Do you know zero-watermarking??
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Zero-watermarking is a technique for copyright protection. In general, the feature data of the content are encrypted with the copyright data to generate ownership share. The master share is the feature data of the content itself. The master share is registered to certification authority for copyright confirmation. When required, the copyright data can be retrieved by decrypting of the master share and the ownership share. Since zero-watermarking does not embed the watermark information into the digital content, the quality of the processed content is not degraded.
We explain the proposal of zero-watermarking using robust VMF (visual map feature). The main idea is to combine the QR decomposition with the 1D-DCT for constructing the robust share files of the zero-watermarking. By using the proposed VMF and PVMF, we easily improve the robustness of zero-watermarking and reduce the computation cost of the proposed methods.
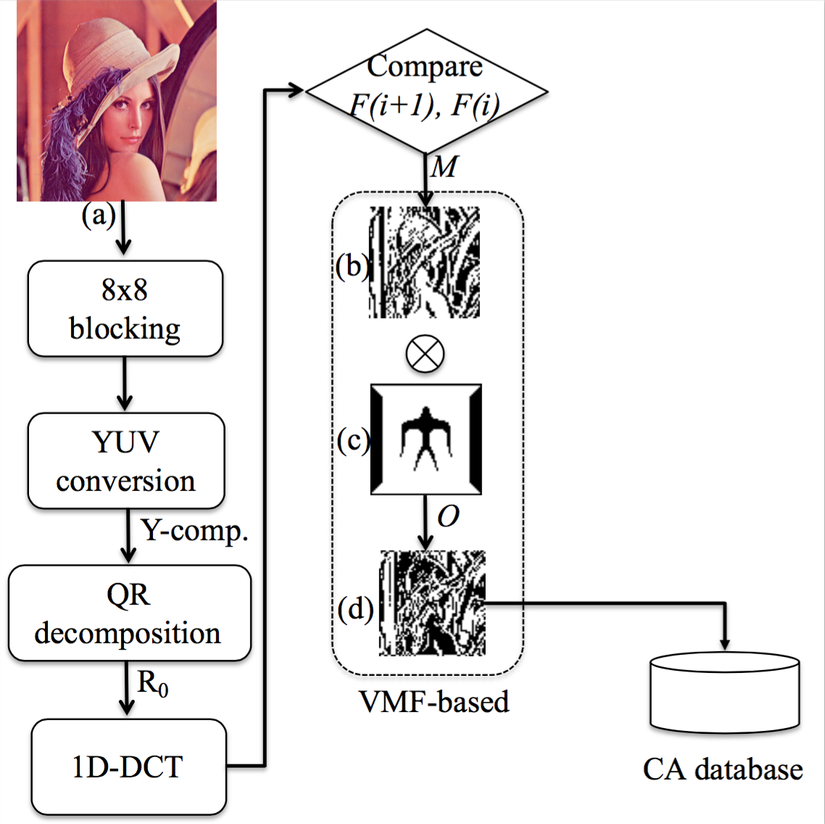
Fig 1. Overview of VMF
Generation of VMF
The overview of our proposed VMF method is shown in Fig. 1. Suppose is image feature generation function. Four steps that involved in to generate the VMF is explained as follows:
- Convert the RGB image to YUV color space. Divide Y-component into the non-overlapping blocks of size . The number of non-overlapping blocks is .
- Apply QR decomposition on each non-overlapping block to obtain .
\begin{equation}
\mathbf B = \mathbf Q \mathbf R,
\end{equation}
where is matrix and is an upper triangular matrix. Let and are described as
$\mathbf B=[\mathbf b_1, \mathbf b_2, ..., \mathbf b_n]$
and
$\mathbf Q=[\mathbf q_1, \mathbf q_2, ..., \mathbf q_n]$
, respectively, where and are column vector.
- Apply 1D-DCT on each to retrieve the DC coefficients .
- Two consecutive DC coefficients are compared to generate the VMF of the original image. This VMF is used as the master share (Fig 1 (b)) and each point of is generated by comparison of and :
M(x,y) = \left\{ \begin{array}{rl}
1 &\mbox{ if $F(i+1) > F(i)$}, \\
0 &\mbox{ otherwise},
\end{array} \right.
where .
Therefore, is generated by . The visibility of can be observed by Fig 1(b). holds the robust edge feature of the original image.
Construction of ownership share
The ownership share (Fig 1(d)) is generated by encryption of the master share with the copyright data (Fig 1(c)). To obtain the ownership share , we apply the XOR operation between and with as follows:
\begin{equation}
O=M\oplus W, ~O_p=M_p\oplus W.
\end{equation}
Copyright identification
Suppose the property dispute concerning the suspected image happens. The CA should judge the rightful owner of the suspected image. The CA asks the owner to provide the secret key and extracts the master share of by using the same algorithm. That means
In case of VMF-based method, CA can obtain the watermark as follows:
\begin{align}
W'=M'\oplus O = \mathbf C (I') \oplus \{\mathbf C (I) \oplus W\} \nonumber \\ \Rightarrow ~W'=W \mbox{ if } \mathbf C (I')=\mathbf C (I).
\end{align}
According to , CA can judge the rightful owner of the suspected image.
Experimental results
To assess the performance of the proposed algorithm, we conduct ten color images of the well known SIDBA (Standard Image Data-BAse) database\footnote{http://decsai.ugr.es/cvg/index2.php}. All test images are with size pixels. The conducted images are shown in \figref{original}. The watermark image is a binary image with size which is shown in Fig 1(c).

Fig 2. Original images
In order to evaluate the quality of watermarked images, we employ PSNR (Peak Signal to Noise Ratio) criterion. The PSNR of pixels image of and is calculated as follows:
\begin{eqnarray}
&&\hskip-1em PSNR = 20\log\frac{255}{MSE}\ \ \ \ \ {\rm [dB]},\\
&&\hskip-1em MSE = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N\times N}\displaystyle \sum^{N-1}_{i=0}\sum^{N-1}_{j=0}\{I(i,j)-I'(i,j)\}^2},\nonumber \\
&&\hskip-1em (MSE: \mbox{Mean Square Error}).\nonumber
\end{eqnarray}
To judge the robustness, we use the normalized correlation (NC) value between the original watermark and the extracted watermark . The NC value is calculated as follows:
\begin{equation}
NC = \frac{\displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^{L}\displaystyle\sum_{j=0}^{L} [W(i,j)\times W'(i,j)]}{\displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^{L}\displaystyle\sum_{j=0}^{L}[W(i,j)]^2},
\label{eq:ncc}
\end{equation}
where is the size of .
Attacked evaluation
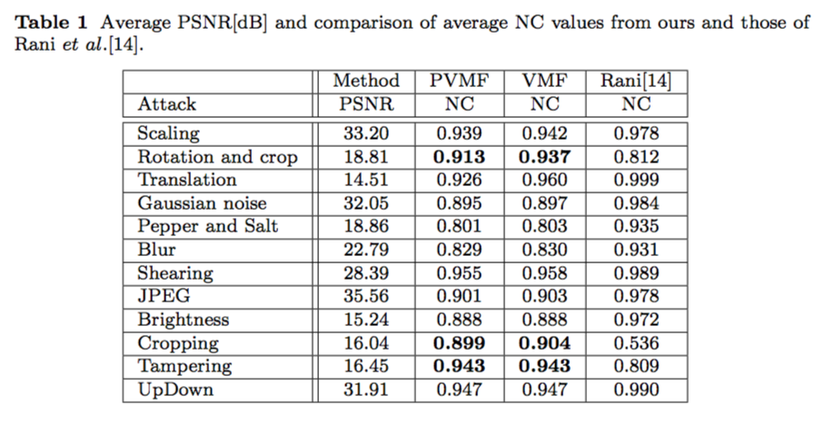
Fig 3. Attacked results
The proposed method is robust against almost the attacks in Fig 3 since the average NC values are over 0.8. Therefore, our method can be applied for the copyright protection applications. Ours is more robust against only `rotation and crop', cropping, and tampering attacks as compared to the method of Rani . The reason is that our VMF can be remained under those attacks whereas the feature of Rani may be strongly affected.
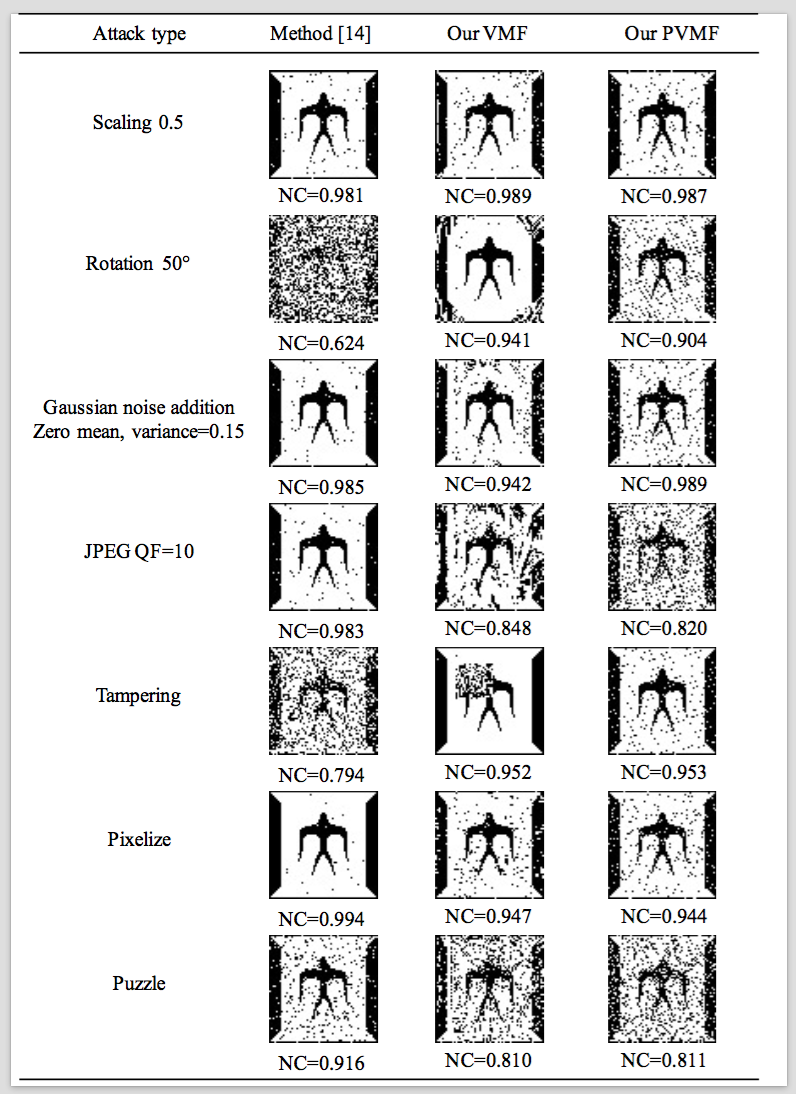
Fig 4. NCs
Some extracted watermarks using the distorted Lena images are shown in Fig 4. The corresponding distorted images are shown in Fig 5. It includes the Photoshop software processing (Pixelize and Puzzle). It is clear that our VMF is more superior than Rani in some cases.
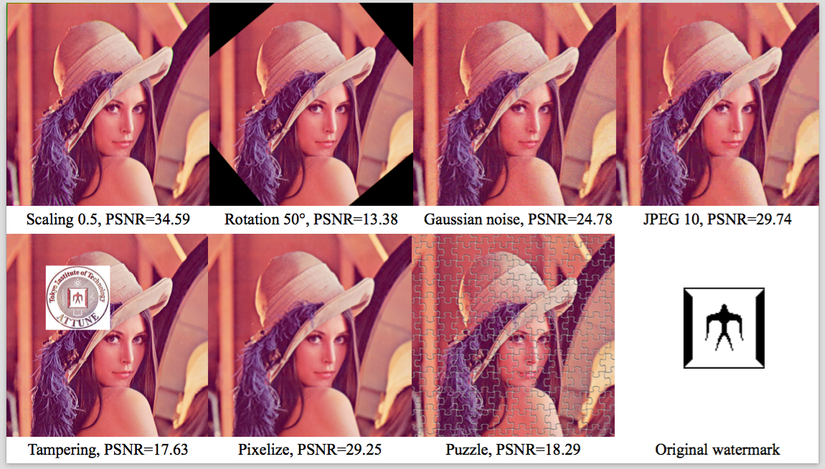

Fig 5. Attacked images
Conclusion
In this work, we have proposed a zero-watermarking method based on the encryption of VMF with the copyright information. In our methods, the original image is not affected by watermark embedding. The watermark size is also not limited. Since our proposed method preserve the feature of entire image, therefore, it especially is robust against strong cropping and tampering attacks. Certainly, it can resist against the common processing and geometric attacks. Moreover, the consuming time of our methods is lower than \cite{Rani2}.
All rights reserved