Start with Vuex the easiest way
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
- Mục đich bài viết này giúp bạn hiểu một cách cơ bản nhất về quản lý state sử dụng vuex thông qua các ví dụ
Thuật ngữ State management
- Nói ngắn gọn: State được lưu trữ trong một đối tượng gọi là store
- Để sửa đổi state bạn sử dụng actions và mutations , 2 cái này cũng được lưu trữ trong store
State
- State là dữ liệu được lưu trữ trong ứng dụng của bạn, các components có thể nhận dữ liệu này, khi state thay đổi thì dữ liệu trong component thay đổi theo.
Store
- Store quản lý state . Nó chỉ được thay đổi (mutated) từ bên trong vì vậy bên ngoài component không thể trực tiếp thay đổi state. Để thay đổi state, components có thể dispatch một action hoặc commit một mutation
Getters
- Getters sẽ lấy giá trị của state trong store. Bạn có thể sử dụng chúng trong actions của bạn hoặc trực tiếp trong component của bạn. Điều này rất hữu ích nếu một số component cần tính toán cùng một thứ dựa trên store data, bạn có thể thực hiện ở một nơi thay vì phải làm riêng cho từng thành phần.
Mutations (thay đổi trạng thái)
- Store là nơi component chỉ có thể đọc dữ liệu và không thể thay đổi trạng thái một cách trực tiếp.
- Để thay đổi trạng thái thì Mutations sẽ đảm nhiệm chức năng này, đây cũng là nơi duy nhất có thể thay đổi trạng thái.
- Một mutation là synchronous (code phía sau phải đợi đến khi mutation done mới có thể thực hiện tiếp được).
- Mutations sẽ thực hiện thay đổi thông qua commit.
Action
- Actions gần giống như mutations, tuy nhiên nó khác nhau ở vài điểm:
- Nó không được phép thay đổi trạng thái, mà cần commit một mutation để thực hiện điều này.
- Nó có thể chứa các hoạt động bất đồng bộ (asynchronous), như lời gọi api để fetch dữ liệu, khi trả về thì commit dữ liệu tới mutations
Bắt đầu
- Mình sẽ bắt đầu bằng một ví dụ trong thực tế để bạn dễ hiểu hơn nhé ^^
- Đầu tiên chúng ta có một cửa hàng điện tử . Larry (the action) làm việc tại bộ phận TV. Larry giám sát Jenny (the mutation) , công việc duy nhất của Jenny là lấy TV từ kho/kệ (the state).
- Ví dụ: Hiện tại có 10 TV trên kệ. Một khách hàng (the component) đến cử hàng để mua TV mới. Người đó nói chuyện với Larry (the action) => Larry yêu cầu Jenny (the mutation) lấy TV từ kệ (the state) => Jenny lấy TV từ kệ => lúc này khách hàng có thể quan sát thấy còn 9 TV trên kệ ( the state)
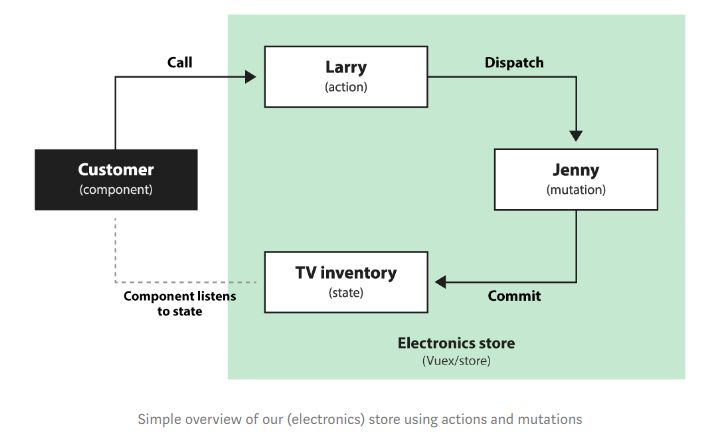
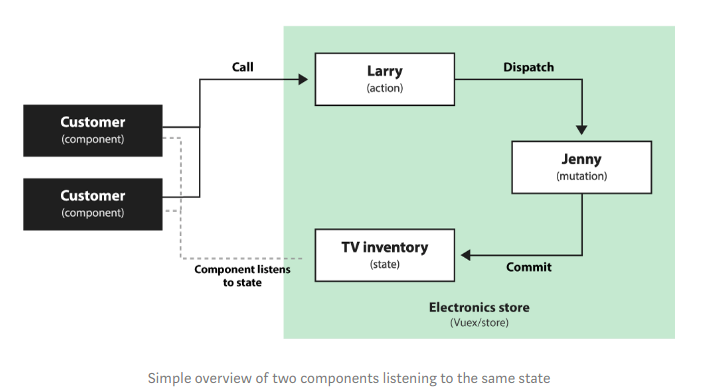
- Trên thực tế, một cử hàng sẽ có nhiều khách hàng nhìn vào kệ hàng của TV, cũng như nhiều khách hàng gọi cho Larry.
- Ví dụ : Một khách hàng khác (anothor component) mua 9 TV => Larry yêu cầu Jenny (mutation) lấy tất cả TV còn lại trên kệ cho khách => Những khách hàng khác đang xem TV bây giờ nhận thấy không còn TV, vì vậy họ có đợi cho đến khi họ được thông báo TV đã được bổ sung hoặc là không mua nữa.
Let’s build your shop!
- Mình mặc định bạn đã biết cách tạo dự án Vue và có một số kiến thức cơ bản về Vue, vì vậy mình sẽ bắt đầu bằng cách sử dụng một template rỗng được tạo bằng Vue CLI.
- Install vuex : Bạn có thể sử dụng npm hặc yarn
- Npm :
npm install vuex --save - Yarn :
yarn add vuex
- Npm :
- Trong src tạo một thư mục mới gọi là store và trong thư mục này tạo một tệp mới gọi là store.js . Trong tệp này, chúng tôi sẽ thiết lập base cho store
//src/store/store.js
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Vue from 'vue'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
totalTvCount: 10 // The TV inventory
},
getters: {
// Here we will create a getter
},
mutations: {
// Here we will create Jenny
},
actions: {
// Here we will create Larry
}
});
- Tiếp theo chúng ta cần import store tới vue
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store/store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app');
-
Bây giờ store đã hoạt động và chúng ta có thể nhận states từ đó. Có 2 cách để làm điều này :
- Nếu bạn chỉ nhận 1 state thì cách đơn giản nhất là sử dụng computed
- Nếu bạn muốn nhận nhiều states thì cách đơn giản là sử dụng Object Spread Operator , nó sẽ có dạng như này
computed: { ...mapState(['someState', 'anotherState']),} -
Chúng ta tạo ra một component có tên là Customer
<template>
<div class="customer">
<h1>I'm a customer</h1>
<p>I see {{ totalTvCount }} TVs!</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Customer',
computed: {
totalTvCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalTvCount
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- Tiếp theo chúng ta sẽ tạo actions (Larry) và mutations (Jenny) để xóa TV khỏi store
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
totalTvCount: 10 // The TV inventory
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
// Jenny
removeTv(state, amount) {
// For now we allow Jenny just to remove
state.totalTvCount -= amount
}
},
actions: {
// Larry
removeTv(context, amount) {
// For now we only remove a tv,
// but this action can contain logic
// so we could expand it in the future.
if(context.state.totalTvCount >= amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
context.commit('removeTv', amount)
}
}
}
});
- Bên ngoài file vue chúng ta tạo một button mua. Khi button mua được nhấn (khách muốn mua hàng) => sẽ dispatch tới actions removeTv (Larry) trong file store.js => Lúc này Larry sẽ check số lượng hàng còn hay không và commit tới jenney => Jenny thực hiện lấy (xóa) hàng từ kho (state)
<template>
<div class="customer">
<h1>I'm a customer</h1>
<p>I see {{ totalTvCount }} TVs!</p>
<p v-show="!totalTvCount">I can't buy any..</p>
<button
:disabled="!totalTvCount"
@click="buyTv">
Buy TV
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Customer',
computed: {
totalTvCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalTvCount
}
},
methods: {
buyTv() {
// Dispatch the action to buy a TV
this.$store.dispatch('removeTv', amount)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Sử dụng object spread operator
- Trường hợp có 1 state thì việc sử computed properties là dẽ dàng và nhanh nhất, nhưng trong trường hợp bạn có nhiều state thì sao nhỉ?
- Ví dụ cửa hàng của mình không chỉ bán TV mà còn bán Điện thoại, máy giặt, tủ lạnh,... lúc đó state của chúng ta sẽ có thêm các thuộc tính:
// store.js
state: {
totalTvCount: 10, // The TV inventory,
totalPhoneCount: 100, // The Phone inventory
totalWashingMachineCount: 100, // The Washing Machine inventory
totalHeadphoneCount: 100, // The Headphone inventory
},
mutations: {
// Jenny
removeTv(state, amount) {
state.totalTvCount -= amount
},
removePhone(state, amount) {
state.totalPhoneCount -= amount
},
removeWashingMachine(state, amount) {
state.totalWashingMachineCount -= amount
},
removeHeadphone(state, amount) {
state.totalHeadphoneCount -= amount
}
},
actions: {
// Larry
removeTv(context, amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
if(context.state.totalTvCount >= amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
context.commit('removeTv', amount)
}
},
removePhone(context, amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
if(context.state.totalPhoneCount >= amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
context.commit('removePhone', amount)
},
removeWashingMachine(context, amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
if(context.state.totalWashingMachineCount >= amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
context.commit('removeWashingMachine', amount)
},
removeHeadphone(context, amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
if(context.state.totalHeadphoneCount >= amount) {
// If we enough TVs, ask Jenny to remove it
context.commit('removeHeadphone', amount)
}
}
- Trong file Customer.vue
<script>
export default {
name: 'Customer',
computed: {
totalTvCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalTvCount
},
totalPhoneCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalPhoneCount
},
totalWashingMachineCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalWashingMachineCount
},
totalHeadphoneCount () {
return this.$store.state.totalHeadphoneCount
},
},
methods: {
buyTv() {
// Dispatch the action to buy TV
this.$store.dispatch('removeTv', amount)
},
buyPhone() {
// Dispatch the action to buy Phone
this.$store.dispatch('removePhone', amount)
},
buyWashingMachine() {
// Dispatch the action to buy WashingMachine
this.$store.dispatch('remove', amount)
},
buyHeadphone() {
// Dispatch the action to buy a TV
this.$store.dispatch('removeHeadphone', amount)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- Nếu sử dung object spread operator thì file .vue của chúng ta sẽ gọn hơn rất nhiều
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
computed: {
...mapState(['totalTvCount', 'totalPhoneCount', totalWashingMachineCount, totalHeadphoneCount])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['removeTv', 'removePhone', removeWashingMachine, removeHeadphone]),
buyTv() {
// Dispatch the action to buy a TV
this.removeTv(1)
},
buyPhone() {
// Dispatch the action to buy phone
this.removePhone(1)
},
buyWashingMachine() {
// Dispatch the action to buy WashingMachine
this.removeWashingMachine(1)
},
buyHeadphone() {
// Dispatch the action to buy Headphone
this.removeHeadphone(1)
}
},
created() {
}
}
</script>
Kết luận
- Trên đây là tất cả những gì cơ bản nhất bạn có thể làm với vuex, hi vọng bài viết sẽ giúp ích cho các bạn mới bắt đầu tiếp xúc. Thank you for reading
- Tham khảo : https://itnext.io/vuex-made-simple-getting-started-6bf229d432cf
All rights reserved