Interpolation Search
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm

Searching and sorting is always one of the main thing to know and improve about. Like sorting, searching also get special attention from the computer scientists. Today we will learn about a special searching algorithm named interpolation sort.
Interpolation Search
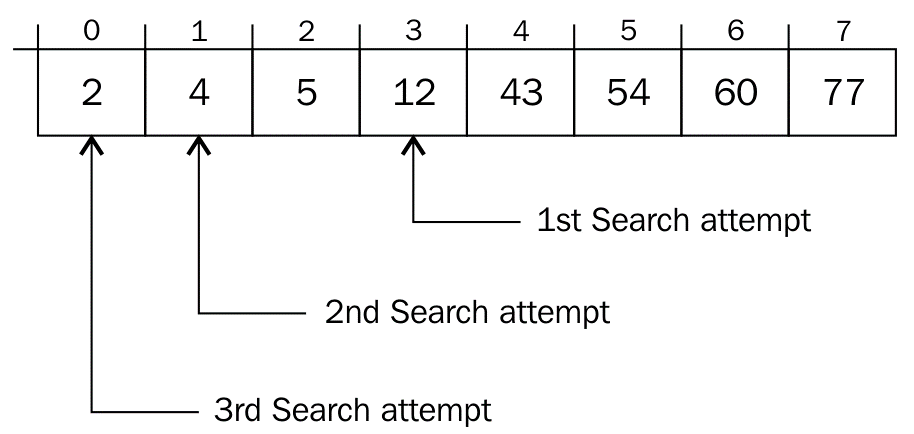
Interpolation search is an algorithm for finding a value in an array that has been sorted by numerical values assigned to the keys. It was first proposed by Mr. W. W. Peterson in 1957. Interpolation search imitates the method by which a person searches telephone directory for a name where the key value by which the book's entries are ordered. Likewise, in each step the algorithm calculates the space in where the remaining search space the searched item can be, depending on the key values at the boundary of the search space and the value of the desired key. The key value actually found at this estimated position is then compared to the key value being searched. If it is not equal, then depending on the comparison, the remaining search atmosphere is reduced to the part before or after the estimated position. This method will only work if calculations on the size of differences between key values are realistic. In compare with binary search, it usually chooses the middle of the remaining search space, emitting one half or the other, depending on the comparison between the key found at the estimated position and the key searched. Morever, it does not require numerical values for the keys, just a total order on them. The remaining search space is reduced to the part before or after the estimated position. The linear search uses equality only as it compares elements one-by-one from the start, ignoring any sorting. In interpolation-sequential search, interpolation is used to find an item near the one being searched for, then linear search is used to find the exact item.
Algorithm
Below are the steps for interpolation algorithm
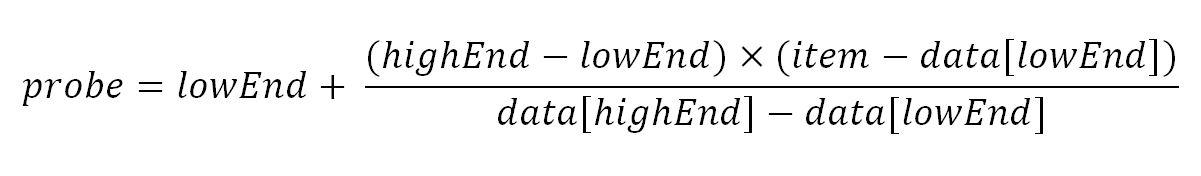
- At first initialize highend as the last value index and lowend to 0. data is the array to be find.
- Therefore in a loop, calculate the value of “pos” using the probe position formula (which is shown above).
- If match is found, return the index of the item, and exit.
- Otherwise if the item is less than the arr[pos], calculate the probe position of the left sub-arrayagain.
- Contrasly calculate the same in the right sub-array.
- Repeat until a match is found or the sub-array reduces to zero.
Implementation
Following is the ruby implementation
def interpolation_search arr key
low = 0
high = arr.size - 1
while (arr[high] != arr[low]) && (key >= arr[low]) && (key <= arr[high])
mid = low + ((key - arr[low]) * (high - low) / (arr[high] - arr[low]))
if arr[mid] < key
low = mid + 1
elsif key < arr[mid]
high = mid - 1
else
return mid
end
end
return low if key == arr[low]
-1
end
Complexity
On an average the interpolation search makes about log(log(n)) comparisons if the elements are distributed uniformely, where n is the number of elements to be searched. In the worst case it can make up to O(n) comparisons. Worst case might happen when the values of the targets increase simultaneously.
Hope it helps. Thank you References: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/interpolation_search_algorithm.htm
All rights reserved