AI làm thơ lục bát - Trí tuệ nhân tạo sáng tác thơ lục bát
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Ý tưởng
Như chúng ta đã biết việc viết ra 1 bài thơ đòi hỏi tác giả phải là người có ngòi bút bay bổng , tâm hồn "lạc vào thơ " bên cạnh đó việc sáng tác bài thơ đòi hỏi phải bỏ rất nhiều công phu, thời gian, tâm huyết. Nên hiện nay việc sáng tác thơ đang bị hao mòn dần so với thế hệ ông cha ta. Liệu có cách nào có thể dùng trí tuệ nhân tạo để sáng tác thơ được hay không ? Xuất phát từ ý tưởng đó, mình đã làm ra 1 ứng dụng sáng tác thơ lục bát không chỉ có vần điệu, mà còn phải hay, giàu tính nghệ thuật .
Nên hiện nay việc sáng tác thơ đang bị hao mòn dần so với thế hệ ông cha ta. Liệu có cách nào có thể dùng trí tuệ nhân tạo để sáng tác thơ được hay không ? Xuất phát từ ý tưởng đó, mình đã làm ra 1 ứng dụng sáng tác thơ lục bát không chỉ có vần điệu, mà còn phải hay, giàu tính nghệ thuật .


 Trong ứng dụng này này sẽ sử dụng các kĩ thuật sau đây :
Trong ứng dụng này này sẽ sử dụng các kĩ thuật sau đây :
- Kĩ thuật crawl thơ lục bát ( truyện kiều, lục vân tiên, thivien.net, bút tre,...) từ các nguồn trên internet sử dụng Selenium
- Kĩ thuật tiền xử lí dữ liệu và xử lí dữ liệu
- Tokenizer và model PhoBERT
- Model GPT-2
- Train model và save model
- Viết web bằng Flask demo kết quả
I. Kĩ thuật crawl data sử dụng selenium
Việc crawl data trên mạng đã không còn xa lạ , hiện này có rất nhiều công cụ crawl data như BeautifulSoup , Selenium, puperteer,.... Nhưng ỏ đây mình sẽ trình bày kĩ thuật crawl data bằng Selenium.
Mình đã crawl các bài thơ lục bát trên mạng ( truyện kiều, lục vân tiên, thơ bút tre, nhị độ mai, thơ Nôm, thơ Phạm,...) và thivien.net. Tổng hợp lại có khoảng 57.000 câu.
Ví dụ crawl thơ nhị độ mai bằng Selenium :
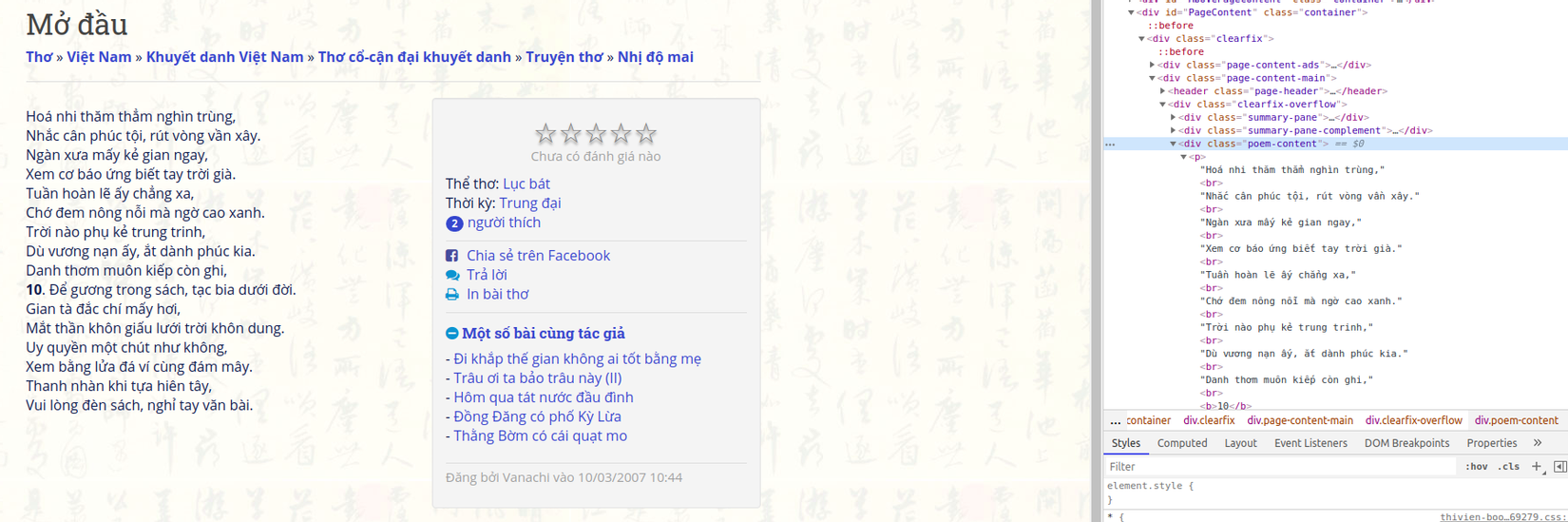
- Import library
!pip install selenium
- Install library with option
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
import time
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument("--incognito")
chrome_options.add_argument("--headless") # run secret , not show webdriver .If want show, remove line
chrome_options.add_argument("--window-size=1920x1080")
# Connect to chromedriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=chrome_options, executable_path="/usr/bin/chromedriver")
- Get all poemtry
# Get data poemtry
'''
<div class ='poem-content'>
<p> Hello... </p>
'''
def get_dataPoemtry(url):
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(3) # time load javascripts
elements = driver.find_elements_by_xpath("//div[@class='poem-content']/p") # absolute path
# open file .txt and save data. If file not exists => make file train.txt
with open('./train.txt', 'a+') as f:
for e in elements:
print(e.text)
f.write(e.text)
f.close()
# Get all poem of 1 author, url of document use absolute path
def get_all_pagePoem(url_main):
'''
Link url ex:https://www.thivien.net/Khuy%E1%BA%BFt-danh-Vi%E1%BB%87t-Nam/Nh%E1%BB%8B-%C4%91%E1%BB%99-mai/group-IEY1qp52H1ytxgP5URFeAw
---------
Struct html
----------
<div class = 'poem-group-list'>
<ol>
<li>
<a href = ... >
---------
Return: save data to 1 file train.txt
'''
driver.get(url_main)
time.sleep(3)
link_url = []
elements = driver.find_elements_by_xpath("//div[@class='poem-group-list']/ol/li/a")
print(len(elements))
for e in elements:
# print(e.get_attribute('href'))
link_url.append(e.get_attribute('href'))
print(link_url)
for url in link_url:
get_dataPoemtry(url)
- Test
url_main = 'https://www.thivien.net/Khuy%E1%BA%BFt-danh-Vi%E1%BB%87t-Nam/Nh%E1%BB%8B-%C4%91%E1%BB%99-mai/group-IEY1qp52H1ytxgP5URFeAw'
get_all_pagePoem(url_main)
 Link code crawl thơ nhị độ mai:
https://github.com/trungtruc123/Crawl_DATA_SELENIUM_BEAUTIFULSOUP/blob/master/Crawl_poemtry.ipynb
Link code crawl thơ nhị độ mai:
https://github.com/trungtruc123/Crawl_DATA_SELENIUM_BEAUTIFULSOUP/blob/master/Crawl_poemtry.ipynb
 Tutorial Use Selenium:
Tutorial Use Selenium:
- https://github.com/trungtruc123/Crawl_DATA_SELENIUM_BEAUTIFULSOUP/blob/master/Craw_data use Selenium.ipynb
- https://selenium-python.readthedocs.io/
II. Kĩ thuật tiền xử lí dữ liệu và xử lí dữ liệu
Sau khi crawl data từ internet thì data của chúng ta vẫn còn "dơ bẩn" . Cần phải làm sạch nó , vậy làm sạch nó bằng cách nào ? Đơn giản chúng ta sử dụng regex (Regular Expression) để xóa đi các chữ số, các kí tự đặc biêt ( , . * : " ' - _ ] ), xóa đi các khoảng trắng đầu,cuối câu và các dòng toàn khoảng trắng. Sau đó chuyển hết data về chữ thường.
import re
def standardize_data(row):
# remove stopword
# Remove . ? , at index final
row = re.sub(r"[\.,\?]+$-", "", row)
row = re.sub(" \d+", " ", row)
# Remove all . , " ... in sentences
row = row.replace(",", "").replace(".", "") \
.replace(";", "").replace("“", "") \
.replace(":", "").replace("”", "") \
.replace('"', "").replace("'", "") \
.replace("!", "").replace("?", "") \
.replace("-", "").replace("?", "") \
.replace("_", "").replace("*", "") \
.replace("(", "").replace(")", "") \
.replace("0", "").replace("1", "") \
.replace("2", "").replace("3", "") \
.replace("4", "").replace("5", "") \
.replace("6", "").replace("7", "") \
.replace("8", "").replace("9", "") \
row = row.strip()
return row
def process_data(path_input, path_out):
with open(path_input, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines() # list
for l in lines :
process = standardize_data(l)
with open(path_out, 'a+') as f1 :
f1.write(process +'\n')
f.close()
f1.close()
process_data(path_input ='train2.txt', path_out ='train2_process.txt')
Link code : https://github.com/trungtruc123/Crawl_DATA_SELENIUM_BEAUTIFULSOUP/blob/master/Processing_Data.ipynb
Nếu bạn nào thấy việc crawl data và xử lí data phức tạp thì có thể sử dụng 2 file data_train_process.txt và data_test_process.txt mình đã chuẩn bị ở đây :
III. Model PhoBERT và tokenizer
1. PhoBERT
Để hiểu được PhoBERT là gì thì chúng ta phải biết BERT là gì ? BERT là model hoạt động dựa trên cơ chế attention (chú trọng các đặc trưng ) nó sẽ khắc phục hoàn toàn các nhược điểm của các model như RNN, LSTM,.. ( bị giới hạn bộ nhớ ).
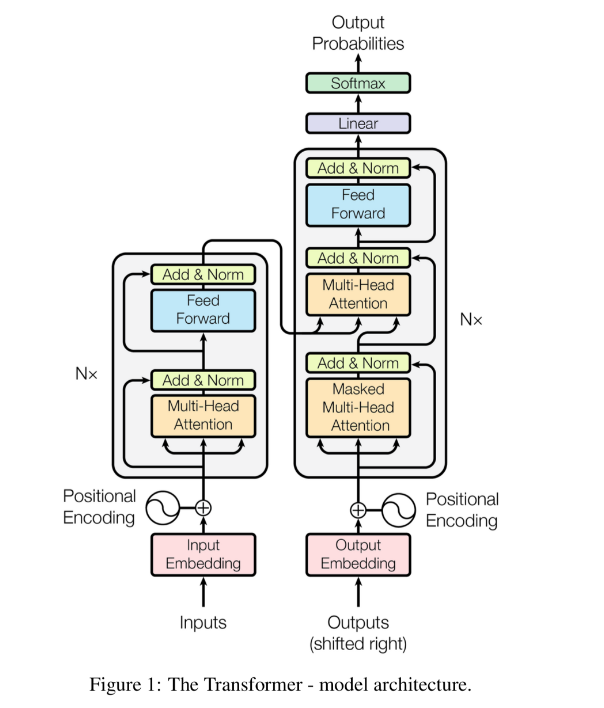
Các bạn muốn hiểu rõ cấu trúc, cách thức hoạt động của model BERT thì có thể tham khảo tài liệu :
- https://phamdinhkhanh.github.io/2020/05/23/BERTModel.html
- https://towardsdatascience.com/bert-explained-state-of-the-art-language-model-for-nlp-f8b21a9b6270
Đối với tiếng Việt thì PhoBERT có thể coi là 1 trong những project đầu tiên của BERT dành cho tiếng Việt được public. Theo mình thấy thì PhoBERT là 1 pre-train model với độ chính xác khá tốt được xây dựng dựa trên kiến trúc RoBERTa. Vậy RoBERTa là gì ?.
 RoBERTa là một project của facebook implement lại model BERT trên pytorch. Đây là một project support khá tốt việc huấn luyện lại trên những bộ dữ liệu mới cho các ngôn ngữ khác ngoài các ngôn ngữ phổ biến như Tiếng Anh, Tiếng Pháp,....
RoBERTa là một project của facebook implement lại model BERT trên pytorch. Đây là một project support khá tốt việc huấn luyện lại trên những bộ dữ liệu mới cho các ngôn ngữ khác ngoài các ngôn ngữ phổ biến như Tiếng Anh, Tiếng Pháp,....
RoBERTa lặp lại các thủ tục huấn luyện từ model BERT, nhưng có sự thay đổi đó là huấn luyện mô hình lâu hơn, với batch size lớn hơn và trên nhiều dữ liệu hơn. Ngoài ra để nâng cao độ chuẩn xác trong biểu diễn từ thì RoBERTa đã loại bỏ tác vụ dự đoán câu tiếp theo và huấn luyện trên các câu dài hơn. Đồng thời mô hình cũng thay đổi linh hoạt kiểu masking (tức ẩn đi một số từ ở câu output bằng token <mask>) áp dụng cho dữ liệu huấn luyện.
Các bạn có thể tìm hiểu RoBERTa là gì thông qua : RoBERTa
2. Tokenize
Tokenize là quá trình rất cần thiết cho việc train model, vậy tokenize là gì ? Tokenize là quá trình mã hóa 1 văn bản thành các index dạng số mang thông tin để máy tính có thể huấn luyện được. Khi đó mỗi một từ hoặc 1 kí tự sẽ được đại diện bởi 1 index ( con số ).
 Trong NLP có nhiều kiểu tokenize:
Trong NLP có nhiều kiểu tokenize:
-
Đây là phương pháp truyền thống như GloVe, word2vec. Phân tách 1 câu thành các token ngăn cách với nhau bởi khoảng trống hoặc dấu câu.Tokenize theo word level: -
Áp dụng trong Tiếng Việt có các model hổ trợ tokenize như : VnCoreNLP, pyvivn, underthesea. Bởi vì trong Tiếng Việt có từ đơn âm tiết và từ đa âm tiết, nếu tách token theo kiểu từ đơn âm tiết sẽ làm sai lệch nghĩa của từ. Vì thế nên tách các từ theo từ điển bao gồm cả từ đơn âm tiết và đa âm tiết.Tokenize theo multi-word level: -
Phương pháp này giải quyết được nhược điểm của 2 tokenize trên là bộ từ điển quá lớn => chi phí tính toán lớn. Phương pháp này hoạt động bằng cách tách 1 từ thành các kí tự character nhỏ, vì các character có thể biểu diễn đc từ. Tuy nhiên có nhược điểm là không có nghĩa nếu tokenize đứng độc lập.Tokenize theo character level -
Đây là phương pháp mới giải quyết được tất cả nhược điểm của các phương pháp trên, hoạt động bằng một kỹ thuật nén từ cơ bản giúp chúng ta index được toàn bộ các từ kể cả trường hợp từ mở (không xuất hiện trong từ điển) nhờ mã hóa các từ bằng chuỗi các từ phụ (subwords). Nguyên lý hoạt động của BPE dựa trên phân tích trực quan rằng hầu hết các từ đều có thể phân tích thành các thành phần con.Mã hóa BPE ( Byte Pair Encoding)
Ví dụ Tokenize :
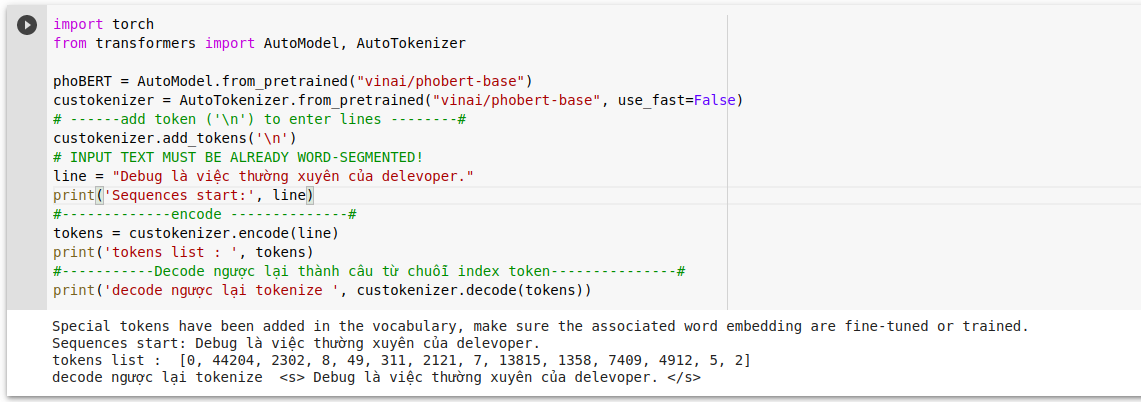
Tham khảo tokenize : link
3. Sử dụng pretrain model PhoBERT xử lí thơ lục bát
Step 1. Load pretrain model PhoBERT ( có 2 cách: sử dụng fairseq, sử dụng transformers). Ở đây mình sử dụng transformers :
import torch
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
phoBERT = AutoModel.from_pretrained("vinai/phobert-base")
custokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("vinai/phobert-base", use_fast=False)
# ------add token ('\n') to enter lines --------#
custokenizer.add_tokens('\n')
# INPUT TEXT MUST BE ALREADY WORD-SEGMENTED!
line = "Debug là việc thường xuyên của delevoper."
print('Sequences start:', line)
#-------------encode --------------#
tokens = custokenizer.encode(line)
print('tokens list : ', tokens)
#-----------Decode ngược lại thành câu từ chuỗi index token---------------#
print('decode ngược lại tokenize ', custokenizer.decode(tokens))
Step 2. Code dataLoader
#--------------Create Dataset----------------#
import os
import torch
from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset
from transformers.tokenization_utils import PreTrainedTokenizer
from filelock import FileLock
from transformers.utils import logging
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
import pickle
import random
import time
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
class PoemDataset(Dataset):
"""
This will be superseded by a framework-agnostic approach
soon.
Parameters:
----------
tokenizers : is pretrain tokenizer of PhoBERT
file_path : path to file train, test
block_size : size of 1 block , optinal
cache_dir : just load 1 once and saved
"""
def __init__(
self,
tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizer,
file_path: str,
block_size: int,
overwrite_cache=False,
cache_dir: Optional[str] = None,
):
assert os.path.isfile(file_path), f"Input file path {file_path} not found"
block_size = block_size - tokenizer.num_special_tokens_to_add(pair=False)
directory, filename = os.path.split(file_path)
cached_features_file = os.path.join(
cache_dir if cache_dir is not None else directory,
"cached_lm_{}_{}_{}".format(
tokenizer.__class__.__name__,
str(block_size),
filename,
),
)
# -----------Make sure only the first process in distributed training processes the dataset,----------------#
# ---------------------------------------and the others will use the cache------------------------#
lock_path = cached_features_file + ".lock"
with FileLock(lock_path):
if os.path.exists(cached_features_file) and not overwrite_cache:
start = time.time()
with open(cached_features_file, "rb") as handle:
self.examples = pickle.load(handle)
logger.info(
f"Loading features from cached file {cached_features_file} [took %.3f s]", time.time() - start
)
else:
logger.info(f"Creating features from dataset file at {directory}")
self.examples = []
with open(file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
text = f.read()
#-----convert text to tokenizers----------------------------#
'''
1. Convert word -> subword (tokenizer.tokenize(text))
2. COnvert subword -> number (tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids)
'''
tokenized_text = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokenizer.tokenize(text))
# ------------- Truncate in block of block_size-----------------#
#-----------Beacuse add_token('\n') -> inds = 64001------------#
#--------If len(block_size)>56 so cut and add_special_tokens (<s>, </s>)---------------#
i = 0
while i < len(tokenized_text) - block_size + 1:
inds = tokenized_text[i : i + block_size]
for j in range(0, len(inds)):
if inds[j]==64001:
inds = inds[j+1:] #remove the first \n
break
for j in range(len(inds)-1, 0, -1):
if inds[j]==64001:
inds = inds[:j-1] #remove \n
break
i += len(inds)
self.examples.append(
tokenizer.build_inputs_with_special_tokens(inds)
)
# Note that we are losing the last truncated example here for the sake of simplicity (no padding)
# If your dataset is small, first you should loook for a bigger one :-) and second you
# can change this behavior by adding (model specific) padding.
start = time.time()
with open(cached_features_file, "wb") as handle:
pickle.dump(self.examples, handle, protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
logger.info(
"Saving features into cached file %s [took %.3f s]", cached_features_file, time.time() - start
)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.examples)
def __getitem__(self, i) -> torch.Tensor:
return torch.tensor(self.examples[i], dtype=torch.long)
#-----------Load dataset-----------------------#
from transformers import LineByLineTextDataset, DataCollatorForLanguageModeling, LineByLineWithSOPTextDataset
def load_dataset(train_path, test_path, custokenizer):
train_dataset = PoemDataset(
tokenizer=custokenizer,
file_path=train_path,
block_size= 56)#256
test_dataset = PoemDataset(
tokenizer=custokenizer,
file_path=test_path,
block_size=56)
data_collator = DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(
tokenizer=custokenizer, mlm=False,
)
return train_dataset,test_dataset,data_collator
train_dataset,test_dataset,data_collator = load_dataset(train_path,test_path,custokenizer)
#-----------Test dataloader----------------#
print(len(test_dataset))
print(len(train_dataset))
#-------------Test decode to sentence ---------------#
print(custokenizer.decode(test_dataset[7]))
IV. Model GPT-2
GPT-2 là gì và nó khác gì so với BERT ? Các bạn có thể tham khảo : GPT-2
Initialize Trainer with TrainingArguments and GPT-2 model:
from transformers import Trainer, TrainingArguments, GPT2Config, GPT2LMHeadModel
#--------------------------Load pretrain model GPT-2--------------------#
model_gpt2 = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('gpt2')
# Random weights => fine-turning model
rand_weight = torch.rand(model_gpt2.lm_head.weight.shape)
print(rand_weight)
model_gpt2.lm_head.weight = torch.nn.parameter.Parameter(rand_weight)
'''
Because GPT2 has vocabulary_size 50257 and (wte): Embedding(50257, 768)
So convert vocabulary_size= 64002, Embedding(64002, 768)
'''
task_gpt2 = {"text-generation": {"do_sample": True, "max_length": 56}} #edit output size
config_gpt2 = configuration = GPT2Config(vocab_size=64002, n_positions=58, n_ctx=58,
task_specific_params=task_gpt2,
eos_token_id = 2,
bos_token_id = 0,
pad_token_id = 1,
sep_token_id = 2,
# eos_token_id=custokenizer.eos_token_id,
# bos_token_id=custokenizer.bos_token_id,
# pad_token_id=custokenizer.pad_token_id,
# sep_token_id=custokenizer.sep_token_id
)
model_gpt2 = GPT2LMHeadModel(config_gpt2)
model_gpt2
#save model_gpt2 (vocabulary_size =64002)
model_gpt2.save_pretrained('/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/save_modelGPT2/')
task = {"text-generation": {"do_sample": True, "max_length": 56}} #edit output size
configuration = GPT2Config(vocab_size=64002, n_positions=58, n_ctx=58,
task_specific_params=task,
eos_token_id = 2,
bos_token_id = 0,
pad_token_id = 1,
sep_token_id = 2,
# eos_token_id=custokenizer.eos_token_id,
# bos_token_id=custokenizer.bos_token_id,
# pad_token_id=custokenizer.pad_token_id,
# sep_token_id=custokenizer.sep_token_id
)
poem = GPT2LMHeadModel(configuration)
# Load weights of model_gpt2 ( random weights)
load_model_gpt2 = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/save_modelGPT2/')
poem.load_state_dict(load_model_gpt2.state_dict())
#-----------Print process training ------------#
from transformers.trainer_callback import TrainerCallback
from transformers import pipeline
class PrinterCallback(TrainerCallback):
def on_epoch_end(self, args, state, control, model=None, **kwargs):
if int(state.epoch)%10==0:
pipe = pipeline('text-generation', model=model, tokenizer=custokenizer, device=0)
with open("/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/sample.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(pipe('<s> tìm về một thuở hạ xưa')[0]['generated_text'])
f.write("\n===========================================\n")
f.close()
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/gpt2-poem", #The output directory
overwrite_output_dir=True, #overwrite the content of the output directory
num_train_epochs=100, # number of training epochs
per_device_train_batch_size=8, # batch size for training
per_device_eval_batch_size=16, # batch size for evaluation
save_steps=5000, # after # steps model is saved
save_total_limit = 2, # delete other checkpoints
warmup_steps=5000, # number of warmup steps for learning rate scheduler
# logging_dir='/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/gpt2-poem/logs', # directory for storing logs
logging_steps=5000,
)
V. Train model và Test model
1. Train model
device = torch.device('cuda')
trainer = Trainer(
model=poem, # GPT2
args=training_args,
data_collator=data_collator,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=test_dataset,
callbacks = [PrinterCallback],
)
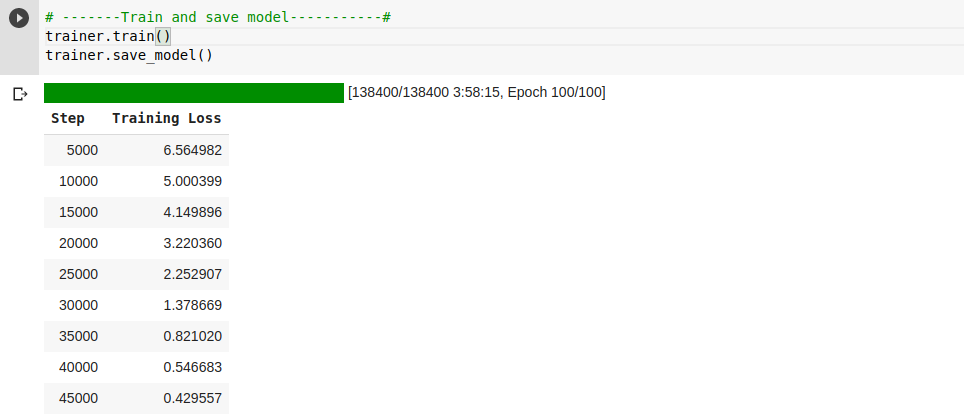
# -------Train and save model-----------#
trainer.train()
trainer.save_model()
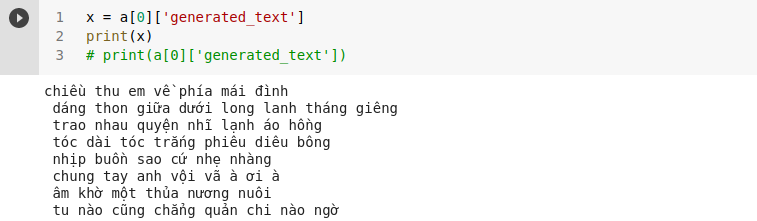
2. Test model
#-------Load model saved-----------------#
from transformers import pipeline
poem = pipeline('text-generation', model="/content/drive/MyDrive/BERT/gpt2-poem", tokenizer=custokenizer, config={'max_length':56})
#Test
a = poem('<s>cuộc sống')
print(a[0]['generated_text'])
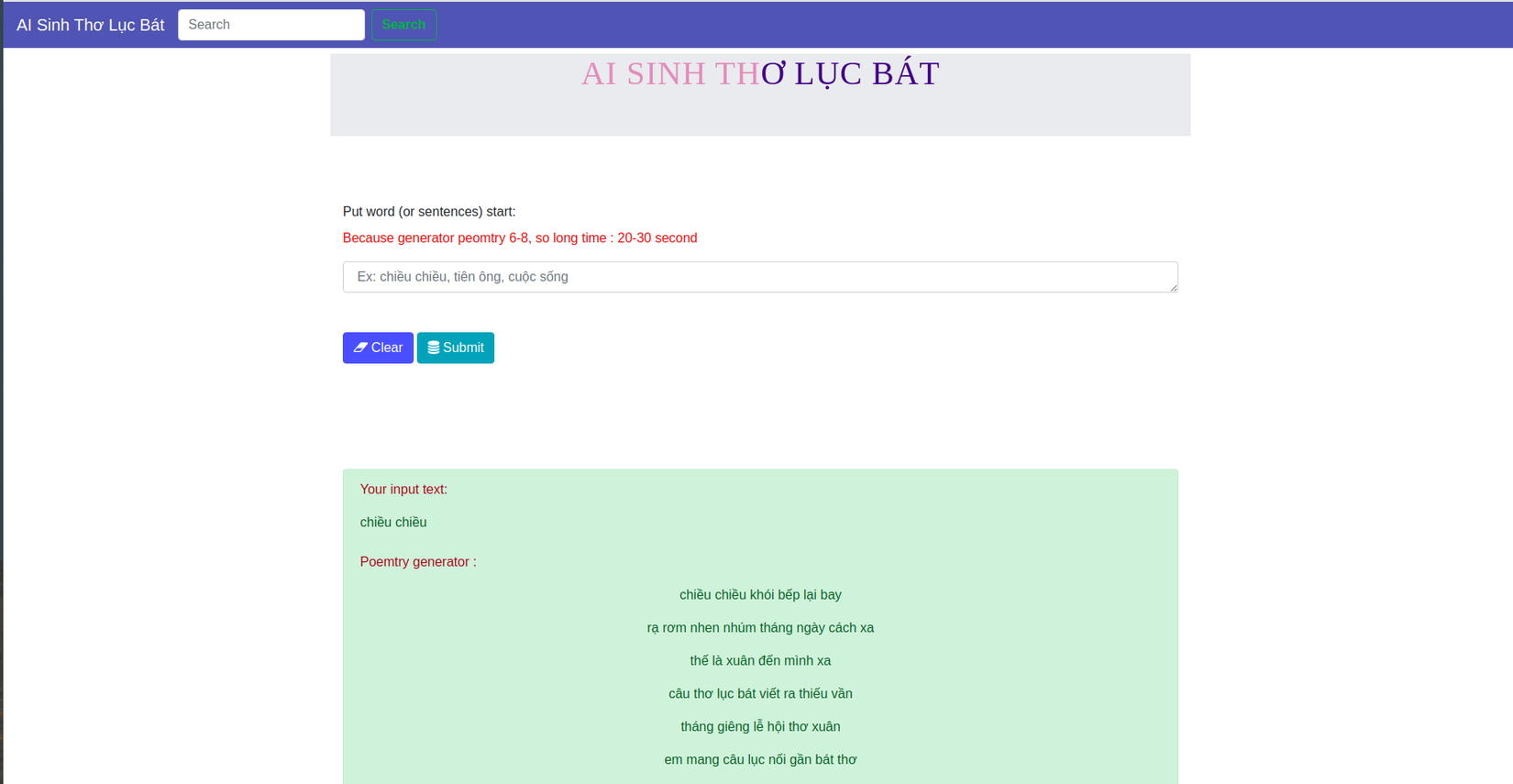
VI. Viết web bằng Flask demo kết quả
Ở đây mình sử dụng FLASK để xây dựng 1 trang web demo kết quả
- Html và CSS : lưu ở templates với static
- Main : lưu ở app.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, url_for, request, send_file, url_for
import torch
import transformers
from transformers import pipeline
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
#-------Load model saved-----------------#
def predict(in_text, max_length):
custokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("vinai/phobert-base", use_fast=False)
poem = pipeline('text-generation', model="./checkpoint-40000/", tokenizer=custokenizer, config={'max_length':1024})
input_raw = '<s>'+in_text
# a = poem(input_raw)
a = poem(input_raw)
out = a[0]['generated_text']
out = out.strip('<s>')
out = out.strip('</s>')
out = out.split('<unk>')
print('out:', out)
return out
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template("poem.html")
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def classify2():
if request.method == 'POST':
raw_text = request.form['rawtext']
results = predict(raw_text,max_length = 500)
return render_template("poem.html", results=results,raw_text=raw_text)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug= True, threaded=True)
Sau khi cài đầy đủ thư viện như Readme thì thực hiện lệnh: python app.py
Kết quả :
Kết luận
Toàn bộ code :
1. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-3U39WyHg_NhhgZmBMJvVzRx7-FcsErq/view?usp=sharing
2. https://github.com/trungtruc123/Poemtry
3. Google drive colab : https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1TdO5jdbeIZfWgZKVgspXKGEQW4_XN1dd?usp=sharing
4. File zip project Flask : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1soD-FsJvhcTT7J5dyM3FcDH6Ex5nxRRj/view?usp=sharing
Bài viết này hơi dài, nên có 1 số mục mình không trình bày rõ , nếu không rõ chỗ nào comment ở dưới để mình giải đáp. Mong được sự góp ý của mọi người 
 Qua bài viết này hi vọng các bạn có thể thấy được các ứng dụng của trí tuệ nhân tạo cho cuộc sống con người, bên cạnh đó có thể nắm 1 số kĩ thuật như : crawl data từ các nguồn trên internet, model PhoBERT, GPT-2, Tokenize, viết web bằng FLASK,...
Qua bài viết này hi vọng các bạn có thể thấy được các ứng dụng của trí tuệ nhân tạo cho cuộc sống con người, bên cạnh đó có thể nắm 1 số kĩ thuật như : crawl data từ các nguồn trên internet, model PhoBERT, GPT-2, Tokenize, viết web bằng FLASK,...
Nếu có thời gian mình sẽ cải tiến sản phẩm , crawl thêm nhiều data tránh overfitting và làm thêm sản phẩm sử dụng AI sáng tác rap 

| Hy vọng bài viết này hữu ích với các bạn |
Tài liệu tham khảo
- https://github.com/trungtruc123/Poemtry
- https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1TdO5jdbeIZfWgZKVgspXKGEQW4_XN1dd?usp=sharing
- https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tune-a-non-english-gpt-2-model-with-huggingface
- https://huggingface.co/
- https://github.com/trungtruc123/Da-poet
- https://phamdinhkhanh.github.io/2020/05/23/BERTModel.html
All rights reserved