Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật trong Javascript
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Hello mọi người, trong series này mình sẽ tổng hợp lại một số cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật phổ biến trong Javascript và chia sẽ đến các bạn.
Bài viết này nhằm mục đích khởi đầu cho một số bạn chuẩn bị phỏng vấn xin việc về cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật.
Cụ thể, trong bài viết này mình sẽ giới thiệu 3 cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật:
- Stack
- Queue
- Binary Search tree
1. Stack
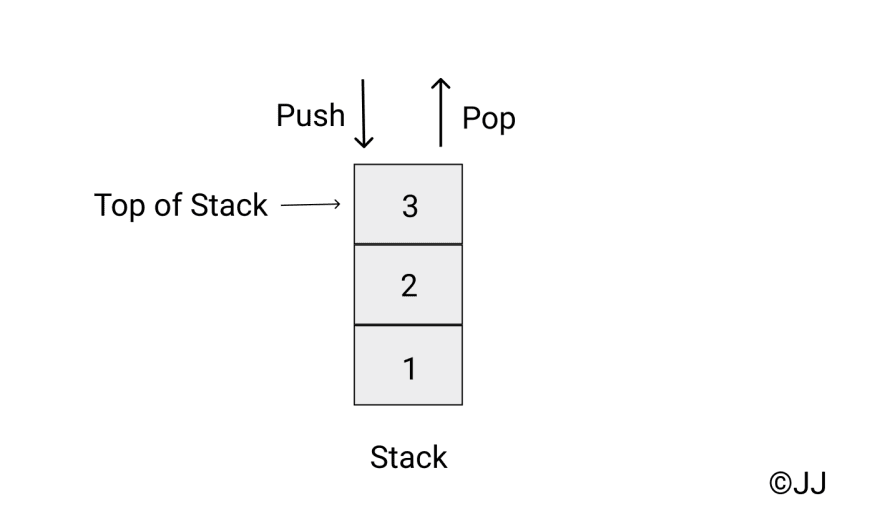
Stack là một cấu trúc dữ liệu tuyến tính tuân theo quy tắc LIFO (Last In First Out) hoặc FIFO (First In Last Out). Có 2 phép tính chính trong stack.
- Push - Thêm một phần tử lên đầu
stack - Pop - Lấy ra một phần tử được thêm gần nhất ( phần tử đầu stack)
![]()
Chúng ta hãy xem code demo dưới đây
class Node {
contructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class Stack {
contructor() {
this.top = null;
}
push(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
node.prev = this.top;
this.top = node;
}
pop() {
if (this.top) {
let value = this.top.value;
this.top = this.top.prev;
} else {
return 'Stack is empty'
}
}
}
let stack1 = new Stack();
stack1.push(1);
stack1.push(2);
stack1.push(3);
console.log(stack1.pop()); // 3
console.log(stack1.pop()); // 2
console.log(stack1.pop()); // 1
console.log(stack1.pop()); // stack is empty
2. Queue
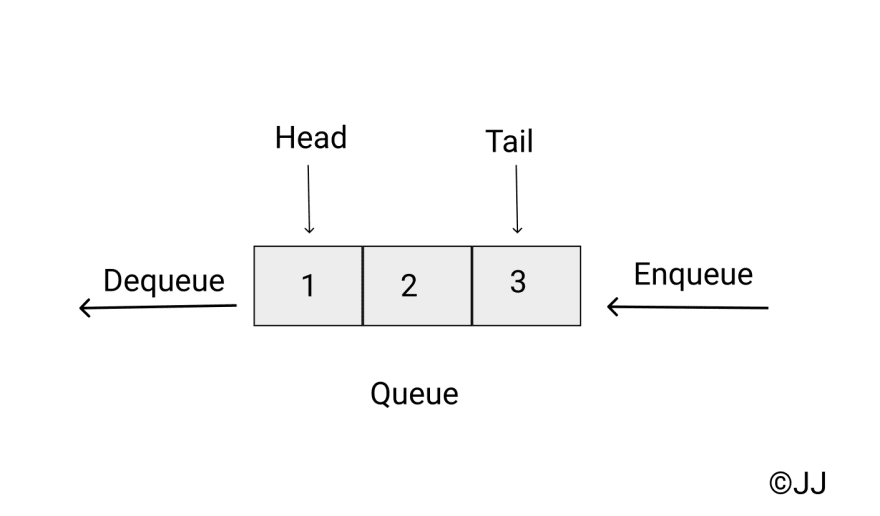
Queue cũng là cấu trúc dữ liệu tuyến tính. Queue tuân theo quy tắc FIFO. Có 2 phép tính chính trong Queue:
- Enqueue - Thêm một phần tử vào cuối Queue
- Dequeue - Xoá một phần tử từ đầu Queue
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.value = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
enqueue(val) {
// to tail
let node = new Node(val);
if (!this.head) {
//if queue is empty, point head and tail to this new node
this.head = this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node; // make new node as tail
}
}
dequeue() {
// from head
if (this.head) {
let val = this.head.value;
this.head = this.head.next;
return val;
} else {
return 'Queue is empty';
}
}
}
let q1 = new Queue();
q1.enqueue(1);
q1.enqueue(2);
q1.enqueue(3);
console.log(q1.dequeue()); // 1
console.log(q1.dequeue()); // 2
console.log(q1.dequeue()); // 3
console.log(q1.dequeue()); // Queue is empty
3. Binary Search Tree
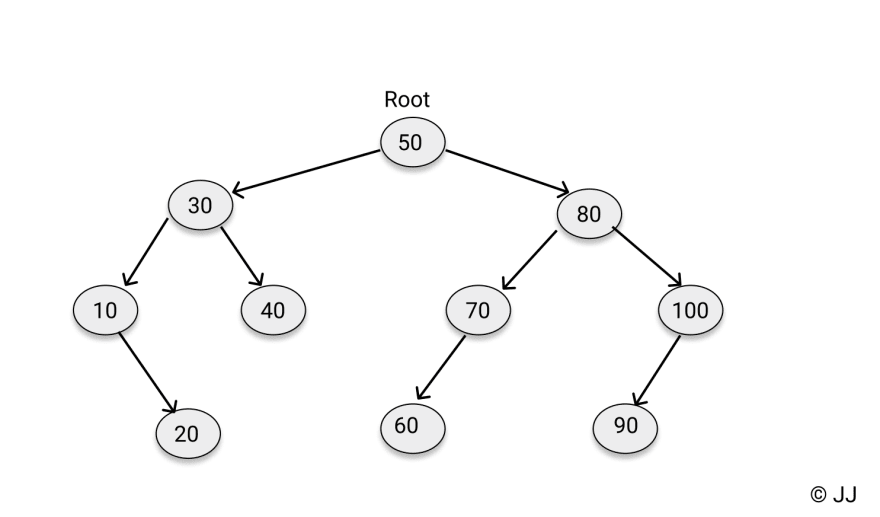
Binary search tree là một cây tìm kiếm nhị phân có thứ tự hoặc được sắp xếp.
- Có root node
- Mỗi node (bao gồm root node) sẽ có một khoá lớn lớn hơn tất cả các khoá của cây con bên trái của node và nhỏ các khoá trong cây con bên phải node
![]()
Chèn phần tử
- Đầu tiên, khoá của node mới được so sánh với root node (node gốc)
- Nếu khoá của node mới nhỏ hơn root node thì node mới sẽ được so sánh với khoá của node con bên trái root node
- Nếu khoá của node mới lớn hơn khoá của root node thì node mới sẽ được so sánh với khoá của node bên phải root node
- Tiến trình này sẽ được lặp cho đến khi node mơi được so sánh với node lá và nó được thêm vào bên phải hoặc bên trái node con, tuỳ thuộc vào khoá của nó. Nếu khoá của nó nhỏ hơn khoá của node lá thì nó sẽ được chèn vào làm node con bên trái của node lá, ngược lại sẽ là bên phải của node lá
Duyệt phần tử
Có 3 cách duyệt một cây nhị phân phổ biến nhất
- Pre-order (Node ->Left->Right)
- In-order(Left->Node->Right)
- Post-order(Left->Right->Node) Việc duyệt theo thứ tự của cây nhị phân sẽ luôn dẫn đến danh sách các node sẽ được sắp xếp tăng dần. Ở đây, mình sẽ triển khai duyệt theo thứ tự:
- Duyệt cây con bên trái bằng cách gọi hàm đệ quy
printNode - In ra khoá node hiện tại
- Duyệt cây con bên phải bằng cách gọi hàm đệ quy
printNode
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.value = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null; // root node
}
insertNode(parentNode, newNode) {
if (newNode.value < parentNode.value) {
//check the left child
parentNode.left !== null
? this.insertNode(parentNode.left, newNode)
: (parentNode.left = newNode);
} else {
// check the right child
parentNode.right !== null
? this.insertNode(parentNode.right, newNode)
: (parentNode.right = newNode);
}
}
insert(val) {
let newNode = new Node(val);
this.root !== null
? this.insertNode(this.root, newNode)
: (this.root = newNode);
}
printNode(node) {
if (node.left !== null) {
this.printNode(node.left); // traverse left subtree
}
console.log(node.value);
if (node.right !== null) {
this.printNode(node.right); // traverse right subtree
}
}
print() {
this.root !== null
? this.printNode(this.root)
: console.log('No nodes in the tree');
}
}
let bst1 = new BinarySearchTree();
bst1.insert(50);
bst1.insert(30);
bst1.insert(10);
bst1.insert(40);
bst1.insert(20);
bst1.insert(80);
bst1.insert(70);
bst1.insert(60);
bst1.insert(100);
bst1.insert(90);
bst1.print();
Trên đây, là chia sẽ của mình về 3 cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật trong Javascript, hi vọng bài viết sau mình sẽ tổng hợp được một số cấu trúc, giải thuật khác để có thể share đến các bạn, cảm ơn mọi người đã theo dõi bài viết :v
All rights reserved