Cách sử dụng Annotation trong TestNG
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Định nghĩa
Trong bài này, mình sẽ đề cập về TestNG Annotation, một trong những thứ quan trọng nhất của TestNG mà chúng ta cần phải nắm rõ. Annotation trong TestNG là những chú thích sẽ định nghĩa những gì sẽ làm tiếp theo hoặc những hàm sẽ được chạy tiếp theo Annotation là tính năng giúp thêm thông tin vào 1 object. Nó có thể được dùng cho class, method, variable, và parameters. TestNG cung cấp rất nhiều loại annotation cho các mục đích khác nhau, trong đó có các annotation phục vụ cho mục đích: xử lý trước và sau method Test.
Vì sao cần xử lý trước và sau Test:
- Cần tạo môi trường trước khi thực hiện test.
- Cần xóa hết các trạng thái sau khi thực hiện test hoặc cần phải thực hiện các hành động không liên quan đến method Test nhưng cần thiết như screenshot, delete session hoặc close connection…
TestNG cung cấp 5 annotation ở dạng Before/After:
- @BeforeSuite/@AfterSuite
- @BeforeTest/@AfterTest
- @BeforeGroups/@AfterGroups
- @BeforeClass/@AfterClass
- @BeforeMethod/@AfterMethod
Khai báo annotation trên 1 class
Thứ tự chạy của chúng sẽ được thể hiện qua ví dụ sau:
public class TestAnnotation {
@BeforeSuite
public void beforeSuite() {
System.out.println("Before Suite");
}
@AfterSuite
public void afterSuite() {
System.out.println("After Suite");
}
@BeforeTest
public void beforeTest() {
System.out.println("Before Test");
}
@AfterTest
public void afterTest() {
System.out.println("After Test");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeClass() {
System.out.println("Before Class");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterClass() {
System.out.println("After Class");
}
@BeforeGroups(groups = { "testOne" })
public void beforeGroupOne() {
System.out.println("Before Group testOne");
}
@AfterGroups(groups = { "testOne" })
public void afterGroupOne() {
System.out.println("After Group testOne");
}
@BeforeGroups(groups = { "testTwo" })
public void beforeGroupTwo() {
System.out.println("Before Group testTwo");
}
@AfterGroups(groups = { "testTwo" })
public void afterGroupTwo() {
System.out.println("After Group testTwo");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("Before Method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("After Method");
}
@Test(groups = { "testOne" })
public void testOneMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method One");
}
@Test(groups = { "testTwo" })
public void testTwoMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method Two");
}
}
Và ta cần thêm 1 config cho file testng.xml
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="First Suite" verbose="1">
<test name="First Test">
<classes>
<class name="testannotation.TestAnnotation">
<methods>
<include name="testOneMethod" />
</methods>
</class>
</classes>
</test>
<test name="Second Test">
<classes>
<class name="testannotation.TestAnnotation">
<methods>
<include name="testTwoMethod" />
</methods>
</class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
Và đây là kết quả:

Từ đây, ta có thể hiểu được thứ tự chạy chúng:
- Khi bắt đầu thì mở từ Suite > Test > Group > Class > Method
- Khi kết thúc thì đóng từ Method > Class > Group > Test > Suite
Khai báo annotation khi có extend
Ở phía trên, chúng ta đã xem về cách sử dụng annation trên 1 class, chúng ta sẽ băn khoăn là thế nhưng chúng ta viết theo dạng POM thì có cả BaseTest, không biết thứ tự run annotation sẽ như thế nào?
Hãy xem ví dụ dưới đây:
Ta có class BaseTest
public class BaseTest {
@BeforeClass
public void beforeBaseClass() {
System.out.println("Parent Before Class method");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterBaseClass() {
System.out.println("Parent After Class method");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeBaseMethod() {
System.out.println("Parent Before method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterBaseMethod() {
System.out.println("Parent After method");
}
}
Class Test:
public class TestClass extends BaseTest {
@BeforeClass
public void beforeChildClass() {
System.out.println("Child Before Class method");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterChildClass() {
System.out.println("Child After Class method");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeChildMethod() {
System.out.println("Child Before method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterChildMethod() {
System.out.println("Child After method");
}
@Test
public void testMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method under TestClass");
}
}
Và file testng.xml:
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Inheritance Suite" verbose="1">
<test name="Inheritance Test">
<classes>
<class name="testannotation.TestClass" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
Đây là kết quả:

Thứ tự chạy khi có extend sẽ là:
- Khi bắt đầu: Parent Before > Child Before
- Khi kết thúc: Child After > Parent After
Trong một project, không nhất thiết phải sử dụng hết tất cả các annotation này, nhưng ta cần phải biết thứ tự để từ đó control code của mình chạy theo thứ tự mình mong muốn, ví dụ như chụp screentshot ở cuối mỗi test, khởi tạo connection để đọc file Excel…
@Test trong TestNG và các attribute của annotation @Test
Annotation @Test:
Đây là annotation đánh dấu method hoặc Class là 1 phần của TestNG Test. Nếu nó được đánh dấu cho Class thì tất cả các Method mà Public thì sẽ được run, các Method không phải public sẽ không được run.
Đây là nơi mà các hàm bên dưới nó sẽ được run như một testcase.
Ví dụ:
Các attribute của annotation @Test
- alwaysRun: có giá trị mặc định là false, nó sẽ bị ignore nếu nó không có dependency method (phụ thuộc) . Nếu đặt là true thì Method sẽ được run kể cả khi các dependency method fail. Eg: @Test(alwaysRun=true)
- enabled: giá trị mặc định là true. Dùng để đánh dấu method run hoặc không run. Nếu false, method đó sẽ được bỏ qua, không run. Nếu true, method đó sẽ được run.
Eg: @Test(enabled=true)
![]()
- description: dùng để thêm thông tin cho test. Attribute này khá hiệu quả khi chúng ta muốn thêm mô tả các test case khi mà method Name không thể diễn tả được hết.
Eg: @Test(description=”Print the second test method”)
![]()
- expectedExceptions: dùng để xác định exception mà Method có thể gặp phải.
Eg: @Test(expectedExceptions={IOException.class})
![]()
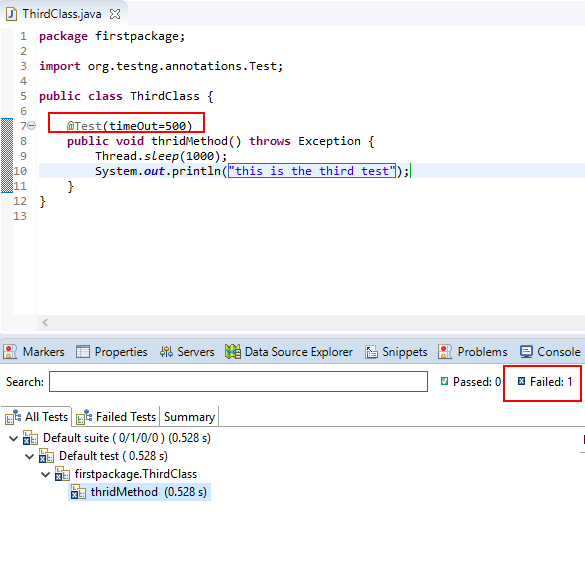
- timeOut: xác định thời gian tối đa mà test có thể run, nếu thời gian run lớn hơn thời gian đã định sẵn thì kết quả test là fail.
Eg: @Test(timeOut=500)
![]()
- dataProvider: điền data vào cho test method, phục vụ cho data-driven testing (sẽ viết ở bài khác)
- dataProviderClass: điền tên class mà TestNG sẽ tìm kiếm data-provider method được nhắc đến ở attribute dataProvider. Mặc định thì nó sẽ tìm ở chính class đó hoặc class base.
- dependsOnGroups: điền list các group mà test phụ thuộc.
- dependsOnMethods: điền list các method mà test phụ thuộc. (sẽ viết ở bài khác)
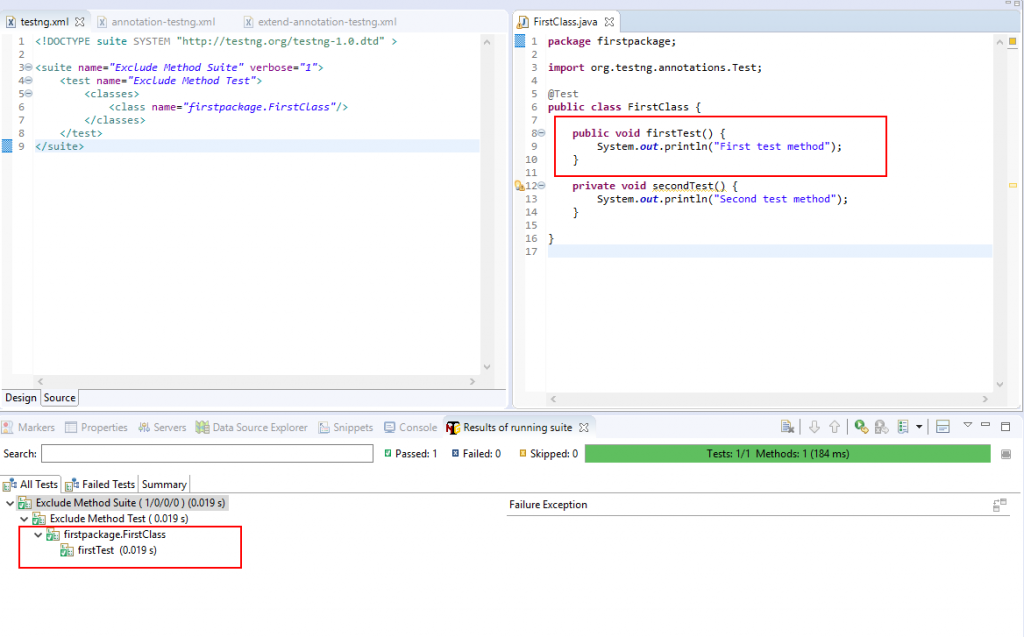
- groups: điền tên group, những test mà có chung tên group sẽ tạo thành 1 tập hợp. Tập hợp này có thể được run từ file testng.xml
Trong 1 test có thể áp dụng nhiều annotation cùng với nhau. Ví dụ:
@Test(enabled=true, description="Print the second test method")
public void secondTest() {
System.out.println("Second test method");
}
Bài viết có tham khảo website GiangTester Blog
All rights reserved