Authorization với JWT trong React+Redux App
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
JSON Web Token là gì?
JWT là một phương tiện đại diện cho các yêu cầu chuyển giao giữa hai bên Client - Server , các thông tin trong chuỗi JWT được định dạng bằng JSON . Trong đó chuỗi Token phải có 3 phần là header , phần payload và phần signature được ngăn bằng dấu “.”
Vậy mục đích sử dụng JWT là gì?
Giả sử có 1 request gửi yêu cầu xóa một user trong DB, nếu không có một phương thức bảo mật nào thì bất kỳ user nào khác cũng đều có thể gửi request này để xóa user đi. Vì vậy JWT sinh ra giúp chúng ta có một phương pháp để server xác định được yêu cầu đó là của user nào, khi đó mới quyết định có thực hiện hay không.
Phạm vi bài viết hôm nay sẽ chủ yếu đề cập đến cách xử lý JWT ở phía frontend. Nếu cần tìm hiểu kỹ hơn về JWT thì bạn có thể tham khảo bài viết này.
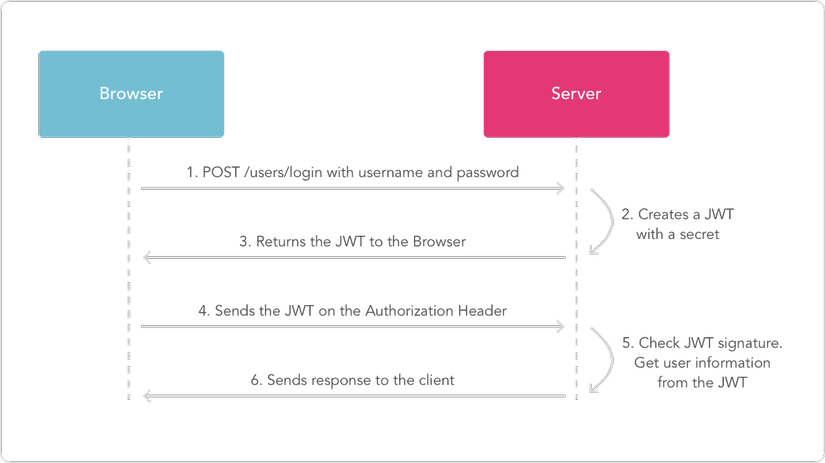
Làm cách nào để Auth hoạt động với Redux và JWT?
Về cơ bản, ta sẽ lưu thông tin của người dùng hiện tại vào store của Redux, đồng thời cũng sẽ lưu JWT liên kết với người dùng đó vào localStorage để việc Login của họ có thể tồn tại giữa các sessions trừ khi họ thực sự Logout ra khỏi hệ thống.
Ở phạm vi bài viết này, giả định ta có 3 API routes:
Route: /users Method: POST
Route: /login Method: POST
Route: /profile Method: GET
Đây là 3 API xử lý 3 phần xác thực cơ bản nhất: khi người dùng tạo tài khoản, đăng nhập vào tài khoản và sau đó quay lại app.
Giờ thì bắt đầu xem sao.
Người dùng tạo tài khoản
Đương nhiên khi người dùng truy cập app, ta sẽ muốn người dùng đăng ký một tài khoản.
Về cơ bản, một request dạng POST sẽ được gửi lên, nếu không có vấn đề gì thì phía backend sẽ tạo một instance của user trong đó có password được mã hóa và trả về user với user key và JWT key. Đây là phần quan trọng đối với việc thực hiện Auth.
Tiếp đó, thông tin user sẽ được lưu vào store của Redux và mã token sẽ được lưu vào localStorage. Các bước để đăng ký tài khoản và tự động đăng nhập được tiến hành như sau:
Tạo Form đăng ký
Ta sẽ tạo form đăng ký trong React App, khi người dùng submit sẽ call tới action.js được tạo trong Redux. Trông giống thế này:
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {userPostFetch} from '../redux/actions';
class Signup extends Component {
state = {
username: "",
password: "",
avatar: "",
bio: ""
}
handleChange = event => {
this.setState({
[event.target.name]: event.target.value
});
}
handleSubmit = event => {
event.preventDefault()
this.props.userPostFetch(this.state)
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<h1>Sign Up For An Account</h1>
<label>Username</label>
<input
name='username'
placeholder='Username'
value={this.state.username}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<label>Password</label>
<input
type='password'
name='password'
placeholder='Password'
value={this.state.password}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<label>Avatar</label>
<input
name='avatar'
placeholder='Avatar (URL)'
value={this.state.avatar}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<label>Bio</label>
<textarea
name='bio'
placeholder='Bio'
value={this.state.bio}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<input type='submit'/>
</form>
)
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
userPostFetch: userInfo => dispatch(userPostFetch(userInfo))
})
export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(Signup);
Xử lý việc nhận request trong Redux
Trong action.js, việc xử lý sẽ thực hiện như sau:
export const userPostFetch = user => {
return dispatch => {
return fetch("http://localhost:3000/api/v1/users", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({user})
})
.then(resp => resp.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.message) {
} else {
localStorage.setItem("token", data.jwt)
dispatch(loginUser(data.user))
}
})
}
}
const loginUser = userObj => ({
type: 'LOGIN_USER',
payload: userObj
})
Lưu ý 1 chút: function userPostFetch sẽ gửi thông tin người dùng để backend xác nhận. Sau khi thành công, sẽ trả về một response JSON dạng:
{
user: {
username: "ImANewUser",
avatar: "https://robohash.org/imanewuser.png",
bio: "A new user to the app."
},
jwt: "aaaaaaa.bbbbbbbb.ccccccc"
}
Lưu token vào localStorage
Trong function userPostFetch: đoạn localStorage.setItem("token", data.jwt) sẽ lưu token ("aaaaaaa.bbbbbbbb.ccccccc") tới localStorage của user tương ứng. Sau này khi user login giữa các sessions sẽ sử dụng tới.
Để cho chắc cú thì có thể chạy localStorage.getItem("token") trong console xem đã lưu thành công hay chưa.
Lưu thông tin người dùng vào store của Redux
Với user, ở đoạn code trên chúng ta đã thực hiện dispatch (loginUser(data.user)). Khi đó trong reducer sẽ nhận được object ({username: “ImANewUser”}) và lưu nó vào store của Redux bằng việc thực thi như dưới đây:
const initialState = {
currentUser: {}
}
export default function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'LOGIN_USER':
return {...state, currentUser: action.payload}
default:
return state;
}
}
User (action.payload) được lưu vào state dưới key tên là currentUser.
Từ nãy đến giờ chúng ta đã đi qua công đoạn đăng ký người dùng mới. Tiếp theo, xem xem việc người dùng đăng nhập sẽ như thế nào.
Người dùng đăng nhập
Thực ra công việc người dùng còn đơn giản hơn công việc đăng ký =))
Công việc của chúng ta chỉ là gửi thông tin đăng nhập về phía backend. Nếu xác nhận thành công, backend sẽ trả về thông tin user tương tự như đăng ký: bao gồm user key và JWT key.
OK lại một lần nữa, yêu thương xa rồi, tôi lại ngồi lưu thông tin user vào store của Redux và JWT vào localStorage =))
Tuy nhiên component Login trong React sẽ khác SignUp ở phần function nơi xử lý trong action.js
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {userLoginFetch} from '../redux/actions';
class Login extends Component {
state = {
username: "",
password: ""
}
handleChange = event => {
this.setState({
[event.target.name]: event.target.value
});
}
handleSubmit = event => {
event.preventDefault()
this.props.userLoginFetch(this.state)
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<h1>Login</h1>
<label>Username</label>
<input
name='username'
placeholder='Username'
value={this.state.username}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<label>Password</label>
<input
type='password'
name='password'
placeholder='Password'
value={this.state.password}
onChange={this.handleChange}
/><br/>
<input type='submit'/>
</form>
)
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
userLoginFetch: userInfo => dispatch(userLoginFetch(userInfo))
})
export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(Login);
Vẫn lại tương tự như phần đăng ký, chúng ta sẽ viết 1 file action.js chứa function userLoginFetch:
export const userLoginFetch = user => {
return dispatch => {
return fetch("http://localhost:3000/api/v1/login", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({user})
})
.then(resp => resp.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.message) {
} else {
localStorage.setItem("token", data.jwt)
dispatch(loginUser(data.user))
}
})
}
}
Để ý một chút, đó là ta sẽ sử dụng lại action loginUser để lưu thông tin vào state. Và BÒM, khi user được lưu vào state và token được lưu vào localStorage, ta có thể coi người dùng đó đã đăng nhập thành công. Tiếp theo, hãy tới phần duy trì phiên đăng nhập của người dùng giữa các phiên.
Người dùng quay lại trang (Xem thông tin cá nhân)
Điểm mấu chốt ở đây chính là khi người dùng quay lại trang, họ muốn cảm thấy như mình đang tiếp tục phiên làm việc của session trước đó.
Chúng ta sẽ để ý tới thằng token trong localStorage, nó sẽ được sử dụng để xác thực xem người dùng đăng nhập hay chưa.
Tuy nhiên hãy nhớ rằng token đó chỉ là 1 đoạn string. Nó không thể hiện được việc người dùng đã đăng nhập, mà chúng ta sẽ phải lấy nó và chuyển nó thành thông tin đăng nhập liên tục.
Để làm được việc đó, mỗi khi gọi đến API /profile, việc truy cập sẽ được xác nhận nếu user có token đã được lưu trong localStorage.
Đơn giản bằng cách ở componentDidMount ta sẽ xử lý việc đó:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Switch, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {getProfileFetch} from './redux/actions';
import Signup from './components/Signup';
import Login from './components/Login';
class App extends Component {
componentDidMount = () => {
this.props.getProfileFetch()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Switch>
<Route path="/signup" component={Signup}/>
<Route path="/login" component={Login}/>
</Switch>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
getProfileFetch: () => dispatch(getProfileFetch())
})
export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(App);
Và trong action.js
export const getProfileFetch = () => {
return dispatch => {
const token = localStorage.token;
if (token) {
return fetch("http://localhost:3000/api/v1/profile", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
'Authorization': `Bearer ${token}`
}
})
.then(resp => resp.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.message) {
localStorage.removeItem("token")
} else {
dispatch(loginUser(data.user))
}
})
}
}
}
Kết luận
Trên đây là cách thực hiện JWT với React+Redux trong trường hợp cơ bản nhất.
Cảm ơn bạn đã theo dõi và mong rằng bài viết sẽ giúp đỡ được phần nào cho bạn trong việc tìm hiểu về JWT.
Tham khảo: https://levelup.gitconnected.com/using-jwt-in-your-react-redux-app-for-authorization-d31be51a50d2
All rights reserved