[Node.js] Inner workings of Node.js
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 2 năm
I. V8 Engine
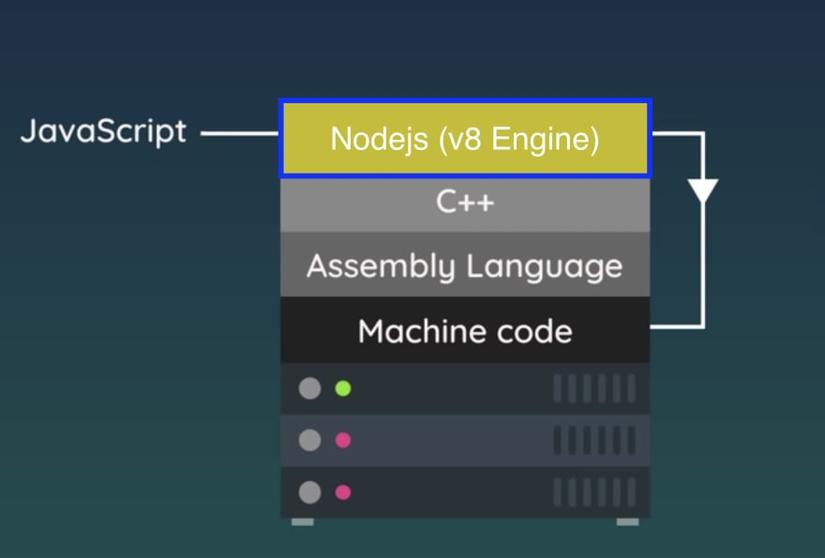
- V8 engine is JavaScript engine embedded in Node.js, it takes JS (computers cannot understand JavaScript) code and converts it into machine code.
II. Common used global objects
- __dirname: returns the current directory's name you are in.
- __filename: returns the absolute path to the current file you are in.
- setTimeout
- setInterval
III. Function expressions
- Using function keyword to define a function inside an expression.
let greeting = function(){
console.log("Hello world!");
}
greeting();
IV. Module & require
1. module
- Node.js treats all JS files as a separate module.
- The code in each module is private to the module unless it is explicitly exported.
// greeting.js aka greeting module
let greeting = function(){
console.log("Hello world!");
}
let greeting2 = function(name){
console.log(`Welcome ${name} to Node.js!`);
}
module.exports = greeting; (1)
// or multiple exports
module.exports.greeting = greeting; (2)
module.exports.greeting2 = greeting2;
2. require('something')
- require keyword refers to a function used to import all objects exported from module.exports from other modules.
- Values return by require function are equal to the module.exports
// app.js
let greeting = require("path-to-greet-module/greeting"); (1)
greeting(); // Hello world!
let greetings = require("path-to-greet-module/greeting"); (2)
greetings.greeting(); // Hello world!
greetings.greeting2("Vivian"); // Welcome Vivian to Node.js!
V. Events module and event emitter
- events module is used to create and handle custom events, it includes EventEmitter class.
- EventEmitter is used to raise and handle custom events.
// gets ref of EventEmitter class
let events = require('events');
// creates an object of EventEmitter
let myEventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
// subscribes for slide using .on or .addListener
// callback fnc will be called when an event is raised
myEventEmitter.on("slide", (data) => {
console.log("Slide is fired: " + data);
});
// raises slide event
myEventEmitter.emit("slide", "Slide smt");
VI. File system
- fs module is used to create, read, update, delete and rename files asynchronously or synchronously.
1. Reading file
- Synchronous operation with fs.readFileSync(path, options).
- Options optional is an object containing the encoding for data specification and flag for operations allowed in the file. Default values are null and r respectedly.
- This version will block code before its finished.
let fs = require('fs');
let output = fs.readFileSync('filename',{encoding: 'utf8', flag: 'r'});
// or
let output = fs.readFileSync('filename','utf8'); // file's content
- Asynchronous operation with fs.readFile(path, options,callbackFnc)
- This version will NOT block code while its reading. callbackFnc is called after reading operation is done.
let fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('filename','utf8',(err, data) => {
if(err)
console.log(err);
else
console.log(data); // file's content
});
2. Writing file
- Synchronous operation with fs.writeFileSync(path,data, options).
- Data can be a string, buffer TypedArray or DataView which can be written to file.
- Options optional is an object containing the encoding for data specification, mode - an integer for file mode and flag for operations allowed in the file. Default values are utf8, 0o666 and w respectedly.
- This version will block code before its finished.
- NOTE: file will be created automatically if it does not exist.
let fs = require('fs');
let data = "Hello world";
fs.writeFileSync('filename',data);
- Asynchronous operation with fs.writeFile(path, data, options)
- This version will NOT block code while its reading.
let fs = require('fs');
let data = "Hello world";
fs.writeFile('filename', data);
3. Creating & removing file/directory
- Removing file
// Synchronous methods
fs.unlinkSync(path)
// Asynchronous methods: delete file if it exists else throw error
fs.unlink(path, (err)=>{});
- Creating & removing directory
// Synchronous methods
fs.mkdirSync("path", options);
fs.rmdirSync("path");
// Asynchronous methods
fs.mkdir("path", () => {});
fs.rmdir("path", () => {}); // throws error if directory is not empty
All rights reserved