Pigeonhole Sort
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 7 năm
In computer science and information technology, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts a group of elements in a specific order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the efficiency of some other other algorithms which require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for normalization data and for producing human-readable output. There are many algorithms for sorting data with different techniques and complexity. Today We will learn about a little unknown sorting technique known as Pigeonhole Sort.
Pigeonhole Sort
Pigeonhole sorting is a sorting algorithm that is suitable for sorting lists of elements where the number of elements and the number of possible key values are approximately the same. It is similar tocounting sort, but differs inthat it moves items twice:once to the bucket array andagain to the final destination counting sort builds an auxiliary array then uses the array tocompute each item's final destination and move the item there.
Working Algorithm
The mechanism of pigeonhole sorting is as follows:
- Find minimum and maximum values in array. Let the minimum and maximum values be ‘min’ and ‘max’ respectively. Also find range as ‘max-min+1’.
- Set up an array of initially empty “pigeonholes” the same size as of the range.
- Visit each element of the array and then put each element in its pigeonhole. An element arr(i) is put in hole at index arr(i) – min.
- Start the loop all over the pigeonhole array in order and put the elements from non- empty holes back into the original array.
Example
Lets take an array to demonstrate pigeonhole sorting. The array in as follows:
A = (8, 3, 2, 7, 4, 6, 8)
So the maximum value is 8 and minimum value is 2 among this group of data.
Range in step 2 will be range: max - min -1 = 8-2+1 = 7
so there is 7 pigeonhole needed from 0..6.
Now we iterate throw each element of A to get the sorted list.
for the first element, 8 the index will be: A(i)-min = 8-2 = 6
for the first element, 3 the index will be: A(i)-min = 3-2 = 1
for the first element, 2 the index will be: A(i)-min = 2-2 = 0
for the first element, 7 the index will be: A(i)-min = 7-2 = 5
for the first element, 4 the index will be: A(i)-min = 4-2 = 2
for the first element, 6 the index will be: A(i)-min = 6-2 = 4
for the first element, 8 the index will be: A(i)-min = 8-2 = 6
So the pigeonhole array will be like
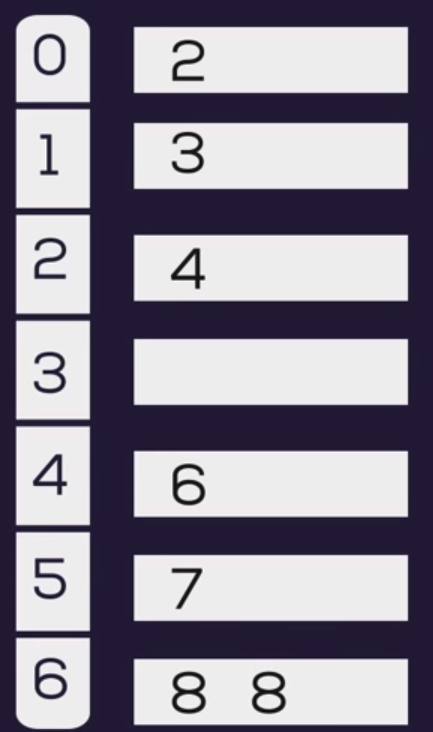
Now we will coppy the elements sequentially to array A to get the sorted array
A = (2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 8)
Ruby implementation
Following is the implementation of pigionwhole algorithm in Ruby:
def pigeonhole_sort(a)
mi =a.min
size = a.max - mi + 1
holes =Array.new size
a.each do |x|
holes[x - mi].push(x)
end
i = 0
holes.each_index do |in|
if holes[in].size > 0
holes[in].each do |n|
a[i] = n
i += 1
end
end
end
a
end
I hope this general information will inspire you to more about pigeonhole sorting. I will come out with more in next. Thank you
All rights reserved