Cách giao tiếp giữa các layer trong c
Hôm nay, tôi sẽ nói về một vấn đề rất hay gặp khi viết các dự án về C:
Làm thế nào để các lớp tách biệt vẫn có thể giao tiếp với nhau trong C?
1. Bài toán đặt ra
Giả sử chương trình của bạn được chia làm 3 lớp (layer):
- Top Layer (Application): Nơi code ứng dụng, chỉ quan tâm đọc dữ liệu và ghi dữ liệu.
- Medium Layer (Service): Đóng vai trò trung gian, cung cấp các hàm
read()/write(). - Bottom Layer (Driver / Hardware): Phần làm việc trực tiếp với phần cứng thật sự (RAM, FLASH, EEPROM, …).
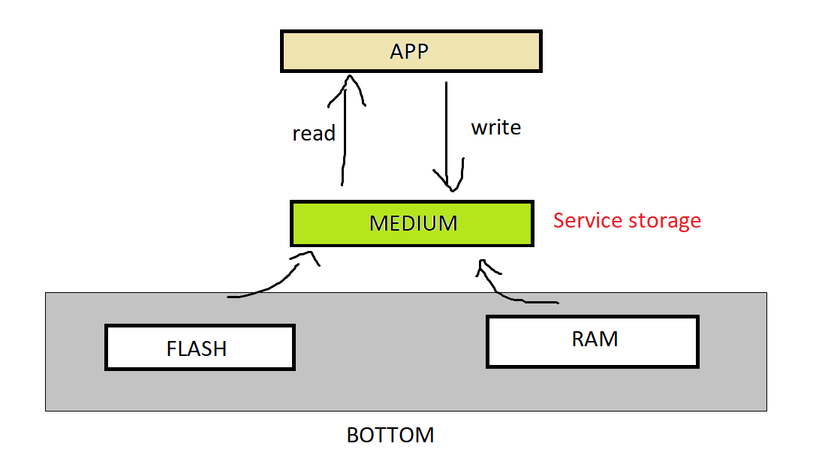
Trong ví dụ này, tôi dùng RAM và FLASH để mô phỏng hai thiết bị lưu trữ khác nhau.
2. Vấn đề
- Cách ghi vào RAM khác với ghi vào FLASH.
- Nhưng Application không cần (và không nên) biết điều đó.
👉 App chỉ cần: read() và write(data).
Vậy câu hỏi là:
Làm sao để RAM và FLASH đều “trông giống nhau” trong mắt App?
3. Giải pháp
Ta sẽ định nghĩa một giao diện chung (ops). Nếu bạn thắc mắc ops là gì? thì nó là viết tắt của
typedef struct {.
void (*write)(int data);
int (*read)(void);
} storage_ops_t;
Cấu trúc storage_ops_t mô tả thiết bị lưu trữ có thể làm gì.
Cài đặt cho từng phần cứng cụ thể
RAM
static int ram_data;
static void ram_write(int data) {
printf("Write to RAM\n");
ram_data = data;
}
static int ram_read(void) {
printf("Read from RAM\n");
return ram_data;
}
storage_ops_t ram_ops = {
.write = ram_write,
.read = ram_read
};
FLASH
static int flash_data;
static void flash_write(int data) {
printf("Write to FLASH\n");
flash_data = data;
}
static int flash_read(void) {
printf("Read from FLASH\n");
return flash_data;
}
storage_ops_t flash_ops = {
.write = flash_write,
.read = flash_read
}
👉 Mỗi thiết bị có cách làm riêng, nhưng đều tuân theo cùng một giao tiếp.
Lúc này, Medium Layer không biết RAM hay FLASH. Lớp này chỉ biết là
- Khi gọi
ops->write(data)thì sẽ ghi dữ liệu xuống nơi nào đó. - Khi gọi
ops->read()thì sẽ nhận dc dữ liệu.
typedef struct {
storage_ops_t *ops; // ← trỏ xuống bottom
} storage_service_t;
Khởi tạo service với thiết bị mong muốn:
void storage_init(storage_service_t *svc, storage_ops_t *ops) { // Lựa chọn device lưu trữ
svc->ops = ops;
}
Các hàm dùng chung:
void storage_save(storage_service_t *svc, int data) {
svc->ops->write(data);
}
int storage_load(storage_service_t *svc) {
return svc->ops->read();
}
Full Code cho bài toán này
#include <stdio.h>
// Bottom layer
typedef struct {
void (*write)(int data);
int (*read)(void);
} storage_ops_t;
// Lưu trữ trong ram
static int ram_data;
static void ram_write(int data) {
printf("Write to RAM\n");
ram_data = data;
}
static int ram_read(void) {
printf("Read from RAM\n");
return ram_data;
}
storage_ops_t ram_ops = {
.write = ram_write,
.read = ram_read
};
// Luu trong flash
static int flash_data;
static void flash_write(int data) {
printf("Write to FLASH\n");
flash_data = data;
}
static int flash_read(void) {
printf("Read from FLASH\n");
return flash_data;
}
storage_ops_t flash_ops = {
.write = flash_write,
.read = flash_read
};
// Medium layer: Service
typedef struct {
storage_ops_t *ops; // ← trỏ xuống bottom
} storage_service_t;
void storage_init(storage_service_t *svc, storage_ops_t *ops) {
svc->ops = ops;
}
void storage_save(storage_service_t *svc, int data) {
svc->ops->write(data);
}
int storage_load(storage_service_t *svc) {
return svc->ops->read();
}
// Top layer: Application
int main(void) {
storage_service_t storage;
// 🔁 đổi dòng này để đổi hành vi
storage_init(&storage, &ram_ops);
// storage_init(&storage, &flash_ops);
storage_save(&storage, 123);
int value = storage_load(&storage);
printf("Value in app: %d\n", value);
// Debug bottom layer
printf("Value in bottom: %d\n", ram_data);
return 0;
}
Output
Write to RAM
Read from RAM
Value in app: 123
Value in bottom: 123 <-- Kiểm tra giá trị được lưu trữ trong RAM
Ý nghĩa của cách làm này
- Các layer được tách biệt rõ ràng.
- Không phụ thuộc vào lẫn nhau nhưng vẫn giao tiếp tốt.
4. ây có phải là OOP không?
Trong C không có class, nhưng cách làm này chính là đa hình (Polymorphism).
👉 Cụ thể:
- Compile-time Polymorphism: chọn thiết bị khi build / init.
- Dùng function pointer để mô phỏng hành vi OOP.
Trong tương lai, tôi sẽ viết tiếp:
- Run-time Polymorphism.
- Sử dụng vtable.
Các bạn có thể đọc bài viết này để biết thêm chi tiết về đa hình (Polymorphism): https://codelearn.io/sharing/tinh-da-hinh-trong-oop
All rights reserved