File quá lớn hoặc format không hỗ trợ
- DynamoDB error: Kiểm tra tên bảng và quyền
- Timeout: Tăng memory hoặc timeout cho Lambda
- Comprehend error: Kiểm tra ngôn ngữ văn bản và giới hạn kích thước
Mẹo Debug:
- Xem CloudWatch Logs để tìm lỗi cụ thể
- Xác minh IAM policy có placeholders đúng
- Xác nhận S3 bucket và DynamoDB table tồn tại
- Test các dịch vụ Textract và Comprehend riêng biệt
Bước Tiếp theo & Tính năng Nâng cao
1. Xử lý PDF Nhiều trang
- Sử dụng Textract async API (
StartDocumentAnalysis) - Kết hợp với SNS để nhận thông báo hoàn thành
- Sửa đổi Lambda để xử lý SNS events
2. Mô hình Comprehend Tùy chỉnh
- Tạo custom entity recognizers cho domain cụ thể
- Sử dụng custom classification models
- Cải thiện độ chính xác phân tích
3. Nâng cao Bảo mật
- Sử dụng KMS để mã hóa dữ liệu DynamoDB
- Bật S3 server-side encryption
- Triển khai Lambda trong VPC để bảo mật cao
- Sử dụng IAM roles thay vì access keys
4. Giám sát & Cảnh báo
- Thiết lập CloudWatch alarms
- Tạo dashboard để giám sát pipeline
- Sử dụng X-Ray để trace requests
Kết luận
Bạn đã thành công xây dựng một pipeline xử lý tài liệu thông minh có thể tự động trích xuất và phân tích nội dung từ các loại tài liệu khác nhau. Giải pháp này cung cấp:
- Xử lý tự động tài liệu đã tải lên
- Trích xuất văn bản thông minh bằng AWS Textract
- Phân tích nội dung với nhận dạng thực thể, trích xuất cụm từ khóa và phân tích cảm xúc
- Lưu trữ dữ liệu có cấu trúc trong DynamoDB để truy vấn dễ dàng
- Kiến trúc có thể mở rộng có thể xử lý các khối lượng công việc khác nhau
Pipeline này có thể được mở rộng cho các use case khác nhau như:
- Phân loại và định tuyến tài liệu
- Kiểm duyệt nội dung
- Trích xuất dữ liệu cho business intelligence
- Kiểm tra tuân thủ tự động
- Phân tích ticket hỗ trợ khách hàng
Sự kết hợp của các dịch vụ AWS cung cấp một giải pháp mạnh mẽ, có thể mở rộng có thể phát triển theo nhu cầu của bạn trong khi duy trì bảo mật và hiệu quả chi phí.
All rights reserved