ASP.NET MVC Tip #25 – Unit Test Views không cần Web Server (p1)
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 6 năm
Trong mẹo này, tôi trình bày cách bạn có thể chạy unit test ASP.NET MVC views mà không cần chạy máy chủ Web. Tôi chỉ cho bạn cách unit test view bằng cách tạo MVC View Engine tùy chỉnh và Controller Context giả.
Càng nhiều ứng dụng web của bạn mà bạn có thể kiểm tra, bạn càng có thể tin tưởng rằng những thay đổi đối với ứng dụng của bạn sẽ không gây ra lỗi. ASP.NET MVC giúp dễ dàng tạo các bài unit test cho các models và controller của bạn. Trong mẹo này, tôi giải thích cách bạn cũng có thể kiểm tra view của mình.
Tạo một Custom View Engine Hãy bắt đầu bằng cách tạo Custom View Engine. Liệt kê 1 chứa mã cho một View Engine thực sự đơn giản có tên SimpleViewEngine. Listing 1 – SimpleViewEngine.vb (VB.NET)
Imports System
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Web.Mvc
Namespace Tip25
Public Class SimpleViewEngine
Implements IViewEngine
Private _viewsFolder As String = Nothing
Public Sub New()
If HttpContext.Current IsNot Nothing Then
Dim root = HttpContext.Current.Request.PhysicalApplicationPath
_viewsFolder = Path.Combine(root, "Views")
End If
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal viewsFolderPhysicalPath As String)
_viewsFolder = viewsFolderPhysicalPath
End Sub
Public Sub RenderView(ByVal viewContext As ViewContext) Implements IViewEngine.RenderView
If _viewsFolder Is Nothing Then
Throw New NullReferenceException("You must supply a viewsFolder path")
End If
Dim fullPath As String = Path.Combine(_viewsFolder, viewContext.ViewName) & ".htm"
If (Not File.Exists(fullPath)) Then
Throw New HttpException(404, "Page Not Found")
End If
' Load file
Dim rawContents As String = File.ReadAllText(fullPath)
' Perform replacements
Dim parsedContents As String = Parse(rawContents, viewContext.ViewData)
' Write results to HttpContext
viewContext.HttpContext.Response.Write(parsedContents)
End Sub
Public Function Parse(ByVal contents As String, ByVal viewData As ViewDataDictionary) As String
Return Regex.Replace(contents, "\{(.+)\}", Function(m) GetMatch(m, viewData))
End Function
Protected Overridable Function GetMatch(ByVal m As Match, ByVal viewData As ViewDataDictionary) As String
If m.Success Then
Dim key As String = m.Result("$1")
If viewData.ContainsKey(key) Then
Return viewData(key).ToString()
End If
End If
Return String.Empty
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Listing 1 – SimpleViewEngine.cs (C#)
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Tip25
{
public class SimpleViewEngine : IViewEngine
{
private string _viewsFolder = null;
public SimpleViewEngine()
{
if (HttpContext.Current != null)
{
var root = HttpContext.Current.Request.PhysicalApplicationPath;
_viewsFolder = Path.Combine(root, "Views");
}
}
public SimpleViewEngine(string viewsFolderPhysicalPath)
{
_viewsFolder = viewsFolderPhysicalPath;
}
public void RenderView(ViewContext viewContext)
{
if (_viewsFolder == null)
throw new NullReferenceException("You must supply a viewsFolder path");
string fullPath = Path.Combine(_viewsFolder, viewContext.ViewName) + ".htm";
if (!File.Exists(fullPath))
throw new HttpException(404, "Page Not Found");
// Load file
string rawContents = File.ReadAllText(fullPath);
// Perform replacements
string parsedContents = Parse(rawContents, viewContext.ViewData);
// Write results to HttpContext
viewContext.HttpContext.Response.Write(parsedContents);
}
public string Parse(string contents, ViewDataDictionary viewData)
{
return Regex.Replace(contents, @"\{(.+)\}", m => GetMatch(m, viewData));
}
protected virtual string GetMatch(Match m, ViewDataDictionary viewData)
{
if (m.Success)
{
string key = m.Result("$1");
if (viewData.ContainsKey(key))
return viewData[key].ToString();
}
return String.Empty;
}
}
}
Lưu ý rằng SimpleViewEngine thực hiện giao diện IViewEngine. Giao diện này có một phương thức mà bạn phải thực hiện: RenderView ().
Trong Liệt kê 1, phương thức RenderView() tải một tệp từ đĩa cứng và thay thế các token trong tệp bằng các mục từ ViewData. Liệt kê 2 chứa một controller sử dụng SimpleViewEngine. Khi bạn gọi hành động HomeControll.Index(), action sẽ trả về một view có tên Index. Listing 2 – HomeController.vb (VB.NET)
Imports Tip25.Tip25
<HandleError()> _
Public Class HomeController
Inherits System.Web.Mvc.Controller
Public Sub New()
Me.ViewEngine = New SimpleViewEngine()
End Sub
Public Function Index() As ActionResult
ViewData("Message") = "Welcome to ASP.NET MVC!"
ViewData("Message2") = "Using a custom View Engine"
Return View("Index")
End Function
End Class
Listing 2 – HomeController.cs (C#)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Tip25.Controllers
{
[HandleError]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public HomeController()
{
this.ViewEngine = new SimpleViewEngine();
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Welcome to ASP.NET MVC!";
ViewData["Message2"] = "Using a custom View Engine";
return View("Index");
}
}
}
View Index được chứa trong Liệt kê 3. Lưu ý rằng tên của tệp là Index.htm. SimpleViewEngine trả về các tệp .htm. Listing 3 – Index.htm
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<head>
<title>Tip 25</title>
</head>
<body>
Here is the first message:
{message}
<br />
Here is the second message:
<b>{message2}</b>
</body>
</html>
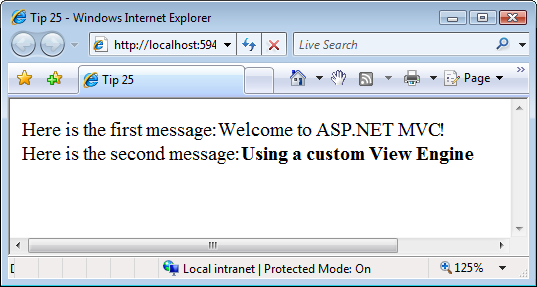
View Index chứa token được đánh dấu bằng dấu ngoặc mở và đóng. Phương thức SimpleViewEngine.RenderView() thay thế mỗi token bằng một mục từ View Data có cùng tên. Khi View Index được SimpleViewEngine hiển thị, bạn sẽ nhận được trang trong Hình 1.
Hình 1 - Trang được hiển thị từ View Index
Nguồn: https://weblogs.asp.net/stephenwalther/asp-net-mvc-tip-25-unit-test-your-views-without-a-web-server
All rights reserved