Object Oriented Programming in Python Development
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Python is a powerful programming language used for web application development. It is also a widely popular programming language used for machine learning and artificial intelligence applications.
With Python, complex programming problem-solving becomes simpler. There are several approaches to problem-solving in Python. OOP is one of those approaches.
In this article, I will introduce you to some fundamental OOP principles in Python development.
What is Object Oriented Programming (OOP)?
Object oriented programming (OOP) is a problem-solving approach in Python programming which involves structuring the programs in a way such that the attributes and behaviour are grouped together in a single object.
For example, a person is an object with attributes like age, gender, address along with behaviours like walking, talking, sleeping, etc. In more technical terms, an email is an object with attributes like recipient, subject, etc., and has behaviors like attachment, save to drafts, send, etc.
OOP in Python programming is based on developing reusable code. It avoids the problem of rewriting the code and follows the principle of Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY).
The OOP paradigm allows Python programmers to model real-world entities and the relationship between them like employees and their salaries, students and their marks, etc. These entities are transformed as software objects and can perform specific activities based on data.
OOP paradigm in Python
OOP, as you know by now, is an approach to problem solving by creating objects and classifying them based on attributes and behaviours. To get started with OOP, here are some of the OOP principles that can help you get started.
Class vs Module:
- Module: A python module is nothing but a package to encapsulate reusable code. Modules usually, but not always, reside in a folder with a init.py file inside of it. Modules can contain functions but also classes. Modules are imported using the import keyword.
- For example: We use views.py, models.py etc. in the django web framework. These all files are basically modules which will have ‘n’ number of classes or functions in it. All these modules can be reused in any project or the same project simply by importing them.
- Classes: Classes, on the other hand, can be defined in your main application code or inside modules imported by your application. Classes are the code of Object Oriented Programming and can contain properties and methods.
- For example: We use several classes in views file or model file or forms file in django development using Python. All these classes are basically combined in modules.
Thus, we can further elaborate both as we can have various classes in modules or can say that modules are nothing but collections of various classes and functions whereas classes are the code of OOP and can contain various props. and methods.
Instance:
- An individual object of a certain class. An object ‘obj’ that belongs to a class Circle, is an instance of the class Circle.
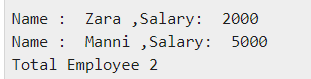
- The following snippet shows how an instance is created.

Output:
Methods:
- A Python method is like a Python function, but it must be called on an object. And to create it, you must put it inside a class.
- For example: we use the get method inside class or post method. We also use init method.
- Methods are different then functions as they must be called on an object.
- There are three types of methods available in python. They are: 1. Instance method 2. Class method 3. Static method
- Instance method: The most common method type. Able to access data and properties unique to each instance.
- It is compulsory to have ‘self’ as a parameter, but we don’t have to pass it everytime.
- By using self, we can access any data or methods that may reside in a class.
- Any method you create will automatically be created as an instance method, unless you tell Python otherwise. Also, no decorator is needed to run the method.
- For example:

- As we can see here in example, we created two methods.
- To access any method we have to first create an instance which we created by “de = DecoratorExample()”.
- After creating an instance, we have accessed the method on the next line.
- We can also call the whole class using ‘de.class’.
- Class method: Can access limited methods in the class. Can modify class specific details.
- Class method is created using ‘classmethod’ decorator.
- As an instance method uses ‘self’ as argument, it is compulsory to pass ‘cls’ as argument.
- They can’t access specific instance data, but they can call other static methods.
- For example:
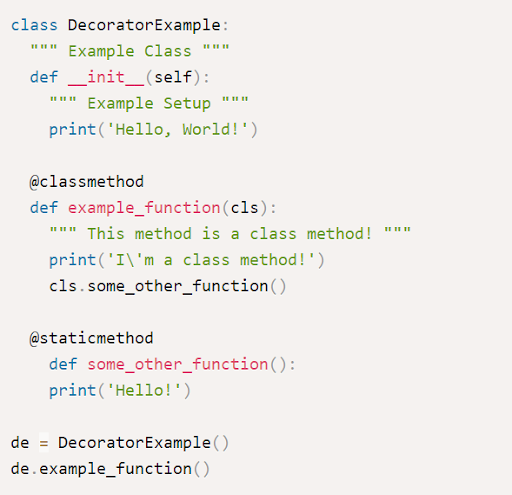
- In the above example, we can see that we have created a class method and accessed class with the help of ‘cls.some_other_function()’.
- We can use class methods to create an instance of class in Python development using OOP.
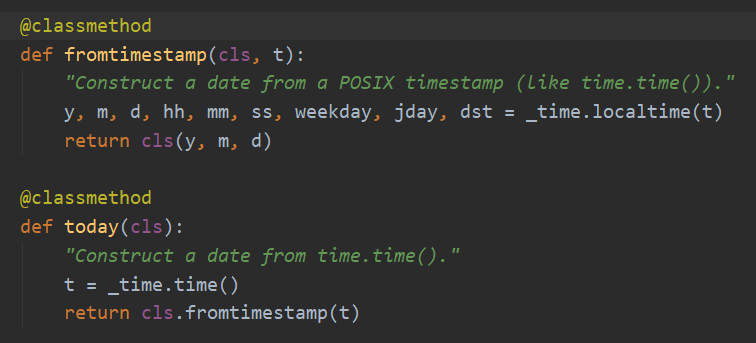
- For an example: we can create an instance of a class by giving values obtained by certain calculations.
- Below is a small example of datetime using classmethod:
- Static method: Cannot access anything else in the class. Totally self-contained code.
- It is created by only using ‘staticmethod’ and no need to create instances or use argument self or cls.
- They should be completely self-contained, and only work with data passed in as arguments.
- You may use a static method to add two numbers or pass a string.

- Static methods can neither modify object state nor class state. Static methods are restricted in what data they can access.
Variables:
- In python programming, we have three types of variables, They are: 1. Class variable 2. Instance variable 3. Global variable
- Class variable: If a variable is assigned inside the scope of a class, then that variable is known as class variable.
- It can’t be accessed outside the class scope.
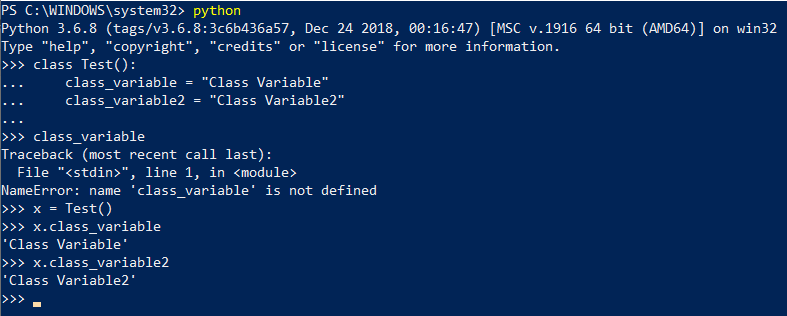
- In the below example, we have created different variables inside a class.
- All these variables are accessed after making a class instance or access class before accessing instance.
- For example: Here in the example, we have created a class and also created a variable inside the class.
- We can fetch that variable by creating an instance of class.
- Without creating it, we cannot fetch any variable. We will get ‘variable’ not defined error.
Instance variable: This variable is created within class in instance method. The variable can be accessed as shown below.
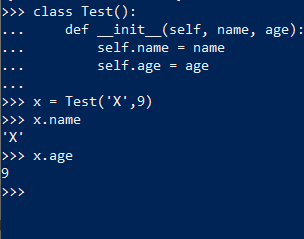
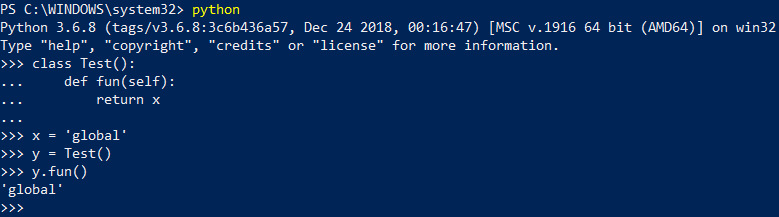
Global variable: It can be accessed anywhere in the project as it is assigned globally. We can access inside class, inside any method of class or inside any function else anywhere in the file.
Overloading/Overriding:
- Method overloading: When a single function acts differently whenever any args are passed.
- Basically, in our example we are passing first arg as data type, which will give us type of datatype. Thereafter, we will work according to it in the function. This whole function is known as overloading method.
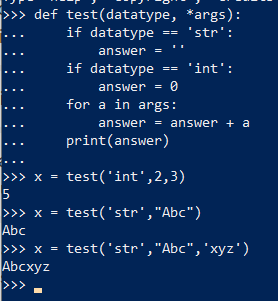
As shown above in the example, if we passed a string as data type then the answer for that is different then if we pass an integer. This method is called method overloading.
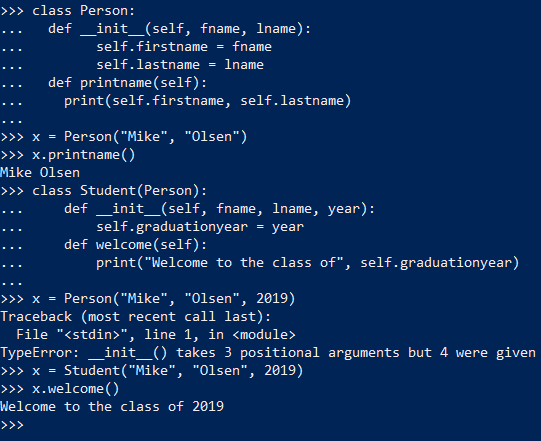
Method overriding: When a parent class is inherited in the child class and the child class has the same name of function, then the parent function of the parent class is overridden. Below example shows how a parent class inherited by a child both having the same init method works differently in both the classes.
Polymorphism:
- Polymorphism is an important feature of class definition in Python web development that is utilized when you have commonly named methods across classes or subclasses. This allows functions to use objects of any of these polymorphic classes without needing to be aware of distinctions across the classes.
- Basically, we can use features of the class in other classes, avoiding the same feature of other classes.
- This is known as “Polymorphism”.
- For example: Let’s assume we have two fish - shark and whale. Both will have common features like swimming but they return different output.
- Thus, we need to call a particular class whenever needed.
- To obtain this, polymorphism comes into the picture. The example below shows how it is obtained.
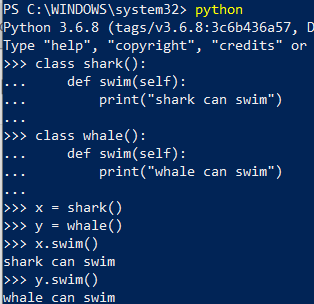
- In the above code, we can see that when an instance of shark class is created it will return a feature of shark class and not of whale class and vice-versa.
- Below is another example of polymorphism.
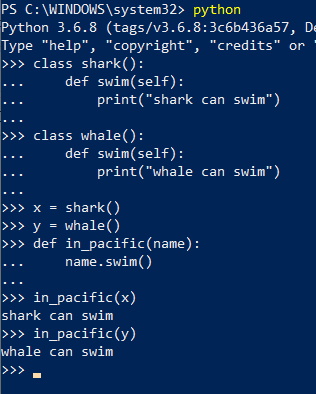
- In the above example, we have made another function which will take any argument and returns the function. Thus, due to polymorphism it will return different methods.
Inheritance:
- Inheritance is shown in the above example of person and student in overriding.
- Inheritance is to use parent’s features in the child.
- Above, we used the parent's init method in the child. We can also use various other methods which are used in the parent.
Abstraction:
- Abstraction means hiding the complexity and only showing the essential features of the object. So in a way, Abstraction means hiding the real implementation and we, as a user, know only how to use it.
- In simple words, we can say that we have to forcefully make a feature which should be inherited by a child class.
- In python development by default, it is not able to provide abstract classes. However, python for web development comes up with a module which provides the base for defining Abstract Base classes(ABC) and that module name is ABC. ABC works by marking methods of the base class as abstract and then registering concrete classes as implementations of the abstract base. A method becomes an abstract by decorating it with a keyword abstractmethod.
- Abstraction is done by using “abstractmethod” decorator above the function.
- For example: In our example we have made the swim function of the parent class as an abstract method. So, this method has to be inherited in each and every child class.
- If not implied, then it will throw an error and also if we try to create an object of parent class, it will throw an error.
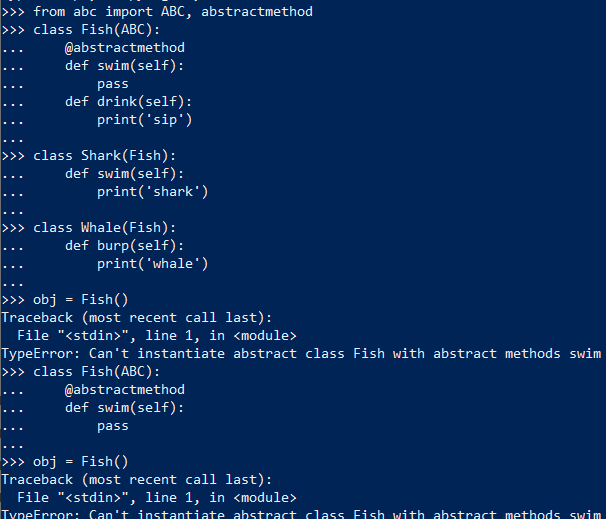
- Above example shows that we cannot make method without using a decorator. and we cannot create object of the parent class.
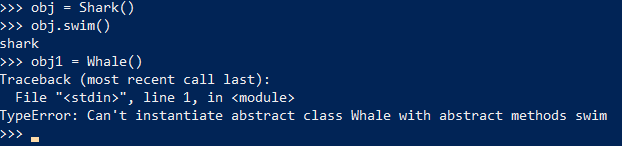
- Also, we have created two child classes - one having an abstract method and one without, and we get the below outputs.
- As shown above, whale class has not imported the method - it throws an error.
Dependency Injection:
- Python is a very flexible interpreted language with dynamic typing. There is a meaning that dependency injection doesn’t work for it as well, as it does for Java. Also, there is a meaning that dependency injection framework is something that Python developers would not ever need, cause dependency injection could be implemented easily using language fundamentals.
- Dependency Injection is performed by us in various manners but we are generally not aware of it.
- Dependency injection is nothing but creating dependency for a class without inheriting that class or creating any instance of that class.
- There are three terminologies in Dependency injection:
- Client : this term is used for class which has dependency on another class. In our example, client is cars.
- Service : this term is used for class which is depended on. In our example, service is engine class.
- Dependency Injector: this term is used for external code that is responsible for creation of objects and injection of dependencies.
- For example, We have a class called subject which has the name of the teacher in it. Now, if we want to pass this name of subject and teacher in another class, we can directly use instance or create its object but this will make our code hardcoded.
- So we will make an object of class which we want for dependency.
- Now this object will be passed as an argument in the client class.
- Thus, this will give us what we needed without any inheritance in both the class or making any instance.
- We can also use three types of dependency injectors: 1. Constructor injectors 2. Property injectors 3. Method injectors
- Further detailed explanation is given in the below link: https://pypi.org/project/dependency-injector/ http://python-dependency-injector.ets-labs.org/introduction/di_in_python.html#useful-links
Conclusion
If you are getting started with OOP in Python programming, you should definitely know what classes are and how & when you should execute them. You should learn to create parent and child classes to ensure that you are structuring your programs in a better way.
One of the important things about learning OOP is that it is not only valuable in Python development, but also helps you in Java, C, C++ and other languages that follow the OOP principles.
Also Read
- Pros and Cons of Python: A Definitive Python Web Development Guide
- #BoostYourBusiness: Pick Python Development For Your Technology Stack Today!
- 5 Common Python Development Mistakes and How to Fix Them
- Tutorial: Python Web Scraping using BeautifulSoup and Selenium
- Machine Learning and Data Science with Python
All rights reserved