Basic Sorting Algorithms with Swift
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Thuật toán sắp xếp là rất cần thiết trong việc quản lý data. Để thuận tiện cho việt truy suất report hay tìm kiếm thông tin đôi khi bạn cần sắp xếp dữ liệu theo quy luật nào đó. Bài này mình sẽ giới thiệu một số thuật toán tìm kiếm phổ biến mà chúng ta đã đc học.
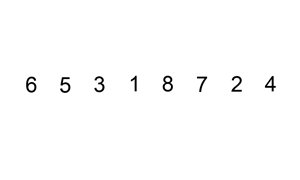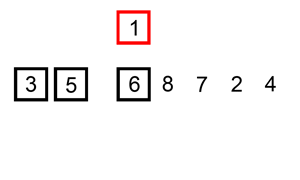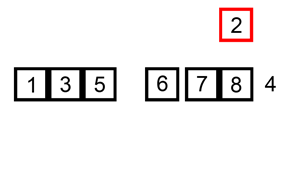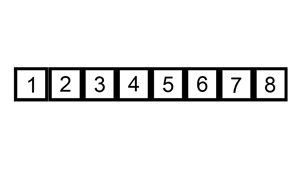
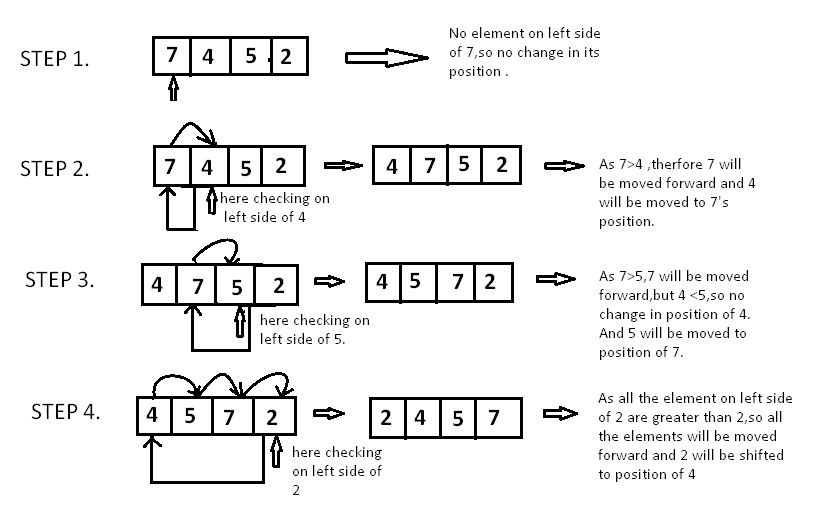
INSERTION SORT
Insertion sort hay còn gọi là sắp xếp chèn bạn hình dung nó giống như khi chơi bài mỗi khi bạn nhận được quân bài bạn sẽ sắp xếp nó vào bộ bài của mình.
extension Array where Element: Comparable {
func insertionSort() -> Array<Element> {
//check for trivial case
guard self.count > 1 else {
return self
}
//mutated copy
var output: Array<Element> = self
for primaryindex in 0..<output.count {
let key = output[primaryindex]
var secondaryindex = primaryindex
while secondaryindex > -1 {
if key < output[secondaryindex] {
//move to correct position
output.remove(at: secondaryindex + 1)
output.insert(key, at: secondaryindex)
}
secondaryindex -= 1
}
}
return output
} }
//execute sort
let results: Array<Int> = numberList.insertionSort()
Độ phức tạp thuật toán: O(n)
BUBBLE SORT
Bubble sort sắp xếp nổi bọt (tiếng Anh: ) là một thuật toán sắp xếp đơn giản, với thao tác cơ bản là so sánh hai phần tử kề nhau, nếu chúng chưa đứng đúng thứ tự thì đổi chỗ (swap). Có thể tiến hành từ trên xuống (bên trái sang) hoặc từ dưới lên (bên phải sang). Sắp xếp nổi bọt còn có tên là sắp xếp bằng so sánh trực tiếp. Nó sử dụng phép so sánh các phần tử nên là một giải thuật sắp xếp kiểu so sánh.
extension Array where Element: Comparable {
func bubbleSort() -> Array<Element> {
//check for trivial case
guard self.count > 1 else {
return self
}
//mutated copy
var output: Array<Element> = self
for primaryIndex in 0..<self.count {
let passes = (output.count - 1) - primaryIndex
//"half-open" range operator
for secondaryIndex in 0..<passes {
let key = output[secondaryIndex]
//compare / swap positions
if (key > output[secondaryIndex + 1]) {
output.swapAt(secondaryIndex, secondaryIndex + 1)
}
}
}
return output
}
}
//execute sort
let results: Array<Int> = numberList.bubbleSort()
Độ phức tạp của thuật toán: O( n^2)
SELECTION SORT
Selection Sort giải thuật sắp xếp chọn là một giải thuật đơn giản. Giải thuật sắp xếp này là một giải thuật dựa trên việc so sánh in-place, trong đó danh sách được chia thành hai phần, phần được sắp xếp (sorted list) ở bên trái và phần chưa được sắp xếp (unsorted list) ở bên phải. Ban đầu, phần được sắp xếp là trống và phần chưa được sắp xếp là toàn bộ danh sách ban đầu.
Với phần tử đầu tiên của array, ta tìm xem coi có phần tử nào trong số còn lại mà nhỏ hơn phần tử đầu tiên và phải nhỏ nhất. Sau đó hoán vị phần tử nhỏ nhất này với phần tử đầu tiên. Cứ như vậy với phần tử thứ 2, thứ 3…. Cho đến hết array.

extension Array where Element: Comparable {
func selectionSort() -> Array<Element> {
//check for trivial case
guard self.count > 1 else {
return self
}
//mutated copy
var output: Array<Element> = self
for primaryindex in 0..<output.count {
var minimum = primaryindex
var secondaryindex = primaryindex + 1
while secondaryindex < output.count {
//store lowest value as minimum
if output[minimum] > output[secondaryindex] {
minimum = secondaryindex
}
secondaryindex += 1
}
//swap minimum value with array iteration
if primaryindex != minimum {
output.swapAt(primaryindex, minimum)
}
}
return output
}
}
//execute sort
let results: Array<Int> = numberList.selectionSort()
Độ phức tạp thuật toán: O(n^2)
All rights reserved