Firebase Cloud Store với Redux-Saga
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Cloud Firestore cùng với Realtime Database là một trong hai lưu trữ đám mây, cho phép client thao tác xử lí database. Cloud Firestore cũng như Realtime Database đều cho phép hỗ trợ đồng bộ dữ liệu theo thời gian thực. Nếu bạn đã từng sử dụng Realtime Database của firebase thì sẽ thấy những câu querry kiểm trả điều hiện hay sort của nó khá phức tạp và đấy là điều đã được cải thiện thành công và trực quan hơn rất nhiều trong Cloud FireStore (gọi firestore cho tiện hơn) Ví dụ một 'doccument' đại diện cho user 'alovelace' sẽ dạng như sau
alovelace
first : "Ada"
last : "Lovelace"
born : 1815
Các doccument tồn tại trong 'collections', nó đơn giản là một thùng chứa các doccument. Ví dụ bạn có tập 'users' collections chứa các người dùng khác nhau, mỗi người dùng là một đại điện của 'doccument'
users
alovelace
first : "Ada"
last : "Lovelace"
born : 1815
aturing
first : "Alan"
last : "Turing"
born : 1912
Firestore lưu trữ dữ liệu như việc lưu trữ doccument, và chúng ta sẽ quen với từ khoá 'collection' nhiều hơn trong việc truy xuất dữ liệu từ các tập doccument.
Trong cloud firestore , đơn vị lưu trữ là 'doccument'. Một 'doccument' là một bản ghi chứa các trường và map đến giá trị của mỗi trường. Mỗi doccument sẽ được định nghĩa bởi một name.
Việc lưu trữ dự liệu được thể hiện một cách trực quan hơn dưới dạng model data hơn là những guidkey- data như trước kia trong RealTime Database
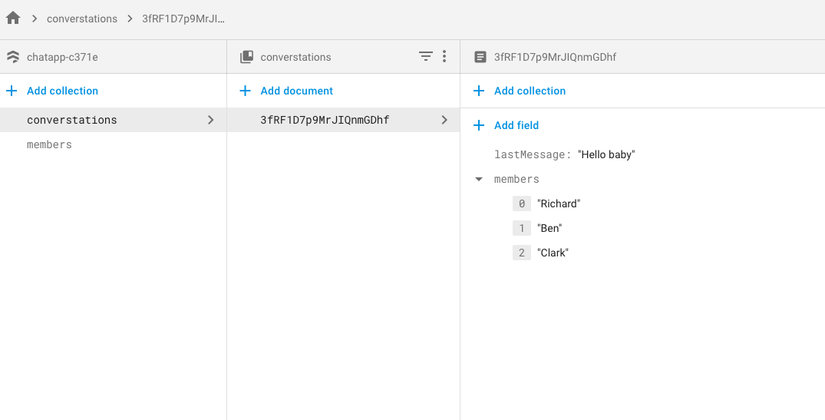 Mình cho rằng đây là điểm đâu tiên khiến cho FIrestore tương lai sẽ là nơi tiếp cận dễ dàng hơn cho người sử dụng.
Mình cho rằng đây là điểm đâu tiên khiến cho FIrestore tương lai sẽ là nơi tiếp cận dễ dàng hơn cho người sử dụng.
Querry database
Tiếp theo là việc query với firestore,
// Create a reference to the cities collection var citiesRef = db.collection("cities");
// Create a query against the collection. var query = citiesRef.where("state", "==", "CA"); Đơn giản chỉ với từ khoá when(trường kiểm tra, toán tử, value kiểm tra) là đã có một câu select kiểm tra. Bạn cũng có thể truy vẫn dữ liệu khó hơn với các toán tử như array-contains, hay những câu select nhiều toán tử kiểm tra citiesRef.where("regions", "array-contains", "west_coast") citiesRef.where("state", "==", "CO").where("name", "==", "Denver")
Hoặc những câu querry vừa kết hợp điều kiện, order và limit khá điển hinh thì cũng được support một cách đầy đủ và đơn giản citiesRef.where("population", ">", 100000).orderBy("population").limit(2)
Phân trang dữ liệu.
Phân trang dữ liệu là một yêu cầu khá là normal gần như bắt buộc phải có. Để làm điều này bạn có thể sử dụng thêm một số câu lệnh như orderBy, startAfter, startAt, limit var first = db.collection("cities") .orderBy("population") .limit(25); Nói chung việc querry data với firestore đã trở nên đởn giản gần gữi hơn rất nhiều. Vì thế mình nghĩ sẽ không hề khó để mọi người tiếp cận hiểu chúng ta cần làm gì để có một câu querry đáp ứng được business
Thế tạo một lớp giao tiếp với Firestore
Thực ra bạn có thể không cần quan tâm gì phần này và bay thẳng tới trang chủ của firebase mình nghĩ nó cũng support khá đầy đủ hơn bất kì đâu. Tuy nhiên như các bạn biết trong 1 dự án có kiến trúc thì việc xử lí việc kết nối, kiểm tra auth hay một đống câu querry dữ liệu từ firebase nếu không được thiết kết tốt thì cũng sẽ khó cho việc tiếp cận phát triển lâu dài. Cũng như một số dự án do điều kiện chúng ta sẽ lựa chọn Firestore như là giải pháp hiện tại và tương lai có thể được thay thế bởi RestAPI chả hạn. Mình sẽ tạo 1 tầng giao tiếp với firestore và đặt nó trong tầng services (đây là tầng thông thường mà bạn có thể đặt các REST API)
import * as firebase from 'firebase';
import 'firebase/firestore';
import Config from 'src/config';
const firebaseConfig = {
apiKey: Config.FIREBASE_API_KEY,
authDomain: Config.FIREBASE_AUTH_DOMAIN,
databaseURL: Config.FIREBASE_DATABASE_URL,
projectId: Config.FIREBASE_PROJECT_ID,
storageBucket: Config.FIREBASE_STORAGE_BUCKET
};
firebase.initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
export { firebase };
Cái này bạn nào chưa biết lấy ở đâu thì hãy vào https://console.firebase.google.com => đi đến project của mình => chọn project overview => project setting sẽ có các thông tin trên nhé mọi người. Tiếp theo là các action CRUD với các documentRef firestore
import { buffers, eventChannel } from 'redux-saga';
import { call, fork } from 'redux-saga/effects';
export const getCollectionRef = (rsf, pathOrRef) => {
return typeof pathOrRef === 'string' ? rsf.app.firestore().collection(pathOrRef) : pathOrRef;
};
export const getDocumentRef = (rsf, pathOrRef) => {
return typeof pathOrRef === 'string' ? rsf.app.firestore().doc(pathOrRef) : pathOrRef;
};
function* addDocument(collectionRef, data) {
const collection = getCollectionRef(this, collectionRef);
return yield call([collection, collection.add], data);
}
function* deleteDocument(documentRef) {
const doc = getDocumentRef(this, documentRef);
return yield call([doc, doc.delete]);
}
function* getCollection(collectionRef) {
const collection = getCollectionRef(this, collectionRef);
return yield call([collection, collection.get]);
}
function* getDocument(documentRef) {
const doc = getDocumentRef(this, documentRef);
return yield call([doc, doc.get]);
}
function* setDocument(documentRef, data, options) {
const doc = getDocumentRef(this, documentRef);
return yield call([doc, doc.set], data, options);
}
function* updateDocument(documentRef, ...args) {
const doc = getDocumentRef(this, documentRef);
return yield call([doc, doc.update], ...args);
}
Sau khi implement các function cho việc thao tác dữ liệu cơ bản, mình sẽ export nó vào chung 1 class để việc sử dụng các function mang tính chung hơn
import firestore from './firestore';
import { firebase } from './initialize';
class WrapFirebase {
constructor(firebaseApp) {
this.app = firebaseApp;
this.firestore = {
addDocument: firestore.addDocument.bind(this),
deleteDocument: firestore.deleteDocument.bind(this),
getCollection: firestore.getCollection.bind(this),
getDocument: firestore.getDocument.bind(this),
setDocument: firestore.setDocument.bind(this),
updateDocument: firestore.updateDocument.bind(this)
};
}
}
const wrapFirebase = new WrapFirebase(firebase);
export default wrapFirebase;
Tiếp theo là việc sử dụng call các function đã implement như là call 1 API REST- nên mình sẽ đẩy em nó vào trong phần gọi sử lí rest api ( cái này chỉ là để cho mọi người hiểu với thiết kế như vậy việc remove 1 lớp firebase sang 1 REST API sẽ không tốn effort nào cả trong tương lai nếu có sự thiết kế trước
import { put, takeLatest, all } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import { GET_ModelXX, GET_ModelXX_FAIL, GET_ModelXX_SUCCESS } from 'reduxConstants/actions';
import { modelXXServices } from 'services';
function* getModelXXWorker(action) {
try {
const data = yield modelXXServices.getDataModelXXsPublic();
yield put({
type: GET_ModelXX_SUCCESS,
payload: { data }
});
} catch (e) {
yield put({ type: GET_ModelXX_FAIL, errors: e.errors });
}
}
export default function* modelXXSaga() {
yield all([takeLatest(GET_ModelXX, getModelXXWorker)]);
}
Và việc gọi service này thì sẽ bình thường trong Redux-Saga như sau
import WrapFirebase from 'services/firebase';
import { call } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import _ from 'lodash';
import RestClient from '../RestClient';
export default class ModelXXServices {
constructor() {
this.wrapFirebase = WrapFirebase;
}
*getDataModelXXsPublic() {
const snapshot = yield call(this.wrapFirebase.firestore.getCollection, 'modelXX');
let result;
snapshot.forEach(obj => {
result = {
...result,
[obj.id]: obj.data()
};
});
return _.map(result, (val, uid) => {
return { ...val, uid };
});
}
}
Thanks mọi người.
All rights reserved