Polymorphic Associations
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
1, Polymorphic association là gì?
Là 1 trong những chức năng của Active Record Associations. Vậy Active Record Associations là gì?
- Là liên kết giữa các Active Record Model. (has_many, belongs_to,....)
1.1 Các Active Record Association có lợi ích gì?
Các Active Record Association giúp ta thực hiện các thao tác CRUD bằng những dòng code gọn gàng hơn.
Ví dụ, với 1 user có nhiều bài post:
class User < ApplicationRecord
end
class Post < ApplicationRecord
end
Để tạo ra 1 post thuộc về 1 user đã tồn tại ta phải làm dư này:
@post = Post.create(published_at: Time.now, user_id: @user.id)
Và để xóa 1 user, chúng ta cũng phải xóa hết các bài post liên quan đến user đấy:
@posts = Post.where(user_id: @user.id)
@posts.each do |post|
post.destroy
end
@user.destroy
Thử tưởng tượng, nếu 1 user cũng có quan hệ 1-N với các bảng photo, page . Thì khi xóa 1 user, ta sẽ phải viết code như thế này:
@posts = User.where(user_id: @user.id)
@posts.each do |post|
post.destroy
end
@photos = User.where(user_id: @user.id)
@photos.each do |photo|
photo.destroy
end
@pages = User.where(user_id: @user.id)
@pages.each do |page|
page.destroy
end
.....
@user.destroy
Việc viết code như trên khá là dài dòng, phức tạp.
Nhưng với Active Record Associations, chúng ta chỉ cần viết lại như sau:
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, dependent: :destroy
has_many :posts, dependent: :destroy
has_many :pages, dependent: :destroy
end
class Post < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
end
Và việc xóa 1 user cùng với tất cả dữ liệu liên quan đến nó trở lên đơn giản hơn:
@user.destroy
1.2 Polymorphics association là gì và dùng như thế nào?
Polymorphic association là một active record association, giúp tạo liên kết giữa 1 Model với nhiều Model khác thông quan duy nhất 1 Association.
Ví dụ, Một user và một fanpage đều có thể có nhiều bài post. Nếu chỉ viết như dưới đây sẽ tạo ra 2 associations :
class Post < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
belongs_to :fanpage
end
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts
end
class Fanpage < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts
end
Và tương ứng với 2 associations, bảng posts sẽ chứa 2 khóa ngoại:
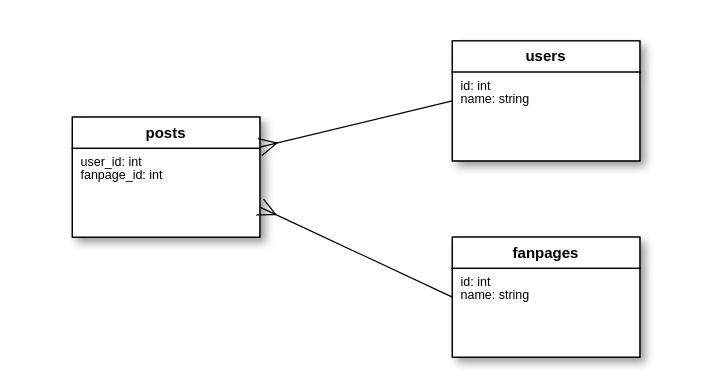
Trên thực tế, bảng các thực thể của bảngusers và fanpages cùng đóng vai trò là owner của posts, vậy nên ta có thể sử dụng polymorphics association như sau:
class Post < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :owner, porlymorphic: true
end
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts, as: :owner
end
class Fanpage < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts, as: :owner
end
Như vậy ở đây, bảng posts chỉ thông qua 1 associations để kết nối với 2 bảng.
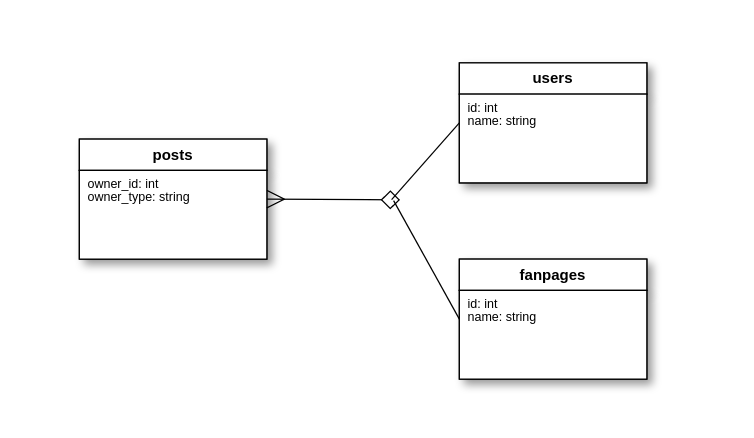
Chúng ta có thể tạo bài posts và update owner của bài post dễ dàng như sau
hieu = User.create name: "Hieu Hoang Trong"
hieu_post = Post.create owner: hieu
=> #<Post id: 1, owner_id: 1, owner_type: "User", created_at: "2019-09-08 15:21:52", updated_at: "2019-09-08 15:21:52">
#Chuyển bài post sang sở hữu của 1 trang fanpage như sau:
fanpage = Fanpage.create name: "Hoa Hau Ky Duyen"
hieu_post.update_attributes owner: fanpage
=> #<Post id: 1, owner_id: 1, owner_type: "Fanpage", created_at: "2019-09-08 15:21:52", updated_at: "2019-09-08 15:28:52">
2. Polymorphic association có lợi ích gì?
Để giải thích lợi ích của chức năng này, chúng ta cùng đến với bài toán "Nút like của facebook".
Đầu tiên, đến với 1 bài toán đơn giản là:
User có thể like bài posts, fanpages và photos.
Mình gọi đây là bài toán "2 vai trò" . Hai vai trò mình nhắc đến là:
- Thực thể tạo like(owner) : User
- Thực thể bị like (likeable): Post, Fanpage, Photo.
Vậy ta sẽ tạo ra các bảng như sau.
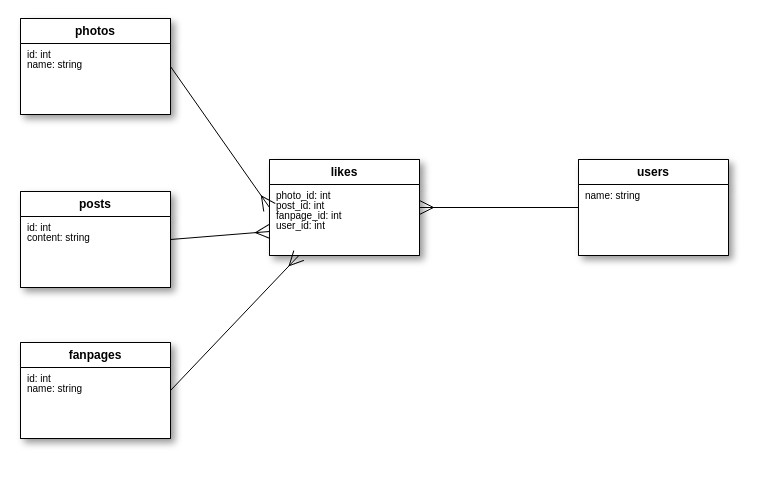
Cách tạo bảng bên trên nhìn thì có vẻ hợp lý. Tuy nhiên nếu xét đến bài toán thực tế mà facebook đang giải, sẽ nảy sinh nhiều vấn đề.
Vấn đề đầu tiên là:
Nếu số bảng ở vai trò likeable không chỉ là 3, mà là 100, điều đó đồng nghĩa với việc bảng likes sẽ phải lưu đến 100 khóa ngoại (photo_id, fanpage_id, post_id, cinema_id, book_id, group_id, ....)
Và phần code của Model Like sẽ được viết rất dài dòng như sau.
class Like < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :photo
belongs_to :fanpage
belongs_to :post
belongs_to :book
belongs_to :app
.....
belongs_to :user
end
Vấn đề số 2 là:
Thực tế 1 bảng có thể đóng cả 2 vai trò likeable và owner . Ví dụ như bảng fanpages .
Như vậy riêng với bảng fanpage, chúng ta sẽ phải viết code theo kiểu:
class Like < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :liked_fanpage, source: Fanpage
belongs_to :owner_like_fanpage, source: Fanpage
......
Đồng nghĩa với việc, bảng likes sẽ có thêm 2 khóa ngoại chỉ đến bảng Fanpage là likeable_fanpage_id và owner_fanpage_id .
Vậy hãy thử tưởng tượng, nếu số vai trò không chỉ là likeable và owner, thì số khóa ngoại lưu trong bảng like sẽ tăng lên 1 cách chóng mặt.
Để giải quyết 2 vấn đề này, chúng ta sẽ hướng đến thiết kế các bảng cơ sở dữ liệu theo 1 hướng khác, tương ứng với chức năng Porlymophic Association như sau:
class Like
belongs_to :likeable, porlymorphic: true
belongs_to :owner, polymorphic: true
end
class User
has_many :likes, as: :owner
end
class Post
has_many :likes, as: :likeable
end
class Photo
has_many :likes, as: :likeable
end
class Fanpage
has_many :active_likes, as: :owner, source: :like
has_many :passive_likes, as: :likeable, source: :like
end
Như vậy , Polymorphics association mang lại 1 lợi ích duy nhất:
Với 1 bài toán nhiều vai trò, sẽ có 1 bảng trung gian. Polymorphics association giúp làm rõ vai trò của các bảng đến bảng trung gian.
3, Bài toán comment
Bài toán comment giống 90% với bài toán like, với 2 vai trò:
- Thực thể tạo comment: owner
- Thực thể bị comment: commentable
Chỉ khác 1 điểm duy nhất, đó là bảng comment cũng có thể đóng vai trò commentable
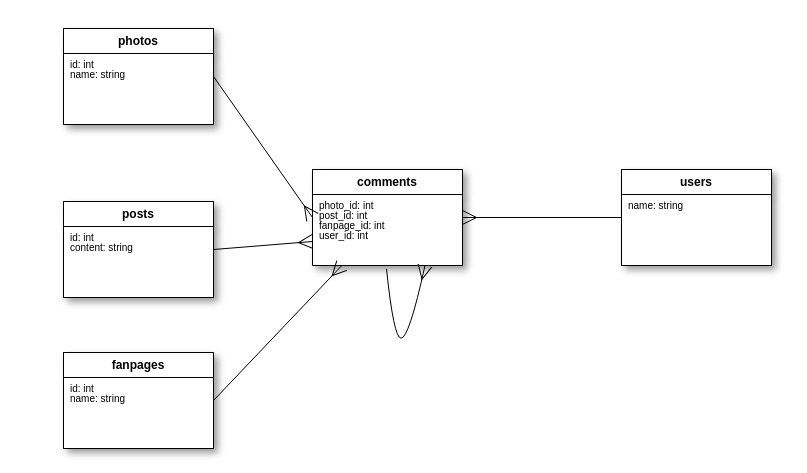
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :owner, polymorphic: true
belongs_to :commentable, polymorphic: true
has_many :comments, as: :commentable
end
4, Polymorphic được sử dụng trong gem public activity để giải quyết bài toán notifications như thế nào?
Gem public_activity được sử dụng cho bài toán notifications.
rails g public_activity:migration
Running via Spring preloader in process 717
create db/migrate/20190908195852_create_activities.rb
class CreateActivities < (ActiveRecord.version.release() < Gem::Version.new('5.2.0') ? ActiveRecord::Migration : ActiveRecord::Migration[5.2])
# Create table
def self.up
create_table :activities do |t|
t.belongs_to :trackable, :polymorphic => true
t.belongs_to :owner, :polymorphic => true
t.string :key
t.text :parameters
t.belongs_to :recipient, :polymorphic => true
t.timestamps
end
add_index :activities, [:trackable_id, :trackable_type]
add_index :activities, [:owner_id, :owner_type]
add_index :activities, [:recipient_id, :recipient_type]
end
# Drop table
def self.down
drop_table :activities
end
end
Gem public_activities biến bài toán notificaitons thành 1 bài toán 3 vai trò:
- owner:
- recipient:
- trackable:
All rights reserved