Linked List in Rails
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Data structure is one of the significant element to know in computer science. Linked list is one of the simplest and most common data structures. They can be used to implement several other common abstract data types, like lists, stacks, queues etc. , though it is not much common practise to implement those data structures directly by using a linked list as the basis. Today we gonna see how we can make linked list in ruby as it is not a data type in ruby.
Linked List
A linked list is a linear data structure where each element is a separate object. Linked list elements are not stored at contiguous location; the elements are linked using pointers. Each node of a list is made up of two items - the data and a reference to the next node. The last node has a reference to null. The entry point into a linked list is called the head of the list. It should be noted that head is not a separate node, but the reference to the first node. If the list is empty then the head is a null reference. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing more efficient insertion or removal of nodes at arbitrary positions. A drawback of linked lists is that access time is linear (and difficult to pipeline). Faster access, such as random access, is not feasible. Arrays have better cache locality compared to linked lists.
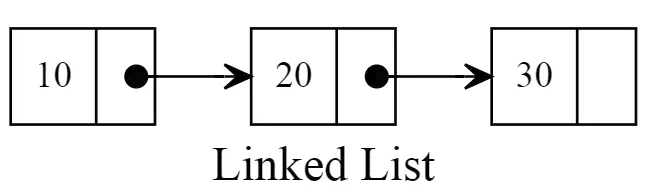
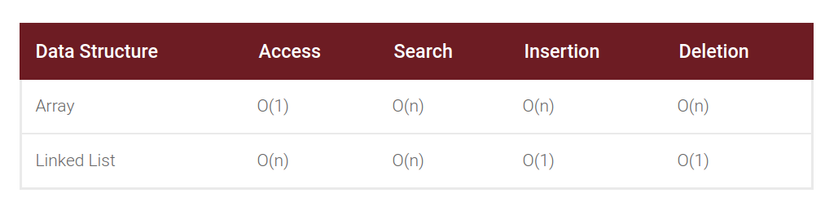
Array vs Linked List
In Ruby it makes no sense to use linked lists due to built-in methods such as shift, unshift, enq, deq, push and pop of array, but it is helpful to know why linked lists can be beneficial. Linked lists’ biggest advantage over arrays is their capability to insert or remove elements without reorganization of the entire data structure. Arrays have indices, so deleting a value at index 0 for example requires every single item to be shifted forward. On the contrary, performing any operations requires access to particular elements of a linked list can be hazardous. For example, finding the last element of a linked list requires scanning every element of the list.
Ruby Implementation
Ruby doesn't have any Linked List class. So we need to create one to use. To implementlinked list class we primarily need a Node class.
class Node
attr_accessor :value, :next
def initialize val, next_node = nil
@value = val
@next = next_node
end
def value
@value
end
def next
@next
end
end
Now that we have a simple Node class. Now we will create our LinkedList Class. In this class, head is the stariong node of the linked list.
class LinkedList
def initialize
@head = nil
end
def head
@head
end
end
Now we will write code to insert data in our list. It finds the last node when appending a new item. Then the LinkedList class will look like -
class LinkedList
def initialize
@head = nil
end
def head
@head
end
def insert value
if @head
find_last.next = Node.new value
else
@head = Node.new value
end
end
def find_last
current_node = @head
while current_node.next != nil
current_node = current_node.next
end
current_node
end
end
Now we will delete an element from the list. Deleting an element also need to be started from head. We need to change to next node of search result node.
class LinkedList
def initialize
@head = nil
end
def head
@head
end
def insert value
if @head
find_last.next = Node.new value
else
@head = Node.new value
end
end
def delete value
return @head = @head.next if @head.value == value
return unless @head.next
current_node = @head
next_node = @head.next
while next_node.next != nil
return current_node.next = next_node.next if next_node.value == value
current_node = next_node
next_node = next_node.next
end
true
end
def find_last
current_node = @head
while current_node.next != nil
current_node = current_node.next
end
current_node
end
end
Now traverse and getting the list. Its just easy. Start from head and get each value until last element.
class LinkedList
def initialize
@head = nil
end
def head
@head
end
def insert value
if @head
find_last.next = Node.new value
else
@head = Node.new value
end
end
def delete value
return @head = @head.next if @head.value == value
return unless @head.next
current_node = @head
next_node = @head.next
while next_node.next != nil
return current_node.next = next_node.next if next_node.value == value
current_node = next_node
next_node = next_node.next
end
true
end
def traverse
return [] unless @head
current_node = @head
list = []
while current_node
list.push current_node.value
current_node = current_node.next
end
list
end
def find_last
current_node = @head
while current_node.next != nil
current_node = current_node.next
end
current_node
end
end
Hope this helps you to get some direction about how to implement linked list in ruby. You can try by yourself other functionalities. Thank you
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list
All rights reserved