Tìm hiểu về thư viện Sigar
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Tìm hiểu về thư viện Sigar
I. Mở đầu
Dạo trước, lúc mình vẫn còn làm nhiều application desktop (code bằng Java), mình có gặp phải bài toán như này: Khi app chạy một job (đa luồng -multi thread) 24/24, cần phải luôn đảm bảo sử dụng CPU + RAM của máy ko tăng quá cao. Số lượng luồng thực thi công việc phải tự điều chỉnh theo cấu hình của máy. (Sử dụng 60% RAM và CPU lúc chạy không được vượt quá 90%)
Mới đầu tiếp nhận vấn đề này, mình cũng tìm kiếm, tra cứu khá nhiều, mất khá nhiều thời gian, công sức để chạy các demo, cũng như so sánh đối chiếu với thông số thật của máy tính. Cuối cùng sau khoảng 3, 4 ngày thì mình có tìm được một thư viện hoàn toàn đáp ứng được nhu cầu của bản thân mình. Đó là thư viện Sigar.
II. Sigar là gì?
Sigar là một thư viện phần mềm miễn phí (theo Giấy phép Apache ) cung cấp giao diện lập trình đa ngôn ngữ, đa nền tảng cho thông tin cấp thấp về phần cứng máy tính và hoạt động của hệ điều hành. Thư viện cung cấp các ràng buộc cho nhiều ngôn ngữ máy tính phổ biến và đã được chuyển đến hơn 25 kết hợp hệ điều hành/ phần cứng khác nhau. Sigar là viết tắt của System Information Gatherer And Reporter và ban đầu được phát triển bởi Doug MacEacéc , tác giả của mô-đun mod_perl phổ biến cho máy chủ web Apache.
III. Hướng dẫn sử dụng thư viện (ngôn ngữ java + sử dụng Intellij)
1. Thêm thư viện Sigar vào project
Bước 1: Tạo một project maven có tên: demo-sigar
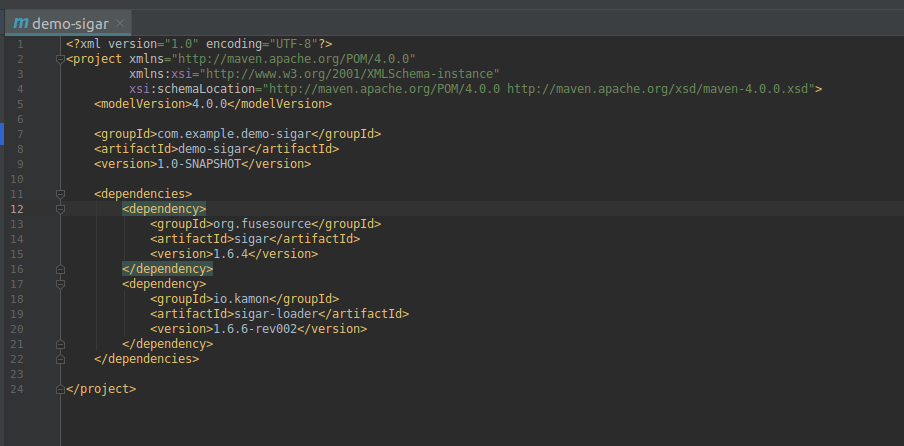
Bước 2: Add các dependency sau
<dependency>
<groupId>org.fusesource</groupId>
<artifactId>sigar</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.kamon</groupId>
<artifactId>sigar-loader</artifactId>
<version>1.6.6-rev002</version>
</dependency>
2. Cấu trúc project demo
3. Các class
Class Infor:
package com.example.demosigar;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Infos {
private long pid;
private String fqdn;
private String hostname;
private double uptime;
private Cpu cpu = new Cpu();
private Mem mem = new Mem();
private Swap swap = new Swap();
private List<Interface> interfaces = new ArrayList<>(2);
@Data
public static class Cpu {
private long sys;
private long total;
private long user;
}
@Data
public static class Mem {
private long total;
private long used;
private long free;
}
@Data
public static class Swap {
private long total;
private long used;
private long free;
}
@Data
public static class Interface {
private String name;
private String type;
private String address;
}
}
Class SigarService
package com.example.demosigar;
import kamon.sigar.SigarProvisioner;
import org.hyperic.sigar.NetInterfaceConfig;
import org.hyperic.sigar.Sigar;
import org.hyperic.sigar.SigarException;
public class SigarService {
private final Sigar sigar;
public SigarService() {
Sigar sigar = null;
try {
SigarProvisioner.provision();
sigar = new Sigar();
// call it to make sure the library was loaded
sigar.getPid();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
this.sigar = sigar;
}
public Infos infos() {
Infos infos = new Infos();
try {
infos.setPid(sigar.getPid());
infos.setFqdn(sigar.getFQDN());
infos.setHostname(sigar.getNetInfo().getHostName());
infos.setUptime(sigar.getUptime().getUptime());
String[] netInterfaceList = sigar.getNetInterfaceList();
for (String netInterfaceName : netInterfaceList) {
// Add net interface
NetInterfaceConfig config = sigar.getNetInterfaceConfig(netInterfaceName);
Infos.Interface netInterface = new Infos.Interface();
netInterface.setName(config.getName());
netInterface.setType(config.getType());
netInterface.setAddress(config.getAddress());
infos.getInterfaces().add(netInterface);
}
// Add cpu
infos.getCpu().setSys(sigar.getThreadCpu().getSys());
infos.getCpu().setTotal(sigar.getThreadCpu().getTotal());
infos.getCpu().setUser(sigar.getThreadCpu().getUser());
// Add mem
infos.getMem().setTotal(sigar.getMem().getTotal());
infos.getMem().setUsed(sigar.getMem().getUsed());
infos.getMem().setFree(sigar.getMem().getFree());
// Add swap
infos.getSwap().setTotal(sigar.getSwap().getTotal());
infos.getSwap().setUsed(sigar.getSwap().getUsed());
infos.getSwap().setFree(sigar.getSwap().getFree());
} catch (SigarException ignored) {
}
return infos;
}
}
Class ApplicationMain
package com.example.demosigar;
public class ApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SigarService sigarService = new SigarService();
System.out.println("Mem total: " + sigarService.infos().getMem().getTotal());
System.out.println("Mem used: " + sigarService.infos().getMem().getUsed());
System.out.println("Mem free: " + sigarService.infos().getMem().getFree());
}
}
4. Kết quả chạy trương trình
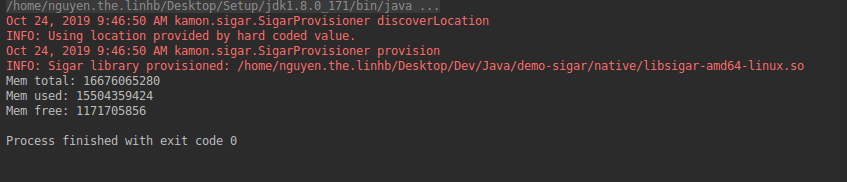
Kết quả ở đây chỉ dung lượng Ram đơn vị tính theo Byte
Ở đây mình làm là ví dụ demo nên chỉ hiển thị memory để test. Còn về vận dụng các bạn có thể lấy được rất nhiều thông số về phần cứng và hệ điều hành của máy.
Hi vọng bài viết của mình sẽ giúp ích được cho các bạn. Cảm ơn!
All rights reserved