Database architecture
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm
Database architecture
I'm a beginer who have just already learned this knowledge so it's inevitable that in this blog there are some flaws. If there's some points in this blog which are wrong, please comment to let me know =(((
Deployment topologies are the arrangement or the architecture for the flow of getting and querying data between clients and the database or DBMS.
In terms of on-premise architectures:
There are 3 kinds of architecture: one-tier, two-tier, and three-tier architecture.
A. On-premise architecture
I. Local architecture
One-tier architecture:
It also refers to the local topology. You can deploy your database on your own laptop which is often limited to a single user, which is useful for testing or development, or when the database resides in the local application.
II. Client-server architecture:
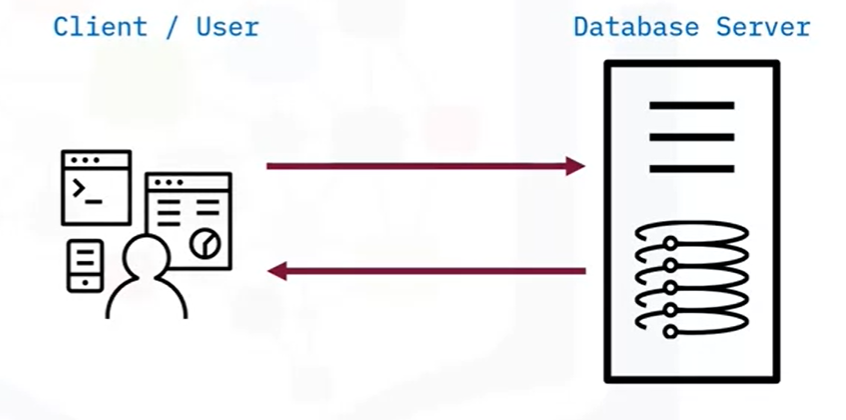
A database resides on a database server that is remote.
Users communicate with the database via the client systems which are webpages or local applications. ( in this case, the client application/server communicates directly to the database server to get the data)
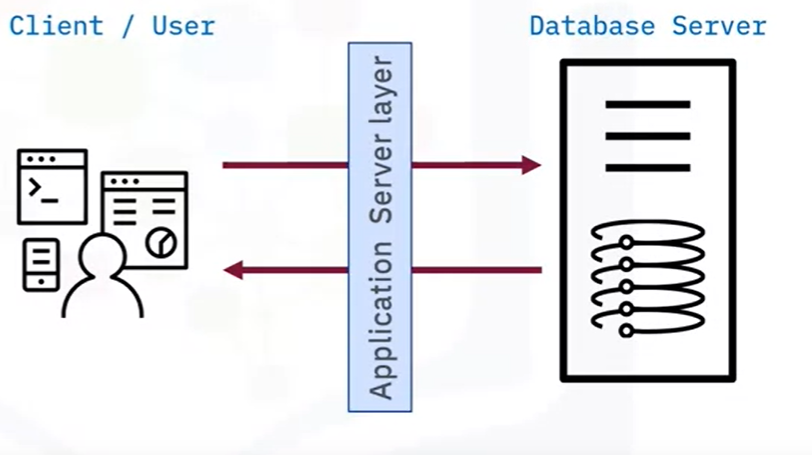
In some cases, there is a middle-tier between a client-server and a database server, which is typical for multi-user scenarios or production. (in this case, there is an intermediate layer, the user gets data via the client application(webpages, apps,..) and the client application communicates with the database server via the application server layer (not in a direct way anymore).
1.Two-tier architecture:
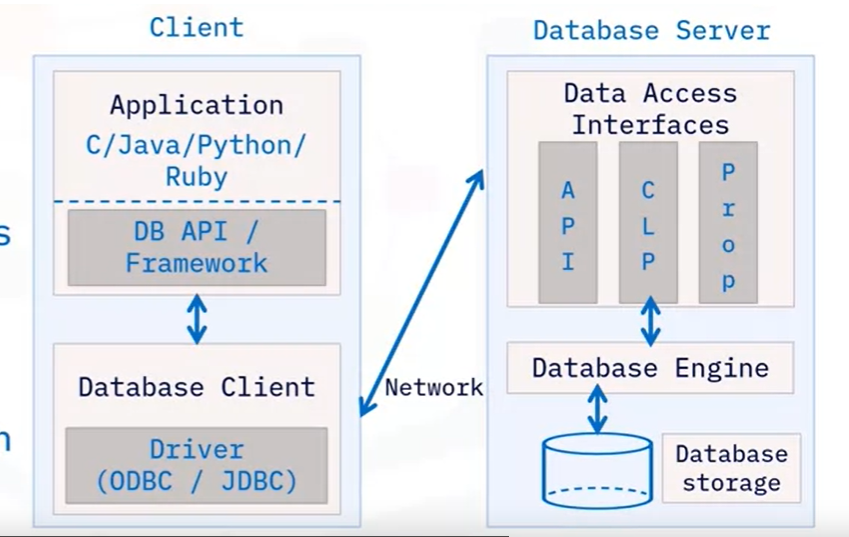
In this architecture, users can get data from the applications. Applications can communicate with databases via some sorts of database APIs or frameworks.
A database client is belonged to the database server but is installed in the client system or local client which has some drivers like ODBC/JDBC to retrieve data.
In the database server (DBMS, there are 3 internal tiers such as a data-access layer, an engine layer, and a storage layer.
The data access layer communicates with the database client. The data access layer contains APIs corresponding to each kind of drivers like ODBC,JDBC; CLP and Prob.
DBMS contains database engine to compile query, retrieve and process data and return the result set.
The database storage is where data resides which can be a local or remote storage.
2.Three-tier architecture:
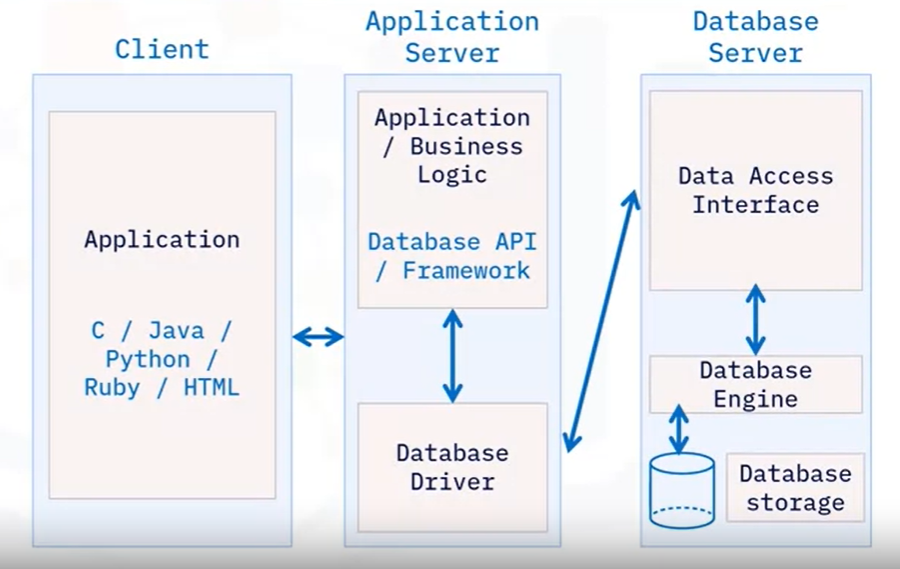
There are 3 layers.
End-users interact with presentation layers which are typically webpages, apps,…
Client applications communicate with the application server over the network.
An application server can have a business logic and database APIs or Frameworks which communicate with the database server via the database driver or APIs which reside on the same tier. (database driver is the database client in the 2-tier architecture).
The database driver or APIs interacts with the database server via the database interface and then compiles, process, and return data in the database engine. Database storage stores data.
B. Cloud-based architecture:
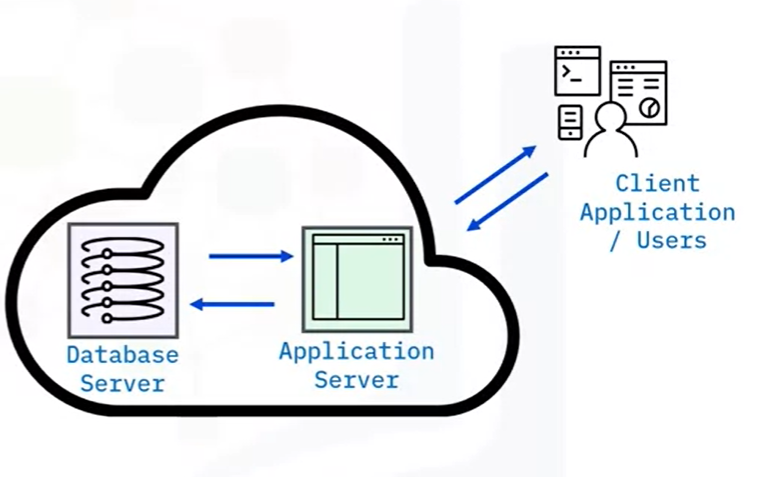
The database resides in the cloud environment.
Users can easily access the cloud without having to download or install DBMS.
Client applications can communicate with cloud servers via the application server or APIs or interfaces.
All rights reserved