Use TensorRT to faster inference and lower latency for Deeplearning Model
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
TensorRT là gì ?
TensorRT là một thư viện được phát triển bởi NVIDIA nhằm cải thiện tốc độ inference, giảm độ trì truệ trên các thiết bị đồ họa NVIDIA(GPU). Nó có thể cải thiện tốc độ suy luận lên đến 2-4 lần so với các dịch vụ real-time và nhanh hơn gấp 30 lần so với hiệu suất của CPU.
 Nội dung bài này chúng ta tập trung một số vấn đề sau đây:
Nội dung bài này chúng ta tập trung một số vấn đề sau đây:
- 👍Tại sao TensorRT cải thiện tốc độ inference
- 👍Việc tốc độ được cải thiện có cần đánh đổi cái gì không?
- 👍Làm sao để sử dụng TensorRT trên deep learning?
TensorRT cải thiện việc tối ưu như thế nào ?
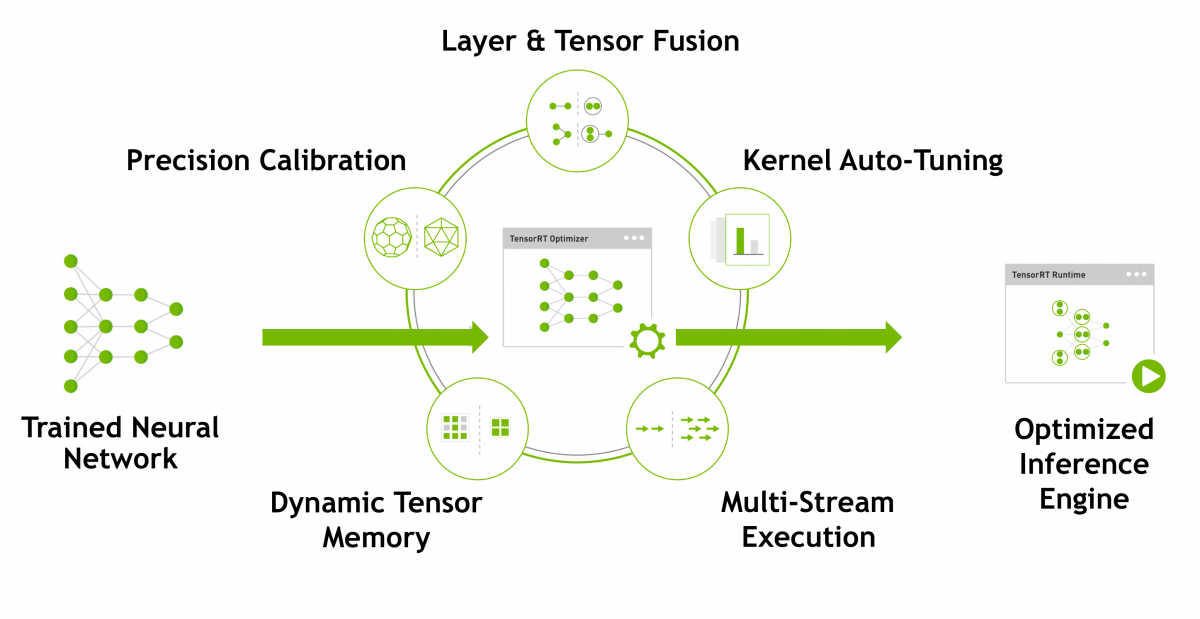
TensorRT sẽ thực hiện 5 loại tối ưu để tăng hiệu suất inference. Chúng ta sẽ thỏa luận 5 loại này ở bên dưới.
1. Precision Calibration
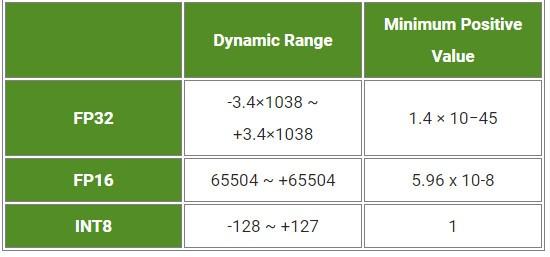
Trong suốt quá trình training, các tham số và hàm kích hoạt activations trong độ chính xác FP32(Float Point 32) sẽ được convert về độ chính xác FP16 hoặc INT8. Việc tối ưu nó sẽ giảm độ trì truệ và tăng tốc độ suy luận nhưng phải trả một cái giá là phải giảm độ chính xác của model mặc dù không đáng kể. Trong nhận diện real-time thì đôi khi vịệt đánh đổi độ chính xác so với tốc độ suy luận là cần thiết.
2. Layer & Tensor Fusion
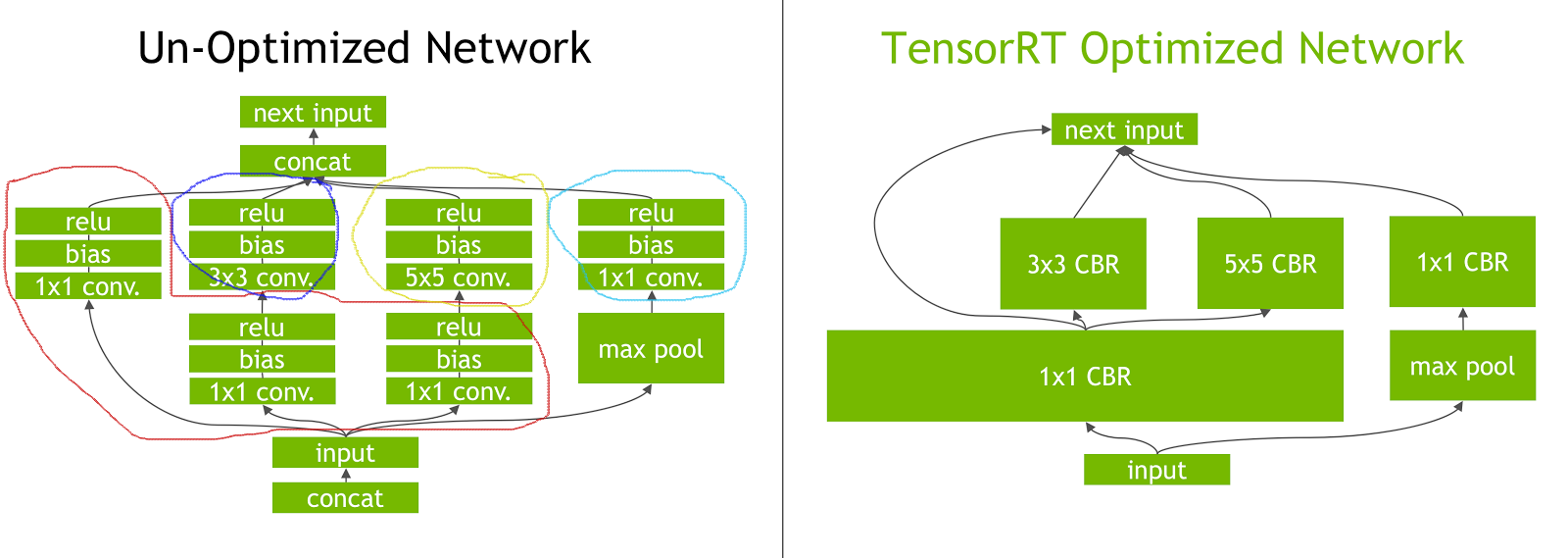
TensorRT nó sẽ gộp layer and tensor để tối ưu hóa bộ nhớ GPU và băng thông bởi việc gộp các nodel theo chiều dọc, chiều ngang hoặc cả hai.
- Improve GPU utilization - less kernel launch overhead, better memory usage and bandwidth
- Vertical fusion = Combine sequential kernel calls
- Horizontal fusion = Combine same kernels that have common input but different weights
![]()
3. Kernel auto-tuning
Trong quá trình tối ưu model, một vài kernel riêng dành cho việc tối ưu sẽ thực thi trong suốt tiến trình.
- There are multiple low-level algorithms/implementations for common operations
- TensorRT selects the optimal kernels based on your parameters e.g: batch_size, filter-size, input data size.
- TensorRT selects the optimal kernel based on your target platform.
4. Dynamic Tensor Memory
- Allocates just the memory required for each tensor and only for the duration of its usage
- Reduces memory footprint and improves memory re-use
5. Multiple Stream Execution
- Allows processing multiple input streams in parallel
Workflow
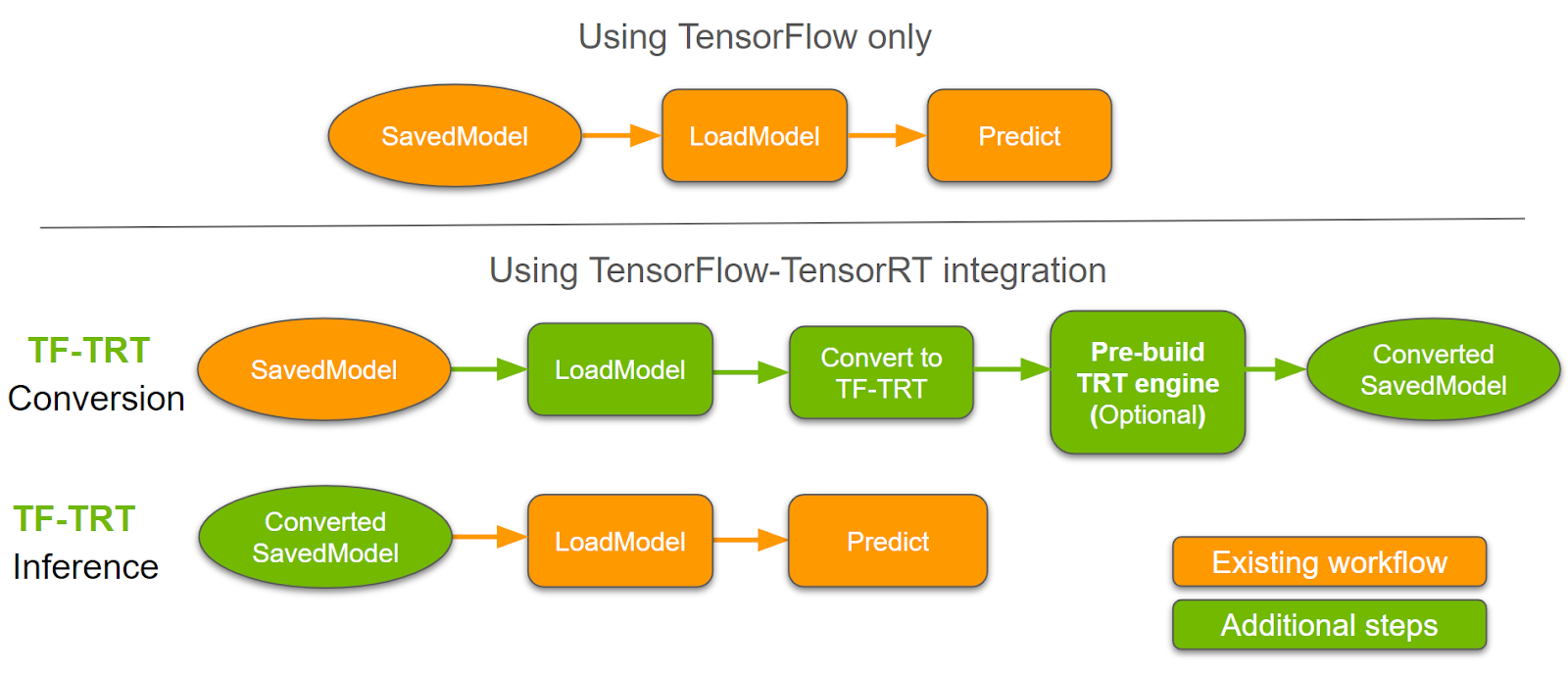
Để áp dụng TensorRT trên deep learning thì chúng ta cần phải convert model tới model-TRT theo như luồng biểu đồ sao đây.
Code
1. Cài đặt môi trường TensorRT
Để cài đặt TensorRT trên hệ thống của bạn thì cần một số yêu cầu sau đây:
- NVIDIA-GPU
- Tensorflow-GPU >=2.0
pip install tensorflow-gpu==2.0.0
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/nvidia-machine-learning-repo-ubuntu1804_1.0.0-1_amd64.deb
dpkg -i nvidia-machine-learning-repo-*.deb
apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libnvinfer5
pip install 'h5py==2.10.0' --force-reinstall
2. Convert model ResNet-50 to TF-TRT
Các bạn có thể convert các model khác tới TensorRT, ở đây mình lấy ví dụ là ResNet-50.
from tensorflow.python.compiler.tensorrt import trt_convert as trt
from tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import ResNet50
import os
import numpy as np
# Load model =>Predict => save model
model = ResNet50(weights='imagenet')
model.save('/content/resnet50_saved_model')
# Convert to TF_TRT => SavedModel
print('Converting to TF-TRT FP32 or FP16 or INT8...')
# Nếu convert TF-TRT FP32 : trt.TrtPrecisionMode.FP32
# Nếu convert TF-TRT FP16 : trt.TrtPrecisionMode.FP16
# Nếu convert TF-TRT INT8 : trt.TrtPrecisionMode.INT8
conversion_params = trt.DEFAULT_TRT_CONVERSION_PARAMS._replace(precision_mode=trt.TrtPrecisionMode.FP16,
max_workspace_size_bytes=8000000000)
converter = trt.TrtGraphConverterV2(input_saved_model_dir='resnet50_saved_model',
conversion_params=conversion_params)
# Converter method used to partition and optimize TensorRT compatible segments
converter.convert()
# Save the model to the disk
converter.save(output_saved_model_dir='resnet50_saved_model_TFTRT_FP32')
print('Done Converting to TF-TRT FP32')
3. Load lại model đã convert
# Load converted model and infer
import tensorflow as tf
root = tf.saved_model.load('/content/resnet50_saved_model_TFTRT_FP32')
infer = root.signatures['serving_default']
# output = infer(input_tensor)
print(infer)
Kết quả
Để so sánh kết quả của việc sử dụng TensorRT với việc inference native thì mình Inference ResNet-50 trên TF-TRT FP32, FP16, INT8 và native.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tensorrt/master/tftrt/blog_posts/Leveraging%20TensorFlow-TensorRT%20integration%20for%20Low%20latency%20Inference/tf2_inference.py
python tf2_inference.py --use_tftrt_model --precision fp16
python tf2_inference.py --use_tftrt_model --precision fp32
python tf2_inference.py --use_tftrt_model --precision int8
python tf2_inference.py --use_native_tensorflow
| FP16 | FP32 | Native |
|---|---|---|
| Average step time: 2.1 msec | Average step time: 2.5 msec | Average step time: 4.1 msec |
| Average throughput: 244248 samples/sec | Average throughput: 240145 samples/sec | Average throughput: 126328 samples/sec |
Qua đó ta thấy được việc khi convert model sang TensorRT sẽ tăng tốc độ inference và giảm độ trì truệ khá đáng kể so với inference truyền thống.
Tài liệu tham khảo
Toàn bộ code : https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15m95GzznIoCRn1XnMQXd9L-onpJiCWM3?usp=sharing
Link tài liệu tham khảo :
All rights reserved