Implement ReactJs in Ruby on Rails using react_on_rails gem
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
In this post, we look at react with webpack inside rails. We will do that using react_on_rails gem.
react_on_rails vs react-rails gem
Why the react_on_rails gem! The key difference with react-rails gem is that,
- react_on_rails gem uses ES6 by default and the state of are javascript tooling including webpack instead of relying completely on Rails asset pipeline.
- It also doesn't depend on Jquery.
- react_on_rails uses webpack for ES6 compilation and than uses the rails asset pipeline to simple include the bundled asset file that webpack generates.
- You can use npm to install javascript libraries instead of having to use gems or manually downloading and including them in our application manifest file.
Hence it gives us a lot more power at the cost of installing and managing a few extra things and most of the power comes from using webpack.
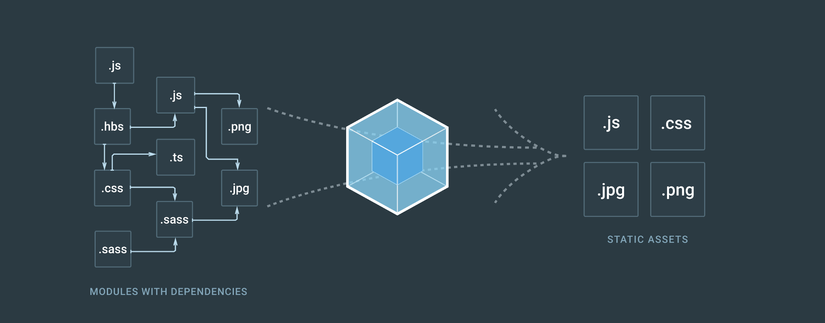
Webpack
So what is webpack! It is a module bundler. It is a tool for processing and bundling our assets in convenient chunks serving them efficiently to the client. It can automatically find all required dependencies. Convert our JSX and es6 codes to es5 and concatenates our assets into bundles making sure all the codes loaded in the correct order. But because it is so powerful, it can be very confusing specially when you are a begineer. You can get lost studying everything about webpack. So for the purpose of this lesson, we're simply going to see how the react_on_rails gem sets up Webpack for us.
Lets start with react_on_rails app. Assume that you have nodejs installed in your pc. You can ckeck the version like as
node -v
I am going to create a new app, lets call it react_on_rails_demo to show you the default setup of the react_on_rails gem.
rails new react_on_rails_demo
Than add the react_on_rails gem to your gem file and install it.
gem "react_on_rails", "11.0.0"
gem "webpacker", "~> 3"
Run the command
bundle install
rails webpacker:install
rails webpacker:install:react
Before running the generator, the gem requires us to commit all our changes.
git init
git add --all
git commit -m "Initial commit"
Now we will run the generator
rails generate react_on_rails:install
This will create a bunch of files, directories and add some configurations to our app. We can run the app using foreman.
Foreman
Forman is a gem to run app where we have more than one process to run at once. We tell foreman what process to run in a procfile. In our case, we need to run rails as well as webpack . The react_on_rails gem generated a procfile that called Procfile.dev. Lets run the foreman using the following command
foreman start -f Procfile.dev
The Procfile.dev file has two processes: The web process will run on port 3000 and the client process will do a cuple of things. First, it deletes all files under public/packs/ directory and than require the webpacker.yml in the bin/webpack file.
web: rails s -p 3000
client: sh -c 'rm -rf public/packs/* || true && bundle exec rake react_on_rails:locale && bin/webpack -w'
If we look at the webpacker.yml file, we can see a lot of configurations here.
- First look at the
source_entry_path. source_entry_path defines the entry point where webpack start reading all dependencies. - Next
public_output_pathdefines where webpack is going to save the bundled output. extenxionswill decide which file extensions will be accepted.
That is briefly the default setup that react_on_rails do for us. If we go to the source_entry_path that is inside the javascripts/packs/hello-world-bundle.js file:
import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails';
import HelloWorld from '../bundles/HelloWorld/components/HelloWorld';
// This is how react_on_rails can see the HelloWorld in the browser.
ReactOnRails.register({
HelloWorld,
});
Here you can see the gem is using the ES6 syntax by default. First it imports ReactOnRails from the react-on-rails. This is the javascript api of the gem. Than it imported HelloWorld component from ../bundles/HelloWorld/components/HelloWorld path. Finally it register it with the gem api. This is how react_on_rails able to use a component from a rails view.
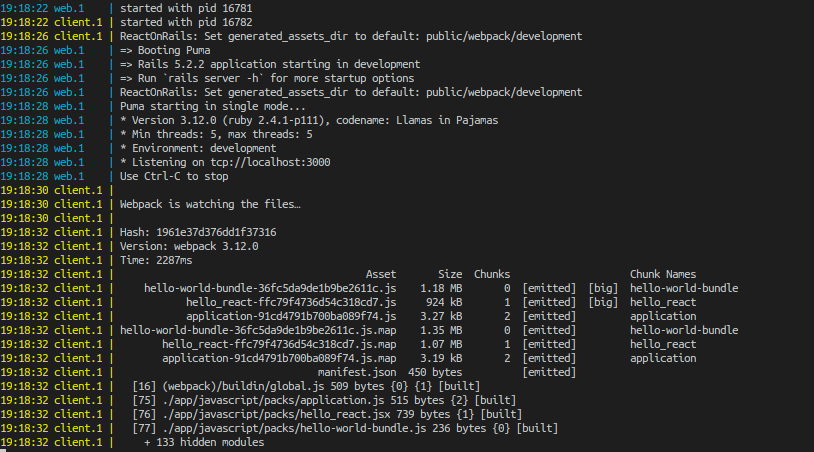
And when the foreman will start and console will be like as follows
Lets look at the package.json file:
{
"name": "react_on_rails_demo",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"@rails/webpacker": "3.5",
"babel-preset-react": "^6.24.1",
"prop-types": "^15.7.2",
"react": "^16.8.2",
"react-dom": "^16.8.2",
"react-on-rails": "11.2.2"
},
"devDependencies": {
"webpack-dev-server": "2.11.2"
}
}
It list a bunch of packages our app needs as its dependencies on the production and development environment. You can see the dependencies is for both of the development and production but devDependencies is only for development. When we run npm install, all these packages get installed and they all go in the directory called node modules.
References: ShakaCode
All rights reserved