Phân biệt Stateful vs. Stateless Components
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Đặt vấn đề
Các bạn tiếp xúc với Angular, React, Vue... hay các lib/framework tương tự chắc cũng không xa lạ gì với stateful/stateless concepts. Bài viết này sẽ định nghĩa và đưa ra sự khác nhau giữa khái niệm stateless component và stateful component nhằm giúp chúng ta nắm rõ được concepts này.
Khái niệm stateful/stateless components không nằm riêng trong Angular nhưng trong bài viết này mình xin phép sử dụng Angular 2 để làm các ví dụ giải thích nhé !
Cùng bắt đầu thôi nàoooo !

Thuật ngữ
Đầu tiên, hãy cùng tìm hiểu những khái niệm chung nhất nhé 😺😺
Stateful
When something is
stateful, it is a central point that stores information in memory about the app/component’s state. It also has the ability to change it. It is essentially a “living” thing that has knowledge of past, current and potential future state changes.
Stateless
When something is
stateless, it calculates its internal state but it never directly mutates it. This allows for complete referential transparency meaning that given the same inputs, it will always produce the same output. These are not essentially “living” as they are merely passed information. This means it has no knowledge of the past, current or future state changes.
Components
A component is an isolated piece of behaviour or functionality that allows us to divide behaviour into roles
Impure vs. Pure functions
Chúng ta sử dụng stateful/stateless concepts cho components. Mỗi component và thường có một chức năng riêng biệt, ở điểm này nó khá giống với các functions trong Javascript.
Impure Function=Stateful Component
Pure Function=Stateless Component
Impure (stateful)
Xem đoạn code tính chỉ số BMI từ cân nặng và chiều cao của con người dưới đây:
const weight = parseInt(form.querySelector('input[name=weight]').value, 10);
const height = parseInt(form.querySelector('input[name=height]').value, 10);
const bmi = (weight / (height /100 * height / 100)).toFixed(1);
Đoạn code này hoạt động đúng. Không sai. Song, chúng ta chẳng thể sử dụng lại nó nếu muốn tính toán một chỉ số BMI khác thì quả là Hard code quá đúng không nào. Mình cùng làm cho nó "pure hóa" hơn ở phần dưới nhé 😺😺
Pure (stateless)
Điểm mấu chốt của một pure function là có thể linh hoạt được đầu vào. Ta có thể tạo ra một hàm xử lý logic nhận biến đầu vào và trả về một giá trị mới mà không phụ thuộc vào các biến muốn tính toán.
Với đoạn code phía trên:
const weight = form.querySelector('input[name=weight]').value;
const height = form.querySelector('input[name=height]').value;
const getBMI = (weight, height) => {
let newWeight = parseInt(weight, 10);
let newHeight = parseInt(height, 10);
return (newWeight / (newHeight /100 * newHeight / 100)).toFixed(1);
};
const bmi = getBMI(weight, height);
Hàm getBMI() được xem như là một pure function, có các điểm đặc trưng đặc trưng như:
- Dễ test với các
mocked data - Có thể tái sử dụng
- Có
Input/Output
Stateful vs. Stateless components
Stateful components
Khá giống với Javascript function, stateful component sẽ quyết định hướng xử lý của dữ liệu.
Một số các đặc điểm của stateful component:
- Xử lý luồng dữ liệu thông qua các hàm
- Hứng dữ liệu (thông qua
httpClientchẳng hạn...) - Nhận dữ liệu khởi tạo cũng như
statehiện tại. - Được thông báo bởi các thành phần phi trạng thái khi có gì đó cần thay đổi
- Có thể giao tiếp được với các
services - Có thể có các
Redux actions(ngrx/storehoặcng2redux...)
Stateful Todo component
Để chỉ ra sự khác biệt của concepts này, ta xét một ứng dụng todo đơn giản.
Mình xin lưu ý một chút là trong bài viết này mình không chỉ cách-tạo-ra-một-ứng-dụng mà chúng ta sẽ chỉ tập trung nhìn vào stateful/stateless paradigms để làm rõ ý tưởng thôi nhé ^^
Ta bắt đầu với một thành phần cơ sở App Component:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<todos></todos>
`
})
export class AppComponent { }
Ở App Component, chúng ta render Todos Component có nội dung như sau:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { TodoService } from './todo.service';
@Component({
selector: 'todos',
template: `
<div>
<todo-form
(onAdd)="addTodo($event)">
</todo-form>
<todo-list
[todos]="todos"
(onComplete)="completeTodo($event)"
(onDelete)="removeTodo($event)">
</todo-list>
</div>
`
})
export class TodosComponent implements OnInit {
todos: any[];
constructor(private todoService: TodoService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.todos = this.todoService.getTodos();
}
addTodo({label}) {
this.todos = [{label, id: this.todos.length + 1}, ...this.todos];
}
completeTodo({todo}) {
this.todos = this.todos.map(
item => item.id === todo.id ? Object.assign({}, item, {complete: true}) : item
);
}
removeTodo({todo}) {
this.todos = this.todos.filter(({id}) => id !== todo.id);
}
}
Bạn có thể thấy trong div.wrap cho 2 components stateless <todo-form> và <todo-list>.
<todo-form> không nhận vào input mà chỉ cho ra một output onAdd(). <todo-list> thì nhận todos data qua [todos] binding cùng 2 outputs (onComplete onDelete) và (onComplete onDelete), cho phép component ngoài khai báo kịch bản xử lý.
Stateless components
Stateless component nhận dữ liệu qua property binding (tương tự như arguments trong Javascript) và thông báo sự thay đổi qua sự kiện (tương tự như return block).
Hay nói cách khác, stateless components không bị tác động bởi các component khác nó. Do đó, chúng ta có thể tái sử dụng, dễ dàng test cũng như xóa chúng đi mà không lo lắng về ảnh hưởng của chúng với ứng dụng.
Một vài điểm đặc biệt của Stateless Components:
- Không thực hiện
request/fetchdữ liẹue - Nhận dữ liệu thông qua
property binding - Bắn dữ liệu ra qua
event callbacks - Có thể
renderrastateless componentcon, hay thậm chí cảstateful components - Có thể có các
local UI state
Stateless TodoForm component
Ở TodoForm Component:
import { Component, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'todo-form',
template: `
<form (ngSubmit)="submit()">
<input name="label" [(ngModel)]="label">
<button type="submit">Add todo</button>
</form>
`
})
export class TodoFormComponent {
label: string;
@Output() onAdd = new EventEmitter();
submit() {
if (!this.label) return;
this.onAdd.emit({label: this.label});
this.label = '';
};
}
Component này không nhận bất kì dữ liệu nào từ property binding. Vai trò của nó chỉ là lấy UI state từ ô input và sau đó emit ra component ngoài để thực hiện chức năng nào đó.
Stateless TodoList component
Trong TodoList:
import { Component, Input, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'todo-list',
template: `
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let todo of todos">
<todo
[item]="todo"
(onChange)="onComplete.emit($event)"
(onRemove)="onDelete.emit($event)">
</todo>
</li>
</ul>
`
})
export class TodoListComponent {
@Input() todos;
@Output() onComplete = new EventEmitter();
@Output() onDelete = new EventEmitter();
}
Cả todoList và todoForm đề là các Stateless Component. Đến đây, bạn đã thấy partern của nó chưa?
Stateless Component "chẳng biết gì" về component xung quanh hết mà chỉ truyền dữ liệu qua property bindings và event callbacks.
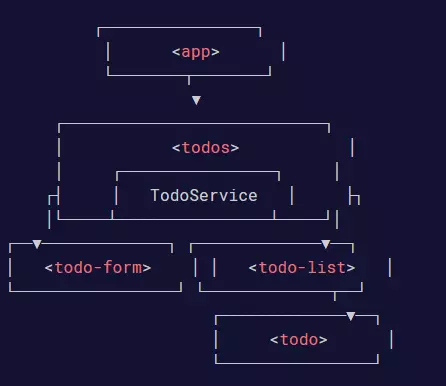
Đây là kiến trúc của App:
Kết
Chúng ta đã điểm qua kiến thức về Stateful/Stateless Component hay khái niệm Pure/Impure. Mong rằng các kiến thức trong bài viết này sẽ phần nào giúp cho các bạn cảm thấy tự tin mỗi khi nói về State Concepts.
Chúng ta nên tận dụng những đặc điểm của chúng để có thể tránh lặp code, dễ bảo trì về sau cũng như làm ra một trang web tối ưu hơn dù bạn sử dụng với bất kì công nghệ nào.

Chúc bạn cuối tuần vui vẻ !
Reference: Ultimates Cources , Medium, Personal Blog.
All rights reserved