Database Sharding
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
When an application sees the rise of consumer and user in a large proportion, it needs to be scaled to balance the number of user and data availability. The applications and websites which lives on data and information, it’s pretty difficult to scale down with the data availability and integrity option. As Nobody can say about the use and user involvement for an application, so some developers follow some techniques to do the scaling dynamically. Sharding is one of them.
Database Sharding
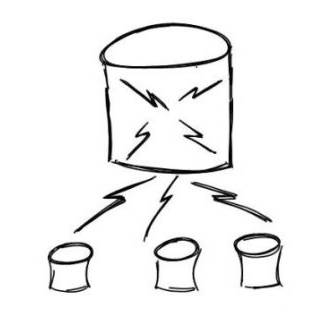
Sharding is the technique of splitting up large jackfruit into smaller chunks called shards that are gathered across multiple servers. A shard is essentially a horizontal data partition that contains a subset of the total data set, and therfore it's duty is responsible is to serve a part of the overall workload. If you do not know what is horizontal partitioning, Then Let me say. Database can be partitioned in two ways.
- Horizontal Partitioning: Data is splitted and stored in different cluster.
- Vertical Partitioning: Database column is splitted in different cluster
![]()
Advantage
-
Database sharding prevents single point error in a very convenient way. As in sharding data is splitted in multiple place, so failure of one cluster will only cause unavailability for that cluster. Other sets can work perfectly. On the other hand unshredded database will cause the whole server down if there is any problem in any part of the data.
-
Sharded database is very bandwidth efficient. Because in sharded data we have multiple data centre. So we can write in them simultaneously without waiting in the queue for others to finish its function.
-
Getting result out of a Big unsharded database through a query is a very slow event. Because it need to search in every row the database to find the desired result. So more the data, less the performance. On the other hand. in shrarded database. finding data almost work in divide and conquror method. Fist it search the key and then based on the key it eliminate clusters which surely do not have the result.
![]()
Disadvantage
-
Like the merge sort, we need to take an attribute as sharding comparator. But sometimes it got defficult to find a value for sharded comparator. So as a result, somtimes one chunk become larger and larger then other chunks of data. in That case all the advantages of sharding neutralised because the that large chunk runs like unsharded database.
-
To be precise, sharding process is very critical like backbone operation of old people. If it is done perfectly, it will ease your applications life. But if this process is not done in correct way, it can create more and more problems like data lose or corrupt table etc. Also fixing problems generated from sharding is another pain in the head. Developers got confused to store data in the system.
-
In some cases, we need to merge data from different shards. This process is way to complex and there is a higher possibility to break the availability in CAP theorem
![]()
Sharding Criteria
-
a. Key or Hash-based partitioning: Under this process, we apply a hash function to some key attributes of the entity we are storing; that yields the partition number. For example, if we have 100 DB servers and our ID is a numeric value that gets incremented by one each time a new record is inserted. In this example, the hash function could be ‘ID % 100’, which will give us the server number where we can store/read that record. This approach should ensure a uniform allocation of data among servers. The fundamental problem with this approach is that it effectively fixes the total number of DB servers, since adding new servers means changing the hash function which would require redistribution of data and downtime for the service. A workaround for this problem is to use Consistent Hashing.
-
b. List partitioning: In this scheme, each partition is assigned a list of values, so whenever we want to insert a new record, we will see which partition contains our key and then store it there. For example, we can decide all users living in Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, or Denmark will be stored in a partition for the Nordic countries.
-
c. Round-robin partitioning: This is a very simple strategy that ensures uniform data distribution. With ‘n’ partitions, the ‘i’ tuple is assigned to partition (i mod n).
-
d. Composite partitioning: Under this scheme, we combine any of the above partitioning schemes to devise a new scheme. For example, first applying a list partitioning scheme and then a hash based partitioning. Consistent hashing could be considered a composite of hash and list partitioning where the hash reduces the key space to a size that can be listed.
Although sharding is not naively supported by every database engine and for that sharding often requires a “mind your own business” mentality. This means that documentation for sharding or tips for troubleshooting problems are often difficult to find. But still it is very useful for data scaling.
Thank you for reading out this article. For more You can see:
http://www.agildata.com/database-sharding/
https://medium.com/@jeeyoungk/how-sharding-works-b4dec46b3f6
All rights reserved